Products
FUBP1 antibody
| Size | Price |
|---|---|
| 100µg | Inquiry |
- SPECIFICATIONS
- FIGURES
- CONDITIONS
- FAQS
- Product Name
- FUBP1 antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab03235
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Immunogen affinity purified
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Isotype
- IgG
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months (Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
- Immunogen
- far upstream element (FUSE) binding protein 1
- Alternative Names
- Far upstream element-binding protein 1 (FBP antibody, FUSE-binding protein 1)|DNA helicase V (hDH V)|FUBP1 antibody
- UniProt ID
- Q96AE4
- Observed MW
- 79 kDa
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500 - 1:2000; IHC: 1:50 - 1:200
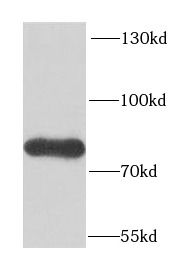 mouse brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab03235( FUBP1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
mouse brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab03235( FUBP1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
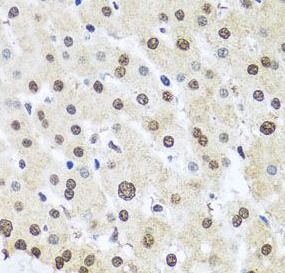 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver injury using FNab03235(FUBP1 antibody) at dilution of 1:100
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver injury using FNab03235(FUBP1 antibody) at dilution of 1:100
- Background
- The protein encoded by this gene is a single stranded DNA-binding protein that binds to multiple DNA elements, including the far upstream element (FUSE) located upstream of c-myc. Binding to FUSE occurs on the non-coding strand, and is important to the regulation of c-myc in undifferentiated cells. This protein contains three domains, an amphipathic helix N-terminal domain, a DNA-binding central domain, and a C-terminal transactivation domain that contains three tyrosine-rich motifs. The N-terminal domain is thought to repress the activity of the C-terminal domain. This protein is also thought to bind RNA, and contains 3'-5' helicase activity with in vitro activity on both DNA-DNA and RNA-RNA duplexes. Aberrant expression of this gene has been found in malignant tissues, and this gene is important to neural system and lung development. Binding of this protein to viral RNA is thought to play a role in several viral diseases, including hepatitis C and hand, foot and mouth disease. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
How many times can antibodies be recycled?
First, usually it's not suggested to recycle antibodies. After use, buffer system of antibodies has changed. The storage condition of recycled antibodies for different customers also varies. Thus, the performance efficiency of recycled antibodies can’t be guaranteed. Besides, FineTest ever conducted the antibody recycling assay. Assay results show recycling times of different antibodies also varies. Usually, higher antibody titer allows more repeated use. Customers can determine based on experimental requirements.
Notes: After incubation, we recycle rest antibodies to centrifuge tube and store at 4℃. High titer antibodies can be stored for a minimum of one week. Reuse about three times.
What are components of FineTest antibody buffer?
Components of FineTest antibody buffer are usually PBS with proclin300 or sodium azide, BSA, 50% glycerol. Common preservative is proclin300 or sodium azide, which is widely applied in the lab and industry.
How about the storage temperature and duration of FineTest antibodies?
Most antibodies are stored at -20℃. Directly-labeled flow cytometry antibodies should be stored at 2 - 8℃. The shelf life is one year. If after sales issues for purchased antibodies appear, return or replacement is available. Usually, antibodies can be still used after the one-year warranty. We can offer technical support services.
Is dilution required for FineTest antibodies? What’s the dilute solution?
Directly-labeled flow cytometry antibodies are ready-to-use without dilution. Other antibodies are usually concentrated. Follow the dilution ratio suggested in the manual. Dilute solution for different experiments also varies. Common antibody dilution buffers are acceptable(e.g. PBST, TBST, antibody blocking buffer).
How to retrieve antibodies for immunohistochemistry?
Common retrieval buffers: Tris-EDTA Buffer(pH 9.0); Citrate Buffer(pH 6.0)
Heat induced antibody retrieval:
Method 1: Water-bath heating: Put the beaker with retrieval buffer and slide in the boiling water bath. Keep the boiling state for 15min. Naturally cool to room temperature;
Method 2: Microwave retrieval: Put the beaker with retrieval buffer and slide in the microwave oven. Heat at high power for 5min, Switch OFF for 3min, Heat at medium power for 5min. Naturally cool to room temperature.
How to choose secondary antibodies?
(1) Secondary antibodies react with primary antibodies. Thus, secondary antibodies should be against host species of primary antibodies. E.g. If the primary antibody is derived from rabbit, the relevant secondary antibody should be against rabbit. E.g. goat anti rabbit or donkey anti rabbit.
(2) Choose secondary antibody conjugates according to the experimental type, e.g. ELISA, WB, IHC etc. Common enzyme conjugated secondary antibodies are labelled by HRP, AP etc. Fluorescin or dye labelled secondary antibodies are applied in immunofluorescence and flow cytometry(e.g. FITC, Cy3).
