Immune checkpoints are general terms for receptors and relevant ligands on T cells. Binding between receptors and ligands activates or inhibits down-stream signal transduction to act as immune activation or inhibition. Immune checkpoints play an important immunoregulation role in maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing autoimmune. Disorder of immune checkpoints will result in over activation or inhibition of immune reaction(e.g. autoimmune diseases, tumor). Most reported immune checkpoint proteins are expressed in cells of adaptive immune system, especially T cells and innate immune system.
Currently, costimulatory and coinhibitory immune checkpoints are found in different cells in tumor microenvironment(TME). Many tumor drugs activate
immune reaction and inhibit tumor via blocking or improving inhibition or stimulation function. Currently, the most widely studied immune checkpoint pathways include CTLA-4, PD-1 and PD-L1.
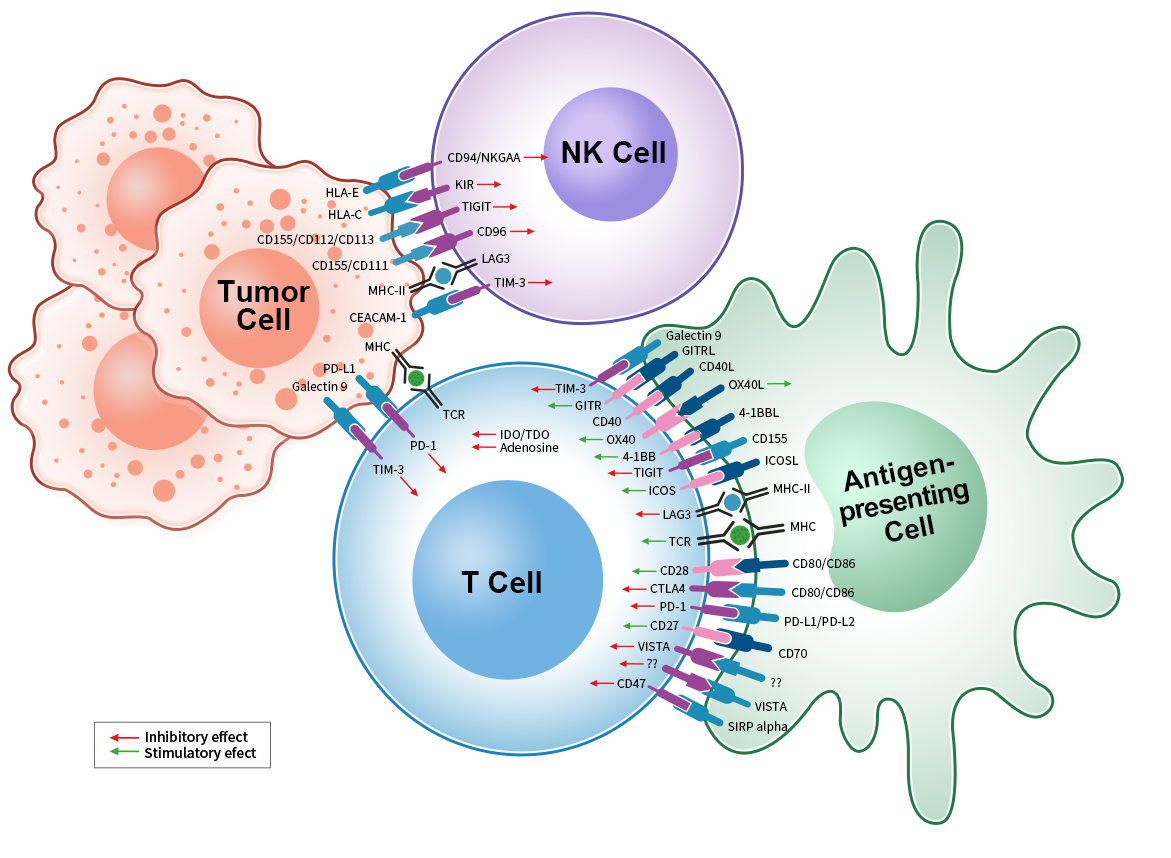
VISTA is the important regulator for immune homeostasis and antitumor immunity. In immunocytes, VISTA is mainly expressed by myeloids(e.g. neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells etc). Naïve T cell and CD4+ T cell weakly express VISTA. The expression level of VISTA in CD8+ T cell, Foxp3+ Treg and CD56dim NK cell is even lower. However, CD56bright NK cell and B cell mostly express negativity of VISTA.
Current researches show VISTA blocker improves the active state of tumor-associated dendritic cells and produces more inflammatory cells to up-regulate costimulation of these cell and antigen-presenting molecules. Thus, VISTA is expected to improve antigen-presenting function of myeloid cells in tumor draining lymph nodes and increase the potential of activation of tumor-reactive T cells and function of effector.
TIM-3 consists of a extracellular domain, a single transmembrane domain and a C-terminal cytoplasmic tail. TIM-3 exists in different types of immunocytes as a negatively regulating immune checkpoint, including T cells, NK cells, monocytes, macrophages and DCs.
TIM-3 can regulate antitumor immunity by binding with different ligands. E.g. Binding between Galectin-9 and sugar chain of TIM-3 regulates immunity of TH1 cell via inducing apoptosis. Interaction between HMGB1 and TIM-3 damages toll-like receptors and cytoplasmic receptor induced innate immune response for nucleic acid, preventing effects of DNA vaccine and cytotoxic chemotherapy.
TIGIT is expressed in CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, NK cells and Treg cells, inhibiting innate and adaptive immunity via various mechanisms.
TIGIT can inhibit CD155 mediated activation of CD226, involved in activating TCR signaling pathway and recognizing NK cell neoplasm. In unstimulated whole blood sample of healthy individuals, 13% CD4+ T cells and 24% CD8+ T cells express TIGIT. TIGIT can up-regulate in damaged CD8+ T cells. Double chemical-block of TIGIT and PD-1 can partially restore the ability of CD8+ T cell. Besides, there are significant individual differences for the expression of TIGIT in NK cells(about 20%-90%, avg 62.57%). Expression level in CD56dim NK cells is higher than CD56bright NK cell.
The protein extracellular region has Ig-like domain. Intracellular region has ITIM motif. The family members include LILRB1, LILRB2, LILRB3, LILRB4, LILRB5.
LILRB2(also called ILT3, CD85k) is mainly expressed in myeloid cells, including monocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages, and neutrophils.
LILRB4(also called ILT3, CD85k) plays a very important role in function of the immune system via expressing in various immunocytes(e.g. T cell and plasma cell) under physiological conditions. LILRB4 is mainly expressed in APC as immune tolerance receptor. Besides, APCs expressed by LILRB4 plays a key role in controlling inflammation. LILRB4 is also the important marker for monocytic leukemia, supports infiltration of tumor cell and inhibits activity of T cell in acute myeloid leukemia cells(AML) via the signal axis ApoE/LILRB4/SHP-2/uPAR/Arginase-1. Blocking the signal transduction of LILRB4 can restrict the development of AML. Thus, LILRB4 is the important target for treating monocytic acute myeloid leukemia.
