1. TNF Alpha and Rheumatoid Arthritis
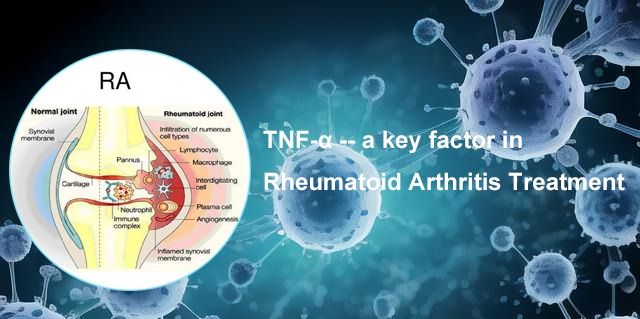
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease involving multiple inflammatory mediators, including tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α). TNF-α, a crucial inflammatory mediator, is a monocyte-derived cytokine primarily produced by monocytes and macrophages, playing an important role in immune responses by regulating inflammation and activation of immune cells. Its precursor is a type II transmembrane protein (mTNF-α). By binding to two receptors, TNFR-1 and TNFR-2, it triggers their activation and trimerization, resulting in a cascade of signal transduction pathways that affect cell survival and apoptosis. In RA patients, TNF-α levels are significantly increased and closely associated with disease severity and progression of arthritis.
2. TNF Alpha Signaling Pathway
TNF-α binds in trimeric form and forms clusters on high-affinity receptors densely present on most cell membranes to exert its effects. The ligand/receptor complexes are rapidly endocytosed via coated pits and ultimately degraded in secondary lysosomes. Upon binding to receptors, TNF-α can activate multiple signaling pathways including NF-κB pathway, MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase) pathway, and JNK (c-Jun N-terminal Kinase) pathway. In the NF-κB pathway, NF-κB binds to IκB proteins in an inactive state. TNF-α induces phosphorylation and degradation of IκB, releasing active NF-κB to enter the nucleus and regulate gene transcription. Additionally, TNF-α can activate the MAPK pathway including ERK1/2, JNK, and p38 MAPK. These kinases further regulate cell proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammatory responses. In certain circumstances, TNF-α induces cell apoptosis. This can occur through activation of apoptotic signaling pathways such as the Caspase cascade. The TNFR1/TRADD complex recruits FADD via death domains, activating Caspase-8 and subsequently Caspase-3, leading to DNA fragmentation and cell apoptosis. TNF-α induces expression of apoptotic initiators like Bid and Bax, activates Caspase-8, and induces tumor cell apoptosis. Moreover, TNF-α induces non-classical Caspase-dependent cell apoptosis, altering mitochondrial permeability, releasing cytochrome C, secreting ROS, and inducing tumor cell death.
3. Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Given the significance of TNF-α in the pathogenesis of RA, inhibiting TNF-α has become one of the primary strategies for treating RA. Biological agents targeting TNF-α are widely employed in the treatment of RA, including TNF-α inhibitors such as corticosteroids and anti-TNF-α biological agents (such as infliximab, etanercept, and adalimumab). By inhibiting the action of TNF-α, these medications can alleviate inflammation, improve joint function, and slow disease progression, thereby providing long-term clinical benefits for RA patients.
4. Recommended ELISA Kits
FineTest provides TNF-α ELISA kits with high specificity, which are suitable for rheumatoid arthritis research.
4.1. Humanized Antibody Drug
|
Catalogue No. |
Product Name |
Detection Range |
Sensitivity |
|
Rituximab antibody ELISA Kit |
1.563-100ng/ml |
0.938ng/ml |
|
|
Human anti-TNF-α Antibody(Anti Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Antibody) ELISA Kit |
1.563-100ng/ml |
0.938ng/ml |
|
|
Infliximab ELISA Kit |
0.313-20ng/ml |
0.188ng/ml |
|
|
Anti-Infliximab antibody ELISA Kit |
1.563-100ng/ml |
0.938ng/ml |
|
|
Human Golimumab ELISA Kit |
0.625-40ng/ml |
0.375ng/ml |
|
|
Human anti-Golimumab ELISA Kit |
0.312-20ng/ml |
0.188ng/ml |
|
|
Human Adalimumab ELISA Kit |
1.563-100ng/ml |
0.938ng/ml |
|
|
Human Anti-Adalimumab antibody ELISA kit |
1.563-100ng/ml |
0.938ng/ml |
4.2. Species Category
|
Catalogue No. |
Product Name |
Detection Range |
Sensitivity |
|
Human TNF-α(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit |
15.625-1000pg/ml |
9.375pg/ml |
|
|
Human HS-TNF-α(High sensitive Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit |
3.12-200pg/ml |
1.875pg/ml |
|
|
Mouse TNF-α(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit |
3.906-250pg/ml |
2.344pg/ml |
|
|
Mouse TNF-α(High sensitive Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha)ELISA Kit |
1.563-100pg/ml |
0.938pg/ml |
|
|
Rat TNF-α(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit |
3.906-250pg/ml |
2.344pg/ml |
|
|
Pig TNF-α (Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit |
31.25-2000pg/ml |
18.75pg/ml |
|
|
Chicken TNF-α (Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha)ELISA kit |
15.625-1000pg/ml |
9.375pg/ml |
|
|
Bovine TNF-α(Tumor necrosis factor alpha) ELISA Kit |
15.625-1000pg/ml |
9.375pg/ml |
|
|
Horse TNF-α(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit |
15.625-1000pg/ml |
9.375pg/ml |
|
|
Rabbit TNF-α(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit |
7.813-500pg/ml |
4.688pg/ml |
|
|
Monkey TNF-α(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit |
31.25-2000pg/ml |
18.75pg/ml |
REFERENCES
[1] Additive efficacy of a bispecific anti-TNF/IL-6 nanobody compound in translational models of rheumatoid arthritis, PMID: 36724239.
[2] TNF-α versus IL-6 Genes Expression levels in Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: Clinical and Laboratory Determinants, PMID: 37787680.
