Abstract: Angiogenesis refers to the neovascularization process completed by endothelial cell migration, proliferation and remodeling of preexisting vessels, relevant to physiological tissue repair, embryonic development and pathological diseases(e.g. tumor, ischemic diseases). Unlike vasculogenesis, angiogenesis happens in adult tissue and relies on the vascular expansion. In recent years, roles of angiogenesis in cancer treatment, ischemic diseases and wound healing are very important, affecting the development of diseases via regulation of endothelial cell migration and matrix remodeling.
Keywords: Angiogenesis in cancer, Cancer Treatment, Anti-angiogenic Therapy, Anti-angiogenic Drugs
1. Principle of Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis produces new blood vessels via activation, proliferation, migration and blood vessels formation. Angiogenesis usually happens in microvascular area of preexisting vessels, alternatively activated by pro-angiogenic factors during wound healing, tumor growth etc. First, release of angiogenic factors(e.g. VEGF, FGF, PDGF etc) supplements oxygen and nutrition, stimulating migration of activated endothelial cells to the target area. Finally, endothelial cells form new blood vessels via interaction of signal transduction.
2. Key Molecules and Signaling Pathway of Tumor Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the complex and dynamic process, relevant to various pro- or anti-angiogenic biomolecules, including growth factors(e.g. VEGF, FGF, TGF, HGF), adhesion factors(e.g. integrin, cadherin), protease(e.g. matrix metalloproteinase), extracellular matrix proteins(e.g. fibronectin, collagen), transcription factors(e.g. HIF, NF-κB), angiogenin, angiostatin, endostatin and interleukin etc. Activated gene expression via transmembrane receptor induces proliferation, survival and angiogenesis of endothelial cells.
Angiogenesis processes can be divided into several stages: First, due to hypoxia or inflammation, histiocytes secrete angiogenic factors(e.g. VEGF, Ang) to stimulate adjacent endothelial cells. Then, these factors bind with receptors on the surface of endothelial cells to activate signaling pathway of PI3K/Akt and MAPK and promote proliferation and migration of endothelial cells. Endothelial cells migrated to neovascular area establish neovascular network to form vessel structure via interaction. Finally, sertoli cells(e.g. smooth muscle cell, pericyte) promote maturity and stability to prevent degeneration via secreting factors(e.g. PDGF).
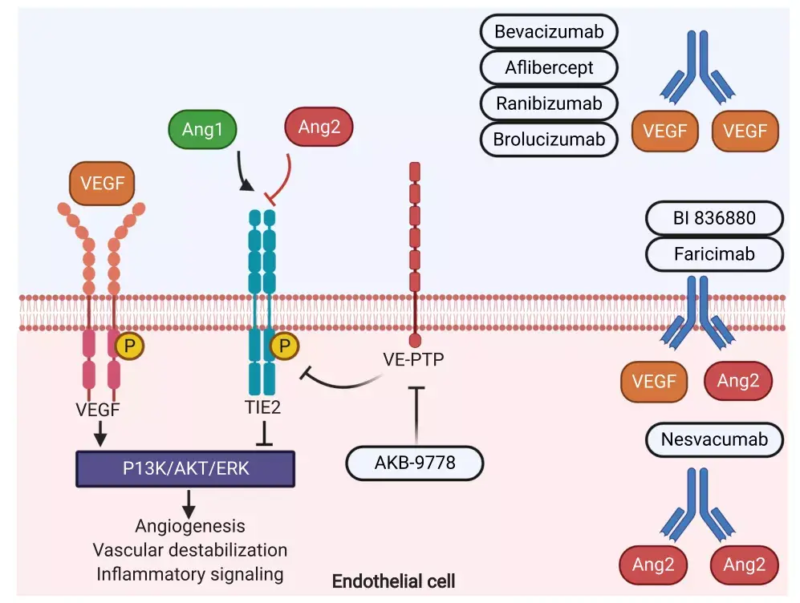
3. Roles of Angiogenesis in Diseases
Roles of angiogenesis in various diseases are very important. Tumor obtains oxygen and nutrition to promote tumor growth and metastasis via angiogenesis. Angiogenesis in ischemic diseases(e.g. heart disease and apoplexia) helps to repair injured vessels and recover blood supply. In diseases like diabetes, retinopathy etc, excessive angiogenesis can cause abnormal vessel growth and visual impairment. Thus, angiogenesis may promote the development of diseases and provide potential therapeutic targets.
4. Anti-angiogenic Drugs Examples
Anti-angiogenic treatment restrains tumor growth and metastasis via inhibiting angiogenesis, primarily regulated by VEGF/VEGFR signaling pathway. Common anti-angiogenic drugs include Bevacizumab(Avastin), Ramucirumab(Cyramza), Olaratumab(Lartruvo) etc. Pegaptanib(Macugen) is also applied in ophthalmic diseases as RNA aptamer. Aflibercept(Eylea) is the recombinant bait protein for VEGF-A. mTOR inhibitors(e.g. Everolimus, Temsirolimus) and small molecules(e.g. TKIs, Sorafenib) also take great effects in anti-angiogenic treatment.
5. Limitations and Challenges for Anti-angiogenic Treatment
Angiogenesis inhibitors in cancer treatment restrain tumor growth via preventing the formation of new blood vessels. Some challenges still exist, e.g. tumor recurrence, drug resistance, adverse reactions and lack of biomarkers. Common side effects include hypertension, thrombocytopenia and proteinuria etc, possibly affecting patients' tolerance. Mechanisms of drug resistance include up-regulation of angiogenesis signaling pathway, recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells, protection of perivascular cells and tumor heterogeneity etc. These factors limit anti-angiogenic curative effects.
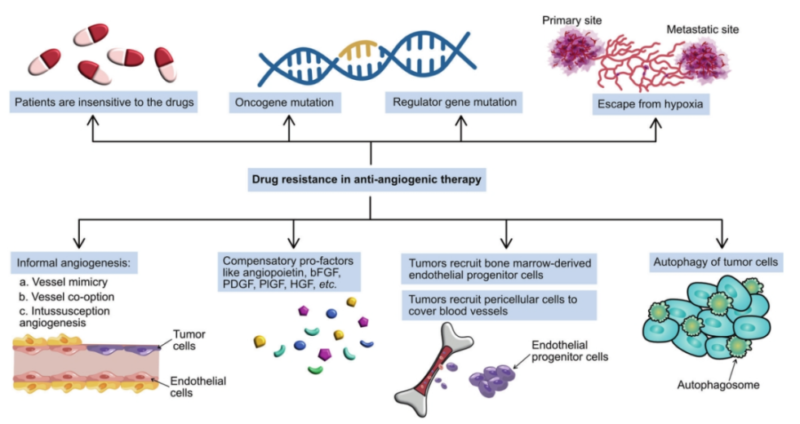
Roles of angiogenesis in cancer proliferation, invasion and metastasis are very important. Anti-angiogenic treatment becomes the hot strategy. However, insufficient curative effects and drug resistance still remain resolved, promoting discovery for new inhibitors, targets and biomarkers. Deep understanding of angiogenesis and drug resistance mechanisms may overcome these challenges. Anti-angiogenic treatment will take great effects in cancer treatment.
6. Recommended Products
| Recommended Recombinant Proteins | |
| Cat.No | Product Name |
| P4791 | Recombinant Human VEGFA |
| Pr22696 | Recombinant Human VEGFB |
| P9018 | Recombinant Human VEGFC |
| Pr22310 | Recombinant Human VEGF-D |
| Pr22536 | Recombinant Human VEGFR1 |
| Pr22214 | Recombinant Human VEGFR2 |
| Pr22639 | Recombinant Human VEGFR2 |
| P8133 | Recombinant Human VEGF165 |
| P5610 | Recombinant Mouse VEGFA |
| Pr22757 | Recombinant Mouse VEGF-D |
| Pr22638 | Recombinant Mouse VEGFR2 |
| Pr22762 | Recombinant Mouse VEGF 164 |
| P3366 | Recombinant Rat VEGFA |
| Pr22531 | Recombinant Rat VEGF 164 |
| Recommended ELISA Kits | |
| Cat.No | Product Name |
| EH0327 | Human VEGF ELISA Kit |
| QT-EH0327 | Human VEGF QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| EH3952 | Human VEGF-B ELISA Kit |
| QT-EH3952 | Human VEGF-B QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| EH0328 | Human VEGF-C ELISA Kit |
| EH3953 | Human VEGF-D ELISA Kit |
| EH3950 | Human VEGF165 ELISA Kit |
| QT-EH3950 | Human VEGF165 QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| EM0205 | Mouse VEGF ELISA Kit |
| QT-EM0205 | Mouse VEGF QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| EM0216 | Mouse VEGFB ELISA Kit |
| QT-EM0216 | Mouse VEGFB QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| EM1444 | Mouse VEGFD ELISA Kit |
| ER0069 | Rat VEGF ELISA Kit |
| QT-ER0069 | Rat VEGF QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| ER0085 | Rat VEGF-B ELISA Kit |
| ER1424 | Rat VEGF-C ELISA Kit |
| QT-ER1424 | Rat VEGF-C QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| ER1425 | Rat VEGF-D ELISA Kit |
| ER0918 | Rat EG-VEGF ELISA Kit |
| QT-ER0918 | Rat EG-VEGF QuickTest ELISA Kit |
| Recommended Antibodies | ||
| Cat.No | Product Name | Host |
| FNab09933 | VEGFA antibody | Mouse |
| FNab09391 | VEGFA antibody | Rabbit |
| FNab09866 | VEGFC antibody | Rabbit |
| FNab10821 | VEGFC antibody | Mouse |
REFERENCES
[1]Single-cell transcriptomic profiling of heart reveals ANGPTL4 linking fibroblasts and angiogenesis in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, PMID: 38346487.
[2]Angiogenesis in the mature mouse cortex is governed in a regional- and Notch1-dependent manner, PMID: 39612246.
