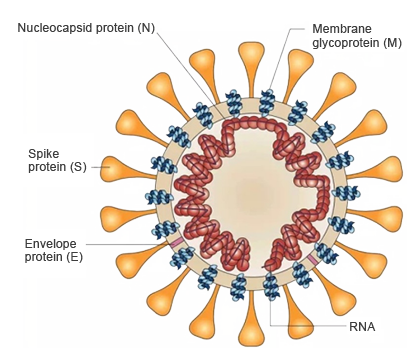
 2019 novel coronavirus is also called 2019-nCoV, SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV2. SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV belong to the same family with differences. Gene is single-stranded RNA. SARS-CoV-2 mainly consists of four structural proteins: spike glycoprotein (S), envelope proteins(E), membrane proteins(M), and nucleocapsid proteins(N).
2019 novel coronavirus is also called 2019-nCoV, SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV2. SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV belong to the same family with differences. Gene is single-stranded RNA. SARS-CoV-2 mainly consists of four structural proteins: spike glycoprotein (S), envelope proteins(E), membrane proteins(M), and nucleocapsid proteins(N).
Spike proteins(including 2 subunits: S1 and S2) are the most important pathogenic proteins. Binding to transmembrane receptor proteins ACE2 on human cell membrane helps to enter the cell. The spike protein is very large and can be divided into two parts: S1 contains receptor binding domain(RBD) which recognizes cell receptors. S2 contains basic components required for membrane fusion process. Current research focuses on S1-RBD protein, which is the target of antibody drugs.
SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2 receptor on host cell surface by the spike protein. After entering cells, spike proteins are cleaved into two subunits: S1 and S2. S1 is responsible for receptor binding. S2 helps the virus fuse with the cell membrane and promotes the virus to enter the cell. RNA genome of the virus encodes several functional proteins, and is responsible for the replication, assembly, and release of the virus by maintaining the transmission and pathogenicity in the host. The virus is transmitted by droplets, air and touching. Asymptomatic or mildly infected individuals can also transmit the virus. SARS-CoV-2 enters the cell by binding to ACE2 receptor on host cell surface, and replicates by host mechanism to cause the virus spread. Overreaction of immune system may cause cytokine storm, resulting in severe symptoms like lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) etc. The virus can also cause thrombosis and increase the risk of cardio-cerebro vascular complications.
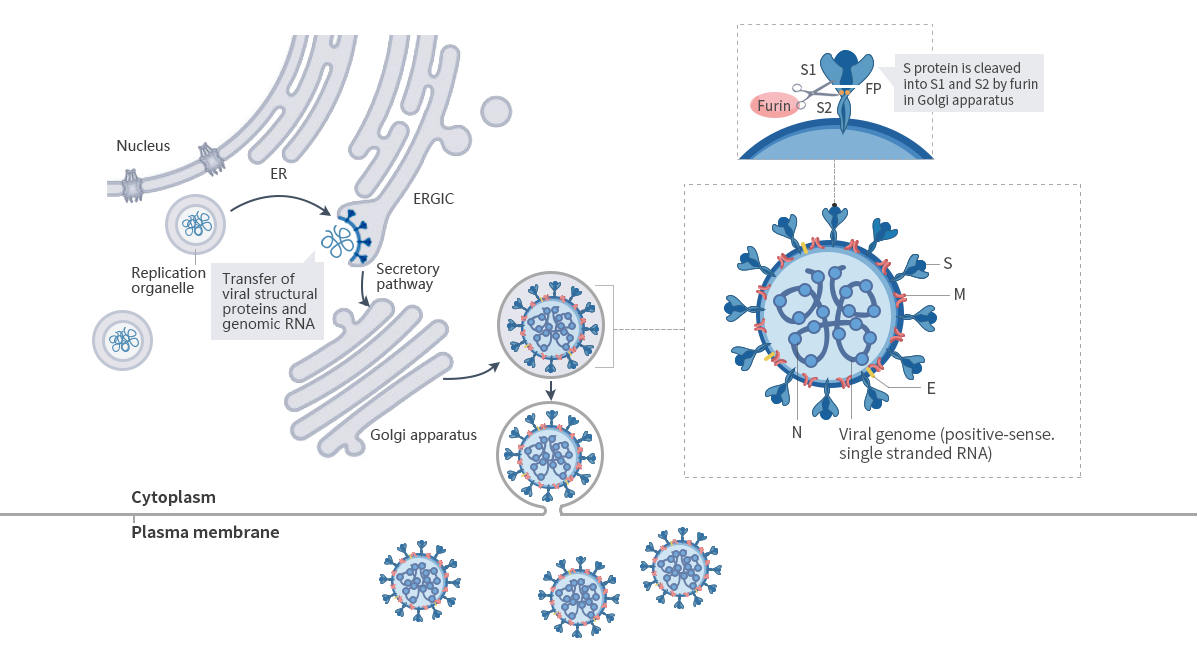
Nucleic acid and protein capsid are the most important components of the virus. Nucleic acid is responsible for reproduction of hereditary substance. Protein capsid protects hereditary substance. SARS-CoV-2 is named for the shape of its capsid. The research shows the spike glycoprotein mainly causes the binding to relevant receptors in human cells. Thus, it's the key target of neutralizing antibodies(nAbs), and also plays an important role in the treatment and vaccine design.
Recommended Products
Proteins:
| Cat.No | Product Name | Host | Expression Region | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3302 | Recombinant S1 Subunit[Omicron B.1.1.529] | HEK293 cells | 16-685 | C-terminal His Tag |
| P3018 | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein | HEK293 cells | 16-1213 | C-terminal His-Avi Tag |
| P3006 | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein RBD | HEK293 cells | 315-535 | C-terminal His Tag |
| P8823 | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein S1 | HEK293 cells | 16-685 | C-terminal His Tag |
| P8790 | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein S2 | HEK293 cells | 686-1213 | C-terminal rbFc-His Tag |
| P8947 | Recombinant ORF8 | HEK293 cells | 16-121 | C-terminal His Tag |
| P3003 | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein | E.Coli | 1-419 | N-terminal His Tag |
| P2908 | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein [Delta B.1.617.2] | E.Coli | 1-419 | N-terminal His Tag |
| P3123 | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein [Omicron B.1.1.529] | E.Coli | 1-419 | N-terminal His Tag |
| P1023 | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein-N1 | E.Coli | 1-182 | N-terminal His Tag |
| P1024 | Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Nucleoprotein-N2 | E.Coli | 227-419 | N-terminal His Tag |
Antibodies:
| Cat.No | Product Name | Host | Clonality | Reactivity | Tested Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FNab10307 | Mouse Anti-Human IgG1 | Mouse | monoclonal | Human | Colloidal Gold-Based, ELISA, IHC, WB |
| FNab10306 | Mouse Anti-Human IgM | Mouse | monoclonal | Human | Colloidal Gold-Based, ELISA, IHC, WB |
| FNab10309 | SARS-CoV-2 N protein antibody | Mouse | monoclonal | 2019 nCOV | ELISA, WB, Colloidal Gold-Based |
| FNab10600 | SARS-CoV-2 N protein antibody | Rabbit | monoclonal | 2019 nCOV | ELISA, WB, Colloidal Gold-Based |
| FNab10601 | SARS-CoV-2 N protein antibody | Rabbit | monoclonal | 2019 nCOV | ELISA, WB, Colloidal Gold-Based |
