Abstract: NF-κB(Nuclear Factor Kappa B) is the important nuclear transcription factor, and involved in cellular response to various stimulation. NF-κB pathway regulates inflammation, immunity, cell survival and proliferation via canonical and non-canonical activation. Rapid response of canonical pathway depends on NF-κB dimer activated by IKK complex. Non-canonical pathway mediates p100 and converts to p52 via NIK and IKKα. The abnormal activation of this pathway is closely related to cancer, inflammation and autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: Nf-Kb Pathway, Inflammation, Immunity, Cancer Treatment
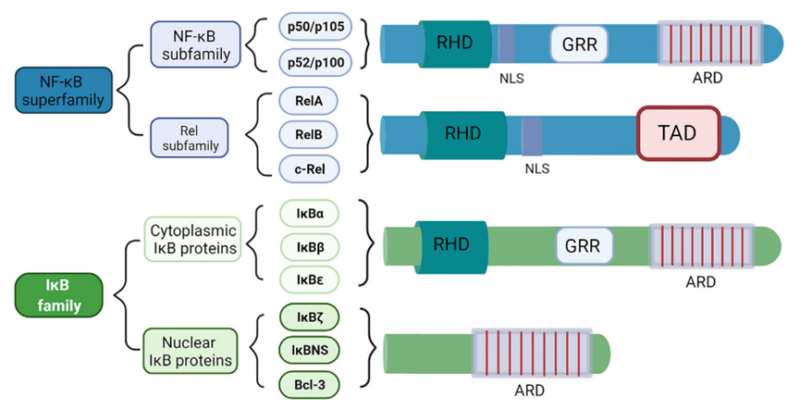
1. NF-κB Family Member and Structure
NF-κB is named for specific binding with kB sequence in the immunoglobulin k light chain enhancer in B cells. Its family includes five members: RelA (p65), RelB, c-Rel, NF-κB1 (p50/p105) and NF-κB2 (p52/p100). These proteins can form homo-or heterodimers(e.g. the most common one: p65/p50 dimer). Each member has the conserved Rel structural domain responsible for DNA binding, dimer formation and regulation of gene transcription. NF-κB is involved in important physiological processes(e.g. immune response, inflammation, cell growth and apoptosis etc).
2. Types of NF-κB Signaling Pathway
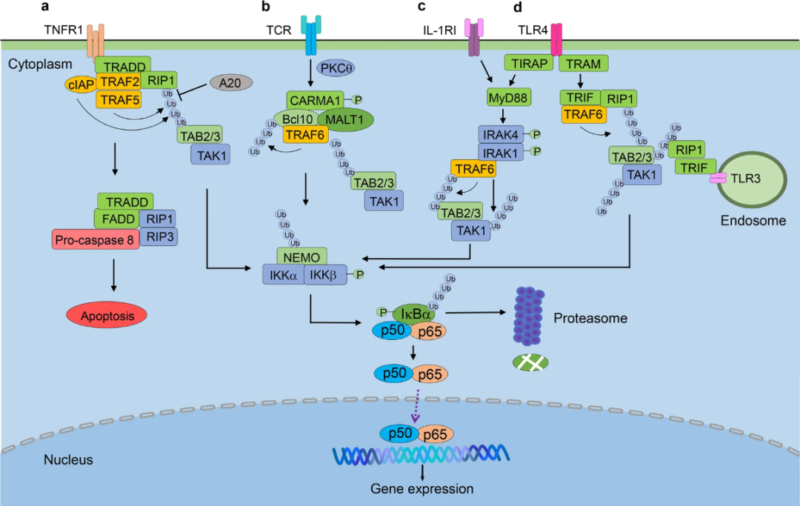
2.1. Canonical NF-κB Pathway
Activation of canonical NF-κB pathway depends on IKK complex mediated-IκB protein phosphorylation. IKK complex consists of two catalytic subunits(IKKα and IKKβ) and regulatory subunit(NEMO). IKKβ plays an important role in response to proinflammatory cytokines and microbial products. IKKα mainly regulates non-canonical pathway. NEMO doesn't have kinase activity but is very important for activating IKK complex. The activated IKKβ promotes phosphorylation and degradation of IκB protein by ubiquitination, releasing NF-κB dimer to further activate gene transcription. This pathway widely regulates immune response and is mainly mediated by p65/p50 dimer. Activation depends on external stimulation(e.g. inflammatory factors: TNF-α, IL-1β), pathogenic molecules(e.g. LPS) and oxidative stress.
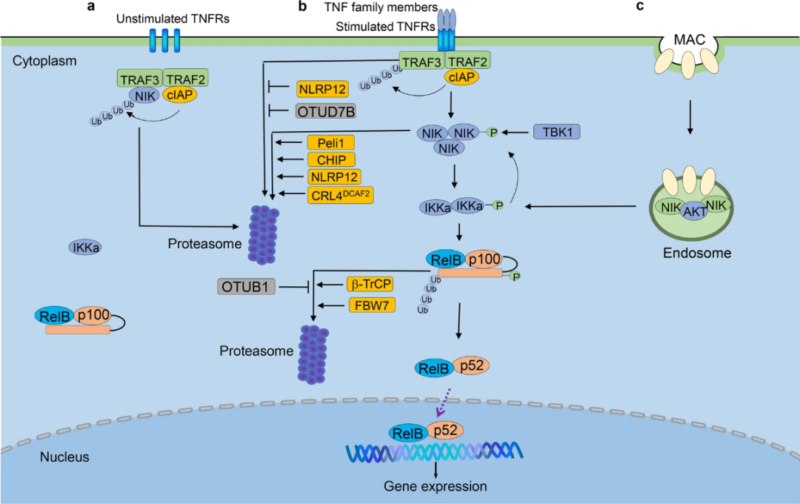
2.2. Non-canonical NF-κB Pathway
Activation of non-canonical NF-κB pathway is slower, usually performed by TNF receptor superfamily members(e.g. CD40, RANK and LT-βR etc). RelB/p52 heterodimer takes effects as transcription factors. p100 is the precursor of p52 and similar to IκB protein, preventing the entry of RelB into nucleus. Hydrolysis of p100 produces p52 and releases RelB, further forming RelB/p52 dimer. The transport to nucleus activates the transcription of specific gene.
2.3. Activation Modes
Ⅰ. Under homeostasis, NIK is mediated and degraded by cIAP-TRAF2-TRAF3 ubiquitin ligase. Inhibit the accumulation and activation of non-canonical NF-κB pathway.
Ⅱ. When specific TNFR superfamily members are activated, they recruit and degrade TRAF3 via TRAF3-TRAF2-cIAP complex, leading to accumulation of NIK. NIK cooperates with IKKα to promote phosphorylation and ubiquitination of p100. The produced p52 releases RelB/p52 dimer.
Ⅲ. Form endosome based-signaling complex via MAC. NIK and AKT stabilize NIK. Activate downstream non-canonical NF-κB pathway via phosphorylated IKKα. Negative regulation is achieved by deubiquitination(e.g. OTUD7B, TRAF3) and various proteins(e.g. IKKα, TBK1, Peli1) mediated NIK degradation.
3. Function of Signaling Pathway
Roles of NF-κB in immunity, inflammation, cell survival, apoptosis, proliferation and differentiation are important. NF-κB regulates inflammatory response and improves immune function via promoting activation and proliferation. NF-κB can protect cell survival via up-regulation of anti apoptotic gene, especially maintaining activation in tumor cells. Besides, NF-κB regulates cell proliferation and differentiation via involvement in cell cycle and normal development. Effects of NF-κB in various physiological and pathological processes are also significant, especially for immune response and tumor development.
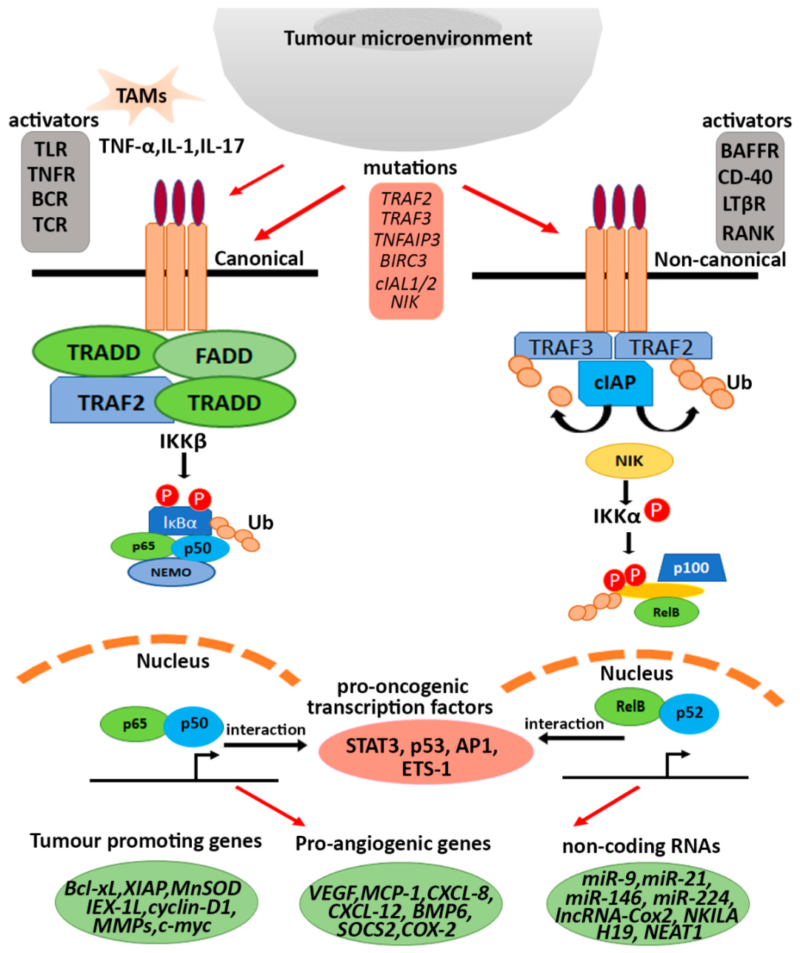
4. NF-κB and Cancer
NF-κB signaling pathway widely regulates in inflammation, immunity and tumor. Thus, NF-κB becomes the important target for cancer treatment. Traditional anti-inflammatory drugs(e.g. aspirin, sodium salicylate etc) can block the activation of NF-κB via degradation of IκB, and also have anti-tumor potential. Besides, drugs(e.g. infliximab) targeting upstream activators(e.g. TNF-α) also show bright therapeutic prospect. In recent years, NF-κB inhibitors together with chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other pathway inhibitors(e.g. STAT3, AP-1) have been validated for improving anti-tumor effects, and also provide more accurate therapeutic strategies.
| Recommended Antibodies | |
| Cat.No | Product Name |
| FNab09483 | CFAP52 antibody |
| FNab04227 | IL17D antibody |
| FNab04228 | IL17F antibody |
| FNab08315 | STC1 antibody |
| FNab08300 | STAT3 antibody |
| FNab08298 | STAT3 antibody |
| FNab10115 | TRAF2 antibody |
| FNab10272 | TRAF2 antibody |
| FNab08920 | TRAF5 antibody |
| Recommended Recombinant Proteins | |
| Cat.No | Product Name |
| P0797 | Recombinant Human IL-17A |
| Pr3582 | Recombinant Human IL-1b |
| P5355 | Recombinant Human STC1 |
| P5159 | Recombinant Human STAT3 |
| P0303 | Recombinant Human TRAF2 |
| P4416 | Recombinant Human TNFA |
| P5991 | Recombinant Mouse IL-17A |
| Pr3583 | Recombinant Mouse IL-1b |
| P0157 | Recombinant Mouse TNFA |
| P2523 | Recombinant Rabbit IL-1B |
| P0171 | Recombinant Rat IL-1b |
| P4812 | Recombinant Rat TNFA |
| P0166 | Recombinant Bovine IL-1b |
| P1413 | Recombinant Hamster IL-17A |
| Recommended ELISA Kits | |
| Cat.No | Product Name |
| EH0185 | Human IL-1β ELISA Kit |
| EH0185-HS | Human IL-1β high sensitivity ELISA Kit |
| QT-EH0185 | Human IL-1β QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| EH12661 | Human STC1 ELISA Kit |
| EH0602 | Human STAT3 ELISA Kit |
| QT-EH0602 | Human STAT3 QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| EH0302 | Human TNF-α ELISA Kit |
| QT-EH0302 | Human TNF-α QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| AQ-H3267-B | Human HS-IL-17 high sensitive Accquant ELISA Kit |
| EH0302-HS | Human HS-TNF-α high sensitivity ELISA Kit |
| EM0109 | Mouse IL-1β ELISA Kit |
| QT-EM0109 | Mouse IL-1β QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| EM1624 | Mouse IL-17α ELISA Kit |
| EM0183 | Mouse TNF-α ELISA Kit |
| EM0183-HS | Mouse TNF-α high sensitivity ELISA Kit |
| ER1094 | Rat IL-1β ELISA Kit |
| QT-ER1094 | Rat IL-1β QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| ER0035 | Rat IL-17 ELISA Kit |
| ER7258 | Rat Stc1 ELISA Kit |
| QT-ER7258 | Rat Stc1 QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| ER0163 | Rat Stat3 ELISA Kit |
| ER1393 | Rat TNF-α ELISA Kit |
| QT-ER1393 | Rat TNF-α QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| EP0309 | Porcine STAT3 ELISA Kit |
REFERENCES
[1]A synergistic effect of triptolide and curcumin on rheumatoid arthritis by improving cell proliferation and inducing cell apoptosis via inhibition of the IL-17/NF-κB signaling pathway, PMID: 39226828.
[2]Isoliensinine suppresses chondrocytes pyroptosis against osteoarthritis via the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway, PMID: 39547017.
