Cell death is the process during which cells stop life activity in vivo under the physiological or pathological condition. It plays an important role in normal biological development, immune response, repair of damage and diseases etc. The process is complex and interrelated, and is also very important for maintaining tissue balance and disease prevention. There are two types of cell death: Programmed Cell Death(PCD) and Accidental Cell Death(ACD).
Types of cell death are various, including ferroptosis, cuproptosis, necrosis, apoptosis, autophagy etc with different morphological characteristics and molecular mechanisms. Understanding various processes of cell death is very important for learning diseases and developing new therapies.
| Cell Death | Ferroptosis | Apoptosis | Autophagy | Necrosis | Pyroptosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biochemical Characteristics | Inhibit xCT and GPX4, decrease GSH. Fe accumulation and lipid peroxidation. | Activation of caspases oligonucleosomal DNA fragments | Increased lysosomal activity | Decreased ATP level; Activation of RIP1, RIP3 and MLK | caspase-1 (non-)dependent activation, GSDMD cutting and release of proinflammatory cytokine |
| Morphological Characteristics | Smaller mitochondria, decrease or disappearance of mitochondrial crista and broken outer mitochondrial membrane | Foamy plasma membrane, decrease of cells and nucleus volume, karyorrhexis | Formation of double-membrane autophagosomes | Broken plasma membrane, organelle swelling, moderate chromatin condensation | Nuclear contraction, cell swelling, cell membrane pores, collapsed and broken cell |
| Key regulatory genes | Positive: VDAC2/3; Ras; NOX; TFR1; p53; CARS | Positive: p53;Bax;Bak;Other pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins | Positive: LC3;ATG5;ATG7;Beclin 1;Other ATG family proteins |
Positive: RIP1;RIP3;MLKL | Positive: CASP1;CASP11;GSDMD |
| Negative: GPX4;SLC7A11;HSPB1;NRF2 | Negative: Bcl-2;Bcl-XL;Other anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins | / | / | Negative: GPX4;ESCRT-III;PKA | |
| Pathway Regulation | xCT and Gpx4, MVA, HSF1-HSPB1, p62-Keap1-Nrf2 pathway, LSH pathway | death receptors, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum pathway; Csapase, P53, Bcl-2 mediated pathway | PI3K-AKT-mTOR, MAPK-ERK1/2-mTOR pathway | TNFα, TNFR1, TLR3, trail, FasL, ROS, PKC-MAPK-AP-1 mediated pathway | Caspase-1, NLRP3 mediated pathway |
| Release of related damaged molecules | HMGB1 | Ecto-CRT, HMGB1, and ATP | HMGB-1 | DNA and IL-6 | HMGB1, ATP, IL-1β, and IL-18 |
| Immunological Features | Pro-inflammation | primarily for anti-inflammation | primarily for anti-inflammation | primarily for pro-inflammation | pro-inflammation |
| Inducer | Erastin,DPI2, BSO, SAS, lanperisone, SRS, RSL3, DPI7, DPI10, FIN56, sorafenib, artemisinin | FASL, DCC, UNC5B | Rapamycin, lithium, sodium, valproate, carbamazepine, C2-ceramide | TNFa, zVAD-fmk, PAMPS | ZnO—NPs, Ivermectin |
| Inhibitor | Desferoxamine, vitamin E, U0126, ferrostatin-1, SRS, CA-1, cycloheximide, aminooxyacetic acid Liproxstatin-1 HCl | XIAP, c-IAP1, c-IAP2, ILP-2, ML-IAP/livin, NAIP, Z-VADFMK | 3-MA, LY294002, wortmannin, PIK-III, compound 31, SAR 405, Vps34-In1, MRT68921, Spautin-1, Bafilomycin A1, hydrochloroquin | Nec-1, NSA, Kongensin- A | Necrosulfonami-de |
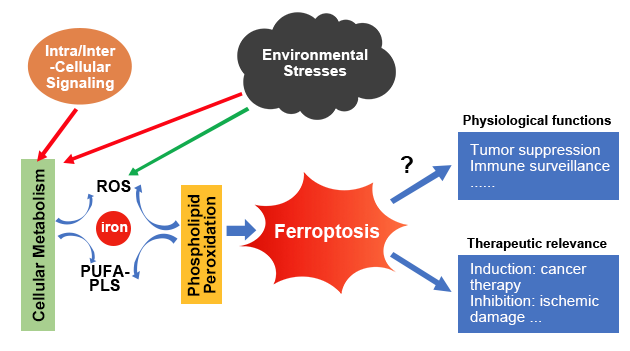
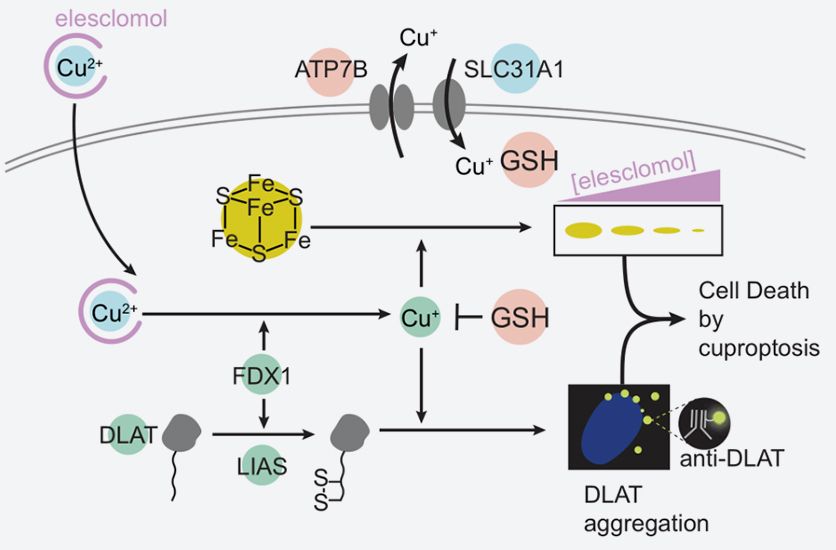
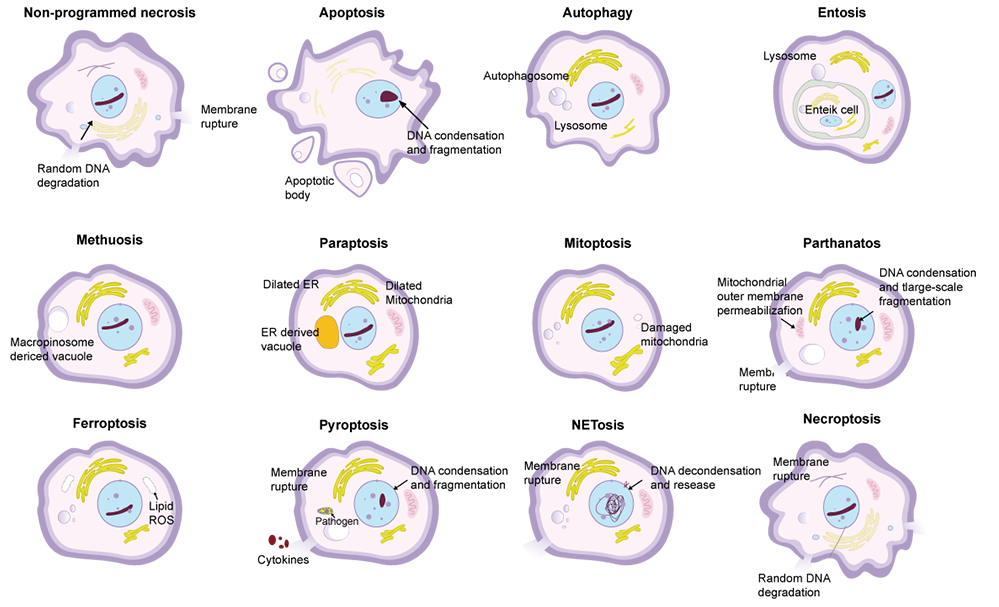
Necrosis is the external stimuli-induced and uncontrollable cell death. Features include cell swelling, broken membrane and release of cellular contents. Apoptosis is the gene regulated-programmed cell death, showing cell contraction, chromatin condensation, membrane bleeding, nuclear division and formation of apoptosome. Apoptosis-formed cells are divided into small membrane apoptosomes. These apoptosomes can be phagocytized and removed by surrounding cells(e.g. macrophage). Contents released by necrotic cells can activate immune response, cause inflammation and may damage adjacent cells.
Autophagic cell death(type II programmed cell death) is caused by abnormal activation of autophagy pathway. Autophagy is the process during which cells isolate and degrade cytoplasmic components via phagocytic vacuoles. In normal situation, it helps to maintain homeostasis and remove toxic substances. Stimulation of nutritional deficiency, oxidative stress or cytotoxicity can cause cell death induced by autophagy disorder. Induction of autophagy depends on ULK1 complex and is regulated by mTOR pathway. During autophagy, cytoplasm components are enveloped and degraded, possibly resulting in autophagic cell death which promotes or inhibit tumor growth.
Pyroptosis is the soluble and inflammatory programmed cell death, which is usually induced by inflammasome and conducted by gasdermin protein. Main features of pyroptosis are cell swelling, membrane perforation and release of cellular contents. Mechanisms include (non-)classical pathway. In classical pathway, inflammasomes like NLRP3 etc activate Caspase-1. Caspase-1 cleaves GSDMD to form active N-terminal, resulting in the membrane perforation and death by promoting the release of IL-1β and improving inflammatory response. In non-classical pathway, LPS directly activates Caspase-4/5/11, and cleaves GSDMD, resulting in pyroptosis via N-terminal and active Pannexin-1 pathway. Release of ATP and K+ active NLRP3 inflammasomes, finally promoting release of IL-1β and cell death.
FineTest has developed a series of products detecting cell death via advanced protein and antibody production platform. These products cover various cell death markers and provide the complete solution to explore mechanisms of cell death via helping scientific staff and accelerating disease research, new drug development as well as clinical applications.
| Cat.No | Product Name | Molecular Weight | Host |
|---|---|---|---|
| P9911 | Recombinant Human LPO | 52.4 kDa | E.Coli |
| P3422 | Recombinant Human P53 | 74 kDa | E.Coli |
| P2052 | Recombinant Human BBC3 | 32.5 kDa | E.Coli |
| P2933 | Recombinant Human GSTA1 | 46.3 kDa | E.Coli |
| P2958 | Recombinant Human OGDHL | 48.3 kDa | E.Coli |
| P8683 | Recombinant Human CST1 | 35.0 kDa | E.Coli |
| P4556 | Recombinant Human GPX1 | 22.2 kDa | E.Coli |
| Cat.No | Product Name | Molecular Weight | Host |
|---|---|---|---|
| P5044 | Recombinant Human CASP1 | 31.2 kDa | E.Coli |
| P3015 | Recombinant Rat NT-proBNP | 7.6 kDa | E.Coli |
| P4367 | Recombinant Human SOD1 | 16.7 kDa | E.Coli |
| P2958 | Recombinant Human OGDHL | 48.3 kDa | E.Coli |
| P9952 | Recombinant Human GPX4 | 21.5 kDa | E.Coli |
| P2575 | Recombinant Human NFE2L2 | 52.2 kDa | E.Coli |
| Cat.No | Product Name | Molecular Weight | Host |
|---|---|---|---|
| FNab04834 | LPO antibody | 80 kDa | Rabbit |
| FNab06083 | TP53 antibody | 53 kDa | Rabbit |
| FNab06956 | BBC3 antibody | 18-21 kDa | Rabbit |
| FNab03686 | GSTA1 antibody | 26 kDa | Rabbit |
| FNab05977 | OGDHL antibody | 115 kDa | Rabbit |
| FNab02032 | CST1 antibody | 15 kDa | Rabbit |
| FNab10956 | GPX1 antibody | 22 kDa | Rabbit |
| FNab05695 | NFE2L3 antibody | 76 kDa | Rabbit |
| FNab10015 | CASP1 antibody | 45-47 kDa, 30 kDa, 35 kDa | Rabbit |
| FNab10151 | NT-proBNP antibody | Mouse | |
| FNab08103 | SOD1 antibody | 16 kDa | Rabbit |
| FNab05976 | OGDH antibody | 116 kDa | Rabbit |
| FNab03622 | GPX4 antibody | 25 kDa | Rabbit |
| FNab05855 | NFE2L2 antibody | 70-100 kDa | Rabbit |
