Neurodegenerative diseases(NDDs) are caused by loss of CNS neurons, following myelin sheath damage and synaptic dysfunction. With the development of NDDs, serious deficiency of neurofunctional disorder appears.
Acute and chronic NDDs are common diseases.
01
02
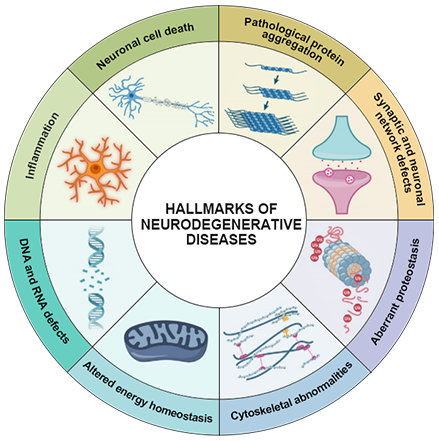
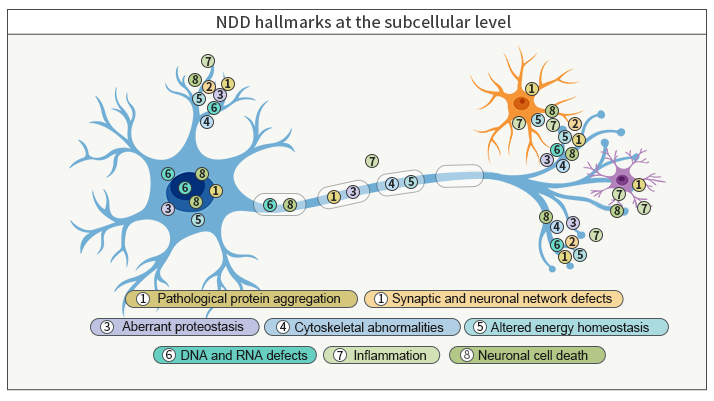
Pathogenesis of these diseases is very complex. Currently, pathological protein aggregation and damage to neurovascular unit are common pathologic features of NDDs, finally resulting in the neuronal death.
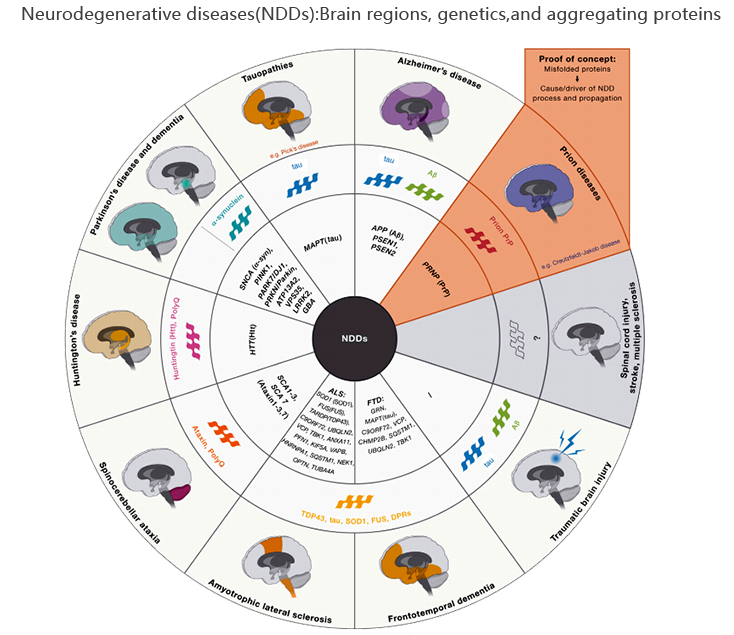
Different NDDs are often accompanied by featured pathological protein aggregation and affected sites: e.g. featured pathological proteins in AD like amyloid β-protein and tau protein deposits in temporal lobe and cerebral cortex. α-synuclein(α-Syn) protein in PD deposits in midbrain substantia nigra. Huntingtin(Htt) proteins deposits in basal ganglia. TDP-43(transactive response DNA binding protein 43 kDa) deposits in temporal cortex and spinal cord. Ubiquitin proteasome system and autophagy-lysosomal are two important pathways responsible for protein degradation in neuron. The damage of the two pathways may be main reasons for pathological protein deposition. Pathological proteins usually exist before clinical symptoms of NDDs. With the development of the disease, these proteins gradually accumulate. Thus, these accumulated pathological proteins are used as specific biomarkers applied in early and differential diagnoses of various NDDs.
Currently, cranial nerve diseases like neurodegenerative diseases are still facing low consultation rate, high misdiagnosis rate and low cure rate. Thus, early diagnosis is very important for timely intervention therapy. FineTest provides a list of targets of neurodegenerative diseases to help in vitro research of cranial nerve diseases.
Alzheimer′s Disease(AD)
Alzheimer′s Disease(AD) is degeneration of central nervous and also manifested as cognitive dysfunction, behavior impairment and incurability. Combined therapy can relief the disease and delay the development. Currently, various theories try to explain the pathological changes, including β - amyloid protein waterfall cascade, Tau protein theory, Neurovascular hypothesis.
Parkinson Disease(PD)
Parkinson Disease(PD) is a common aged degenerative disease of nervous system. Symptoms include slow movement, shaking of hands and feet or other parts of the body. The body loses flexibility and becomes stiff. Pigment cells in the substantia nigra decreases. Dopaminergic neuron is lost. Glial cells increase. Lewy body appears. Inhibitory transmitter in the striatum and excitatory transmitter acetylcholine are relatively imbalanced.
| Alpha-Synuclein | CNTF R alpha | DDC | GFR alpha-like | LRRK2 | MAOA | MAOB | APOE |
| CALB1 | COMT | DRD1 | DRD2 | DRD5 | GLUD2 | MFN1 | MFN2 |
| PINK1 | PPP1R1B | RORC | SLC18A2 | UBB | UBE2K | UBQLN1 |
Huntington Disease(HD)
Huntington Disease(HD, also called Huntington's chorea) is a rare autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder. Symptoms of patients are unconsciously dancing like movements. Abnormal mental behavior and cognitive function may appear. This is a genetic disease caused by abnormally repeated CAG fragment of HTT gene on Chromosome 4.
| HTT | PSMC6 | FIS1 | CCNH | SIRT1 | SUZ12 |
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis(ALS)
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis(ALS) is a fatal neurodegenerative disease, caused by deficiency of brain and spinal motor neurons. This disease results in gradual powerlessness and myatrophy of hands, feet, body, chest and abdomen, affecting movement, communication, swallowing and respiratory function till death. SOD1 is found to be closely related to familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and the important disease gene.
| SOD1 | SOD2 | TDP-43 | FUS | NGFR | C9orf72 | TARDBP | UCP1 |
| AOX1 | CHMP2B | CSF3R | IGF1R | SLC1A2 | SLC1A3 | UBE2K | VAPB |
| VEGFA |
Multiple Sclerosis(MS)
Multiple Sclerosis(MS) is a immune-mediated disease featured with pathological inflammatory demyelination of the central nervous system. Various research data show B cell and its autoantibody play an important role in the development of multiple sclerosis. Several B cell specifically expressed CD20 antibody drugs for treating multiple sclerosis have been developed.
| CIITA | GATA3 | IFNGR1 | IL10RA | IL17RA | IL17RB | IL1RAP | IL22RA1 |
| IL24 | IL2RB | IL4R | IL6 | IL6R | IL7 | MAG | MPO |
| MPP5 | NF2 | RARA | RORC | RTN4 | SPHK1 | TBX21 | TGFB1 |
| TPO | TSLP |
Diabetic Neuropathy(DN)
Diabetic neuropathy(DN) is a degenerative neurological disorder and the most common diabetic chronic complication. Without any other secondary peripheral neuropathy, this disease will affect the body or autonomic peripheral nervous system of diabetic patients. About 50% diabetic patients finally develops into diabetic neuropathy.
| AKT1 | AKT2 | AKT3 | BDNF | GLP1R | GNAS | GRM5 | HSPB1 |
| HSPBP1 | MAPK11 | MAPK12 | MAPK13 | NGF | NRG1 | NRG3 | NTF3 |
| NTRK2 | PIK3C2B | PIK3CB | PIK3CD | PIK3R1 | PIK3R2 | PIK3R4 | PIK3R5 |
| RAB7A | SOD2 | SOD3 | TNFRSF1A | TNFRSF1B | VEGFA |
