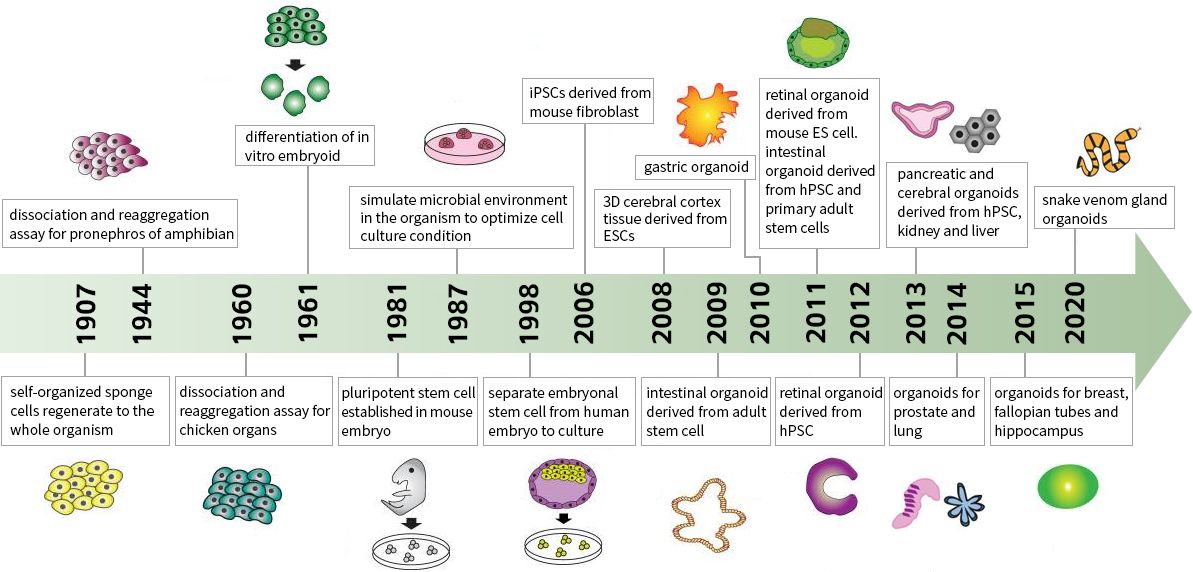
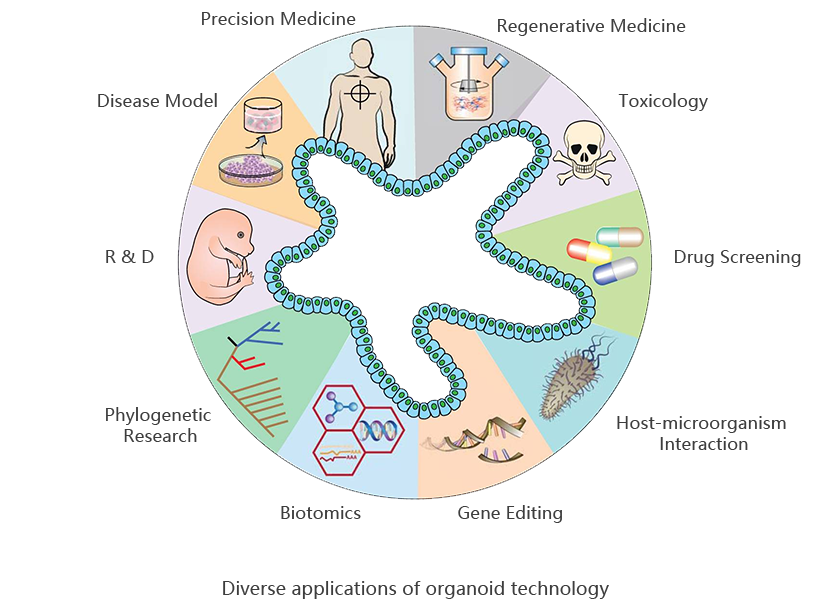
Organoid is derived from tissues or stem cells of organisms, and can differentiate or form relevant human organs with specific functions and structures via self-organization and 3D cultivation technology in vitro. Human-derived organoid can partly simulate characteristics of organs in vivo under healthy or sick states. Long-term amplification of organoid in vitro shows genome stability and can form living biobank to perform high throughput screening. As the closely concerned in vitro model, organoid together with new technologies like gene editing, organ chip and single cell RNA sequencing etc can break through traditional model, providing valuable information to the establishment of disease model, drug development, precision medicine and regenerative medicine.
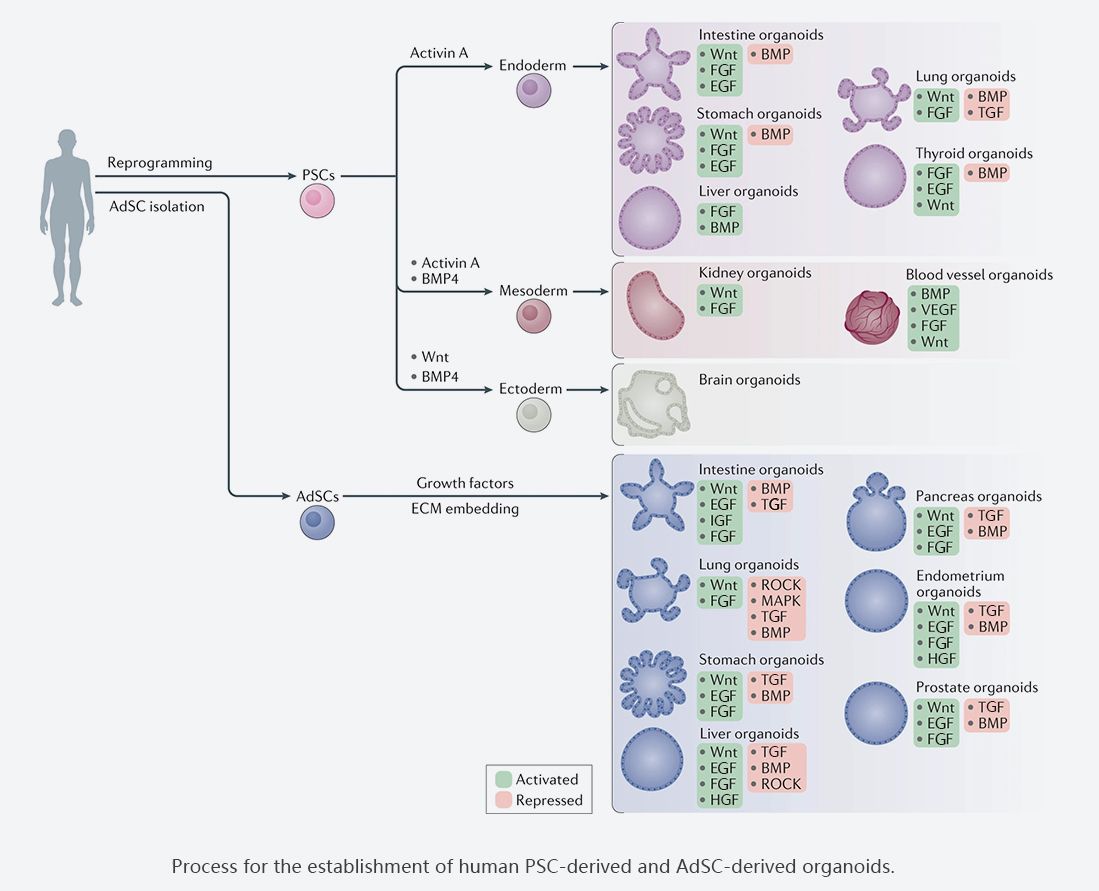
Due to different sources of cells, Organoids include adult stem cell(ASC), pluripotent stem cell(PSC) or patient-derived organoid(POD). There are two types of pluripotent stem cell(PSC) : embryonic stem cell(ESC) and induced pluripotent stem cell(iPSC). Features and applications of different organoids are also varied. e.g. Neuroectoderm(such as optic cup and cerebral organoid) only derives from PSC. Thus, PSC is usually applied in the research on mental genetic disorders and developmental biology. ASC derives from precursor cells with regenerative ability in the tissue and mainly applied in the research on adult tissue biology, tissue regeneration and precision medicine.
Add different combinations of cytokines/chemical small molecule inhibitors/activators during organoid culture to get the required organoid via promoting or inhibiting ignaling pathway involved in formation of organoid according to different sources of cells and final differentiation type.
FineTest has developed a series of recombinant growth factors with high purity, biological activity, stability and low endotoxin to facilitate the best growth of organoid, ensuring the better reproducible assay results.
Some hot-selling Products
| Cat.No | Product Name | Host | Expression Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| P4572 | Recombinant Mouse IL-4 | E.Coli | 21-140 |
| P2940 | Recombinant Human TGFB1 | HEK293 cells | 30-390 |
| P0775 | Recombinant Human FGF2 | E.Coli | 143-288 |
| P0150 | Recombinant Mouse IFNG | E.Coli | 23-155 |
| P6053 | Recombinant Human EGF | E.Coli | 971-1023 |
| P9778 | Recombinant Human IL-13-FC | HEK293 cells | 21-132 |
| P4827 | Recombinant Rat Tgfb1 | E.Coli | 30-278 |
| P8133 | Recombinant Human VEGF165 | HEK293 cells | 27-191 |
| P0149 | Recombinant Human IFNG | E.Coli | 24-166 |
| P2602 | Recombinant Mouse TGFB1 | E.Coli | 279-390 |
| P4949 | Recombinant Human BDNF | E.Coli | 129-247 |
| P1643 | Recombinant Human FGF10 | E.Coli | 38-208 |
| P0146 | Recombinant Bovine IFNG | E.Coli | 24-166 |
| P1966 | Recombinant Human LIF | E.Coli | 23-202 |
| P3366 | Recombinant Rat VEGFA | E.Coli | 27-214 |
| P5419 | Recombinant Human Wnt3a | E.Coli | 19-352 |
| P1682 | Recombinant Human CXCL12 | E.Coli | 22-89 |
| P4733 | Recombinant Rat FGF2 | E.Coli | 9-154 |
| P1777 | Recombinant Human FGF4 | E.Coli | 71-206 |
| P4917 | Recombinant Human FGF7 | E.Coli | 32-194 |
| P5148 | Recombinant Human GDNF | E.Coli | 78-211 |
| P1641 | Recombinant Chicken HGF | E.Coli | 493-721 |
| P5794 | Recombinant Human IFNG | E.Coli | 1-144 |
| P2663 | Recombinant Human IGF-1 | E.Coli | 49-118 |
| Pr22216 | Recombinant Human IL-13 | Mammalian Cells | Gly21-Asn132 |
| P4879 | Recombinant Mouse IL-13 | E.Coli | 22-131 |
| P6627 | Recombinant Human IL-22 | E.Coli | 34-179 |
| P4402 | Recombinant Human NGF | E.Coli | 122-239 |
| P5020 | Recombinant Rat Pdgfa | E.Coli | 87-196 |
| P0443 | Recombinant Human PDGFB | E.Coli | 82-190 |
| P9633 | Recombinant Mouse TGFB1 | HEK293 cells | 30-390 |