Products
Angiotensinogen antibody
Category:
Research Area:
| Synonyms: | AGT antibody, Ang I Angiotensin 2 antibody, Ang II Angiotensin 3 antibody, Ang III antibody, Angiotensin I antibody, Angiotensin II antibody, Angiotensin III antibody, Angiotensinogen antibody, ANHU antibody, Des Asp[1] angiotensin II antibody, FLJ92595 antibody, FLJ97926 antibody, Serpin A8 antibody, SERPINA8 antibody | ||
| Catalogue No.: | FNab00395 | Reactivity: | Human |
| Host: | Mouse | Tested Application: | ELISA, WB, IHC |
| Clonality: | monoclonal | Isotype: | IgG2b |
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- Angiotensinogen antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab00395
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Protein A+G purification
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- monoclonal
- Isotype
- IgG2b
- Clone ID
- 0F2
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- angiotensinogen(serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A, member 8)
- Alternative Names
- AGT antibody, Ang I Angiotensin 2 antibody, Ang II Angiotensin 3 antibody, Ang III antibody, Angiotensin I antibody, Angiotensin II antibody, Angiotensin III antibody, Angiotensinogen antibody, ANHU antibody, Des Asp[1] angiotensin II antibody, FLJ92595 antibody, FLJ97926 antibody, Serpin A8 antibody, SERPINA8 antibody
- UniProt ID
- P01019
- Observed MW
- 53 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500-1:5000; IHC: 1:20-1:200
Validated Images
 HepG2 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab00395(AGT antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
HepG2 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab00395(AGT antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
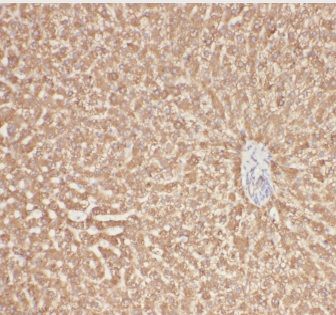 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver cancer using FNab00395(AGT antibody) at dilution of 1:50
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver cancer using FNab00395(AGT antibody) at dilution of 1:50
- Background
- Angiotensinogen is a precursor of angiotensin II(Ang II), is expressed and synthesized largely in the liver and is cleaved by the enzyme renin in response to lowered blood pressure. It has a key role in mediating vascular constriction and regulating salt and fluid homeostasis. The resulting product, angiotensin I, is then cleaved by angiotensin converting enzyme(ACE) to generate the physiologically active enzyme angiotensin II. Mutations in this gene are associated with susceptibility to essential hypertension, and can cause renal tubular dysgenesis, a severe disorder of renal tubular development. Defects in this gene have also been associated with non-familial structural atrial fibrillation, and inflammatory bowel disease.



