Abstract: Macrophages are derived from monocytes and produced by the differentiated monocytes in the blood. They’re a kind of leukocyte in the tissue. The volume, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, lysosome and phagocytic function increases, after monocytes enter connective tissues. Some macrophage polarization markers are specified below.
Keywords: Macrophage Polarization, Macrophage and Monocyte, Macrophage Function
1. Macrophage and Monocyte
Macrophages and monocytes are both phagocytes. They’re involved in non-specific defense(innate immune) and specific defense(cellular immunity). Macrophages belong to immunocyte with multiple functions, and play an important role in the research on phagocytosis, cellular immunity and molecular immunology. Macrophages are easily obtained, cultured and can be purified. In the suitable condition, they can live for 2-3 weeks and usually be used for primary culture.
2. Macrophage Function in Immune System
2.1. Macrophages and Phagocytosis
Macrophages can phagocytize and kill intracellular parasites, bacteria, tumor cell, aging cells and dead cells. They also play an important role in immunologic defence, immune homeostasis and immunosurveillance.
Phagocytosis is very important in the chronic inflammation. Neutrophils are main factors in the early stage of inflammation. If neutrophils are aged, the released chemokine can absorb macrophages.
When phagocytosis absorbs pathogen, the pathogen blocked in the phagosome fuses with lysosome. In the phagocytized lysosome, enzyme and toxic peroxides digest pathogen. However, some bacteria(e.g. M.tuberculosis) produce resistance to decomposition method. Thus, fibrotic lesions are found in the lung. Finally, macrophages can phagocytize hundreds of bacteria before the death.
2.2. Antigen Presentation
Macrophages are antigen-presenting cells(APC) and non-self antigens(e.g. bacterial antigen or soluble antigen), which unspecifically binds with macrophages. Non-self antigens absorb antigens via phagocytosis, pinocytosis, absorption, FcR/CR1 mediated regulation. Natural antigen is degraded in phagolysosome.
3. M1 and M2 Macrophages
Macrophages are properly stimulated into different inflammatory states, including M1 and M2. M1 macrophage has the pro-inflammatory effect, and is related to immune reaction in bacteria and intracellular pathogen. However, M2 macrophage has the anti-inflammatory effect, and plays an important role in angiogenesis and wound healing. It's also related to the reaction of Th2 cell, e.g. anti-worm immunity, asthma and allergy.
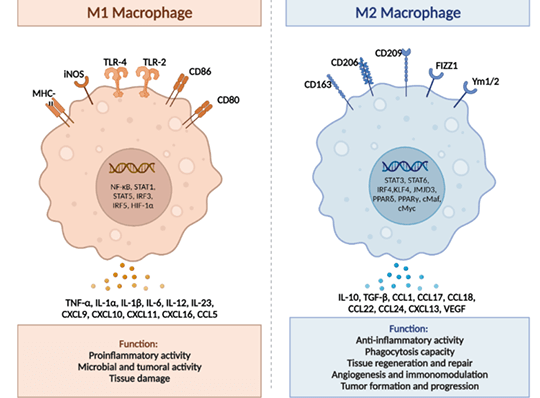
Figure Source: Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 29;24(21):15732. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115732.
3.1. M1 Macrophage
M1 macrophage is mainly recruited in Th1 cell via innate and adaptive immune responses, and also plays an important role in anti-pathogen and tumor control. It's mainly activated by pathogen, LPS, GM-CSF, IFNG and TNFα. Genetic markers related to M1 polarization include IL1a, IL1b, IL6, NOS2, TLR2, TLR4, CD80 and CD86.
3.2. Alternatively Activated Macrophages
M2 macrophage is activated by cytokines like IL4, IL1 and IL13. Phenotype of M1 and M2 is continuous. Thus, macrophage in the middle range can synchronously express some markers.
Alternatively activated subtypes express opposite expression profile: downregulation of IL-12 and IL-23, upregulation of IL-10 and IL-1RA. Besides, M2 macrophage expresses lower level of inflammatory cytokines like IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-α. M2 macrophage also plays a role in pathogen elimination, anti-inflammatory response and metabolism, wound healing, tissue remodeling, immune regulation, tumor progression and malignant tumor.
3.2.1. M2 Macrophage Subtype
There are four stimulated M2 subtypes: M2a, M2b, M2c and M2d. These different subtypes depend on cell surface markers, secreted cytokines and biological functions. However, all M2 macrophage subtypes express IL-10.
M2a Macrophage: Activated by IL-4 or IL-13. IL-4 promotes the expression of CD206. It proves that further upregulation of IL-10, TGF-b, CCL17, CCL18 and CCL22 can promote cell growth, tissue repair and endocytosis.
M2b Macrophage: Activated by immune complexes, toll-like receptor/ligand and IL-1b. After activation, the subtype releases pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines(e.g. TNF-α, IL-1b, IL-6 and IL-10). M2b macrophage plays a role in immune reaction and inflammation regulation.
M2c Macrophage: Activated by glucocorticoid, IL-10 and TGF-b(inactivated macrophage). The subtype is featured with high-level expression of anti-inflammatory factor IL-10, pro-fibrogenic factors(e.g. TGF-b, CCL16, CCL18) and MerTK. MerTK can promote phagocytosis of apoptotic cell.
M2d Macrophage: Activated by TLR antagonist, IL-6 and adenosine. Adenosine can promote the expression of IL-10 and VEGF. This process can accelerate angiogenesis and tumor progression.
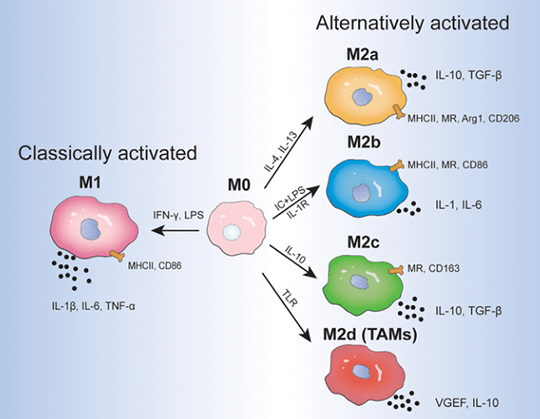
Figure Source: Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 30:13:888713. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.888713.
4. Macrophage Surface Markers
CD68 and CD11b are markers expressed by all macrophages. M1 and M2 macrophages have their own specific markers.
M1 macrophage can select CD80, CD86, CD64, CD16 and CD32 as markers. Besides, the expression of iNOS in M1 can be used for phenotypic markers.
Main markers of M2 macrophage are CD163 and CD206. Besides, Arg1 and DECTIN-1 are suitable phenotypic markers for identification of M2 macrophage.
It's reported that FIZZ1, Ym1 and Ly6C can be also used as surface markers related to M1 or M2 macrophage subsets.
5. Recommended Antibodies
|
Catalogue No. |
Product Name |
Type |
Reactivity |
Applications |
|
CD68 antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human, Mouse |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
|
|
CD68 antibody |
Mouse mAb |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
|
|
CD68 antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
|
|
CD11B antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
|
|
CD11B antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human |
ELISA, IHC |
|
|
CD80 antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human, Mouse |
ELISA, WB, IF, FC |
|
|
CD80 antibody |
Mouse mAb |
Human, Mouse |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
|
|
CD86 antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
|
|
CD16 antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human |
ELISA, WB, IHC |
|
|
CD32 antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human |
ELISA, WB |
|
|
iNOS antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
|
|
iNOS antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human, Rat |
ELISA, IHC |
|
|
CD163/M130 Antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human, Mouse |
ELISA, WB, IHC, FC |
|
|
CD163 Antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human, Mouse |
ELISA, WB |
|
|
CD206 antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC, FC |
|
|
CD206 antibody |
Mouse mAb |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, IP, WB |
|
|
liver Arginase antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, IHC, IP, IF, FC, WB |
|
|
liver Arginase antibody |
Mouse mAb |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, WB, IHC, IF |
|
|
ARG1 antibody |
Rabbit pAb |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
ELISA, IF, WB |
REFERENCES
[1]The Role of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovitis, PMID: 35663975.
[2]Macrophage Polarization: Different Gene Signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. Classically and M2(LPS-) vs. Alternatively Activated Macrophages, PMID: 31178859.
