Products
RB1CC1 antibody
Category:
Research Area:
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- RB1CC1 antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab07144
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Immunogen affinity purified
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Isotype
- IgG
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- RB1-inducible coiled-coil 1
- Alternative Names
- KIAA0203 antibody, RBICC antibody
- UniProt ID
- Q8TDY2
- Observed MW
- 180-200 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC, IF
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500-1:2000; IHC: 1:20-1:200; IF: 1:20-1:200
Validated Images
 HeLa cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab07144(RB1CC1 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
HeLa cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab07144(RB1CC1 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
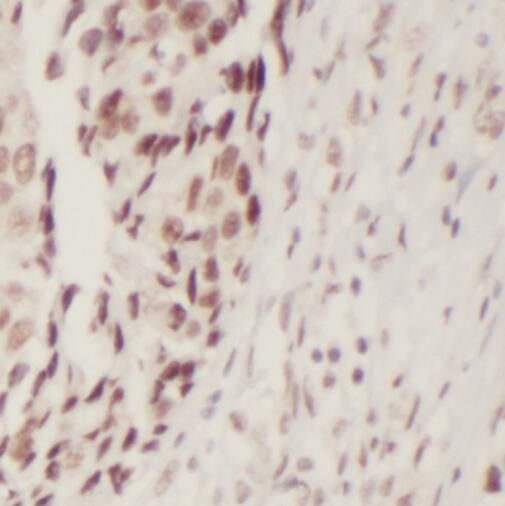 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer using FNab07144(RB1CC1 antibody) at dilution of 1:200
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer using FNab07144(RB1CC1 antibody) at dilution of 1:200
- Background
- Plays a role as a modulator of TGF-beta-signaling by restricting substrate specificity of RNF111. Involved in autophagy. Regulates early events but also late events of autophagosome formation through direct interaction with Atg16L1. Required for the formation of the autophagosome-like double-membrane structure that surrounds the Salmonella-containing vacuole(SCV) duting S.typhimurium infection and subsequent xenophagy. Autophagy positively regulates repair of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation and negatively regulates apoptosis. Plays an indispensible role in fetal hematopoiesis and in the regulation of neuronal homeostasis(By similarity). Implicated in the regulation of RB1 expression. Functions as a DNA-binding transcription factor. Is a potent regulator of the RB1 pathway and a mediator that plays a crucial role in muscular differentiation. Expression is, thus, a prerequisite for myogenic differentiation. Inhibits PTK2/FAK1 and PTK2B/PYK2 activity and activation of downstream signaling pathways.



