Abstract: TGF Beta signaling pathway consists of ligands, receptor complex and signaling molecule SMADs from TGF Beta family, including Smad dependent pathway and non-Smad pathway. TGF Beta is the versatile immune cytokine. Members of TGF Beta superfamily also include bone morphogenetic protein(BMPs), activin and inhibin etc. In mammals, there are three subtypes of TGF Beta encoded by different genes: TGF-β1, TGF-β2 and TGF-β3. Although the structure and function are highly similar, biological roles are varied.
Keywords: TGF Beta Signaling Pathway, Immune Cytokine, SMAD Signaling Pathway, Role of TGF Beta
1. TGF Beta Structure
TGF Beta is initially synthesized by signal peptide, LAP and mature precursor. After protease cleavage, the mature TGF Beta is released and forms the complex via LAP. Then, through binding with LTBP, inactive TGF Beta is stored in extracellular matrix. TGF Beta is the homodimer and each subunit contains 112 amino acids. Nine cysteine formed - disulfide bonds maintain stability.
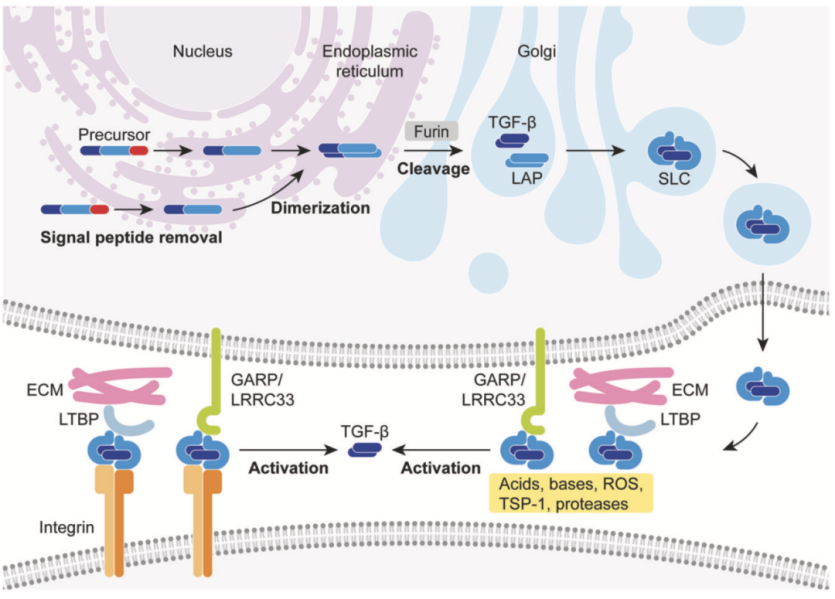
2. TGF Beta Signaling Pathway
2.1. TGF Beta SMAD Signaling Pathway
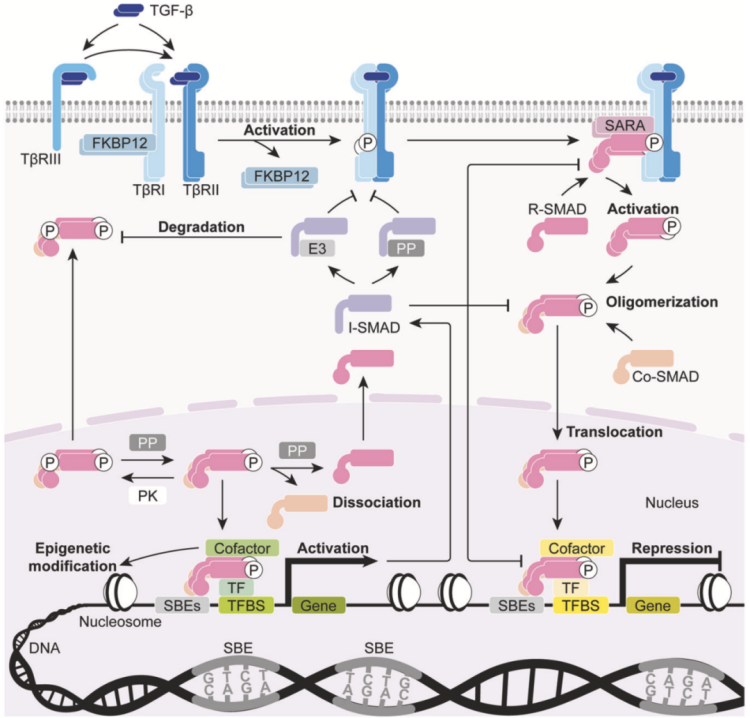
TGF Beta signaling is enabled via binding with TGF-βRII receptor. Then, TGF-βRII recruits and phosphorylates TGF-βRI, activating downstream signal transduction. Activated TGF-βRI phosphorylates R-Smad further(e.g. Smad2, Smad3). Binding with Smad(Smad4) enters nucleus. Recognition of specific DNA sequence regulates transcription process of the target gene.
Main Regulatory Functions:
(1) Promote inhibition of cell cycle(e.g. up-regulation of p21 and p15, inhibition of cell proliferation)
(2) Regulate cell differentiation and apoptosis
(3) Involved in fibrosis process(induction of α-SMA, expression of Type I/III collagen protein)
(4) Regulate immunosuppression(promotion of Treg cell function, inhibition of T cell differentiation)
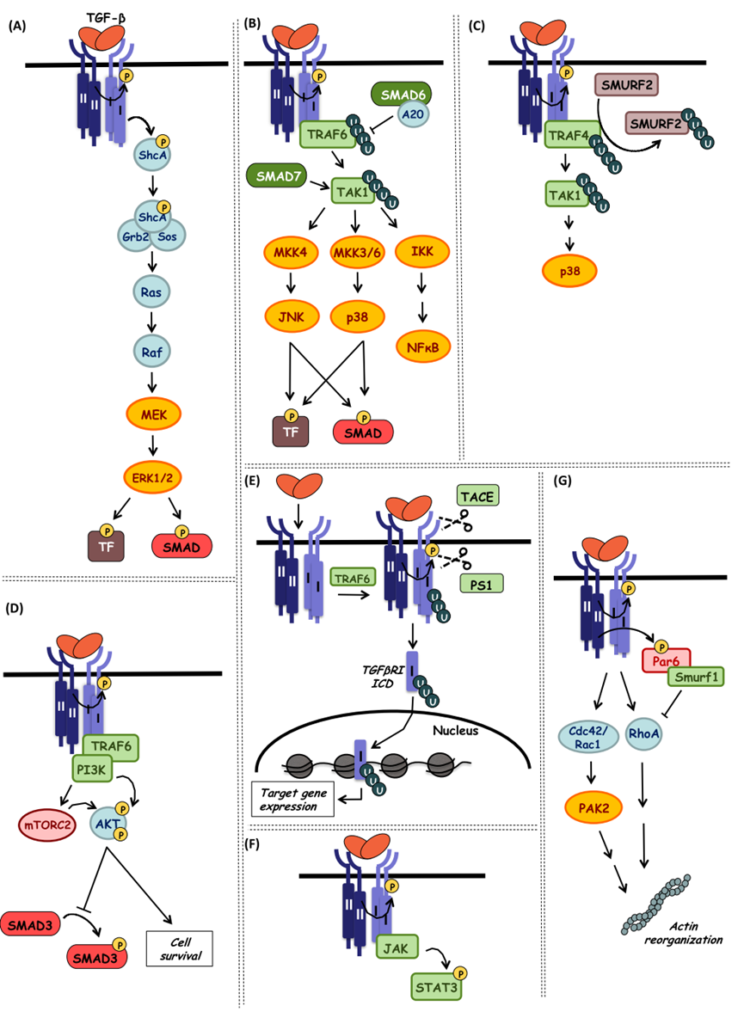
2.2. Non Canonical TGF Beta Signaling Pathway
Besides the classical SMAD pathway, TGF-β can also activate various non canonical signaling pathways, including MAPK(ERK, JNK, p38), PI3K-AKT-mTOR, Rho GTPases and NF-κB etc. These pathways play an important role in cell survival, epithelial-mesenchymal transition(EMT), immunoregulation and tumor progression. E.g. TGF-β can improve cell survival via PI3K-AKT, alternatively promote migration and invasion of tumor cells.
3. Role of TGF Beta Signaling Pathway
TGF Beta plays an important role in embryonic development, maintenance of tissue homeostasis, immunoregulation and development of various diseases etc.
3.1. Development and Tissue Homeostasis
Roles of TGF Beta in biological process are very significant. TGF Beta can inhibit various cells, especially proliferation of epithelial cells and immunocytes. For differentiation, TGF Beta is involved in stem cell differentiation and tissue formation in embryonic development. Besides, TGF Beta can also promote the synthesis of collagen, fibronectin and proteoglycan, thus maintaining the stabilization of tissue structure and extracellular matrix.
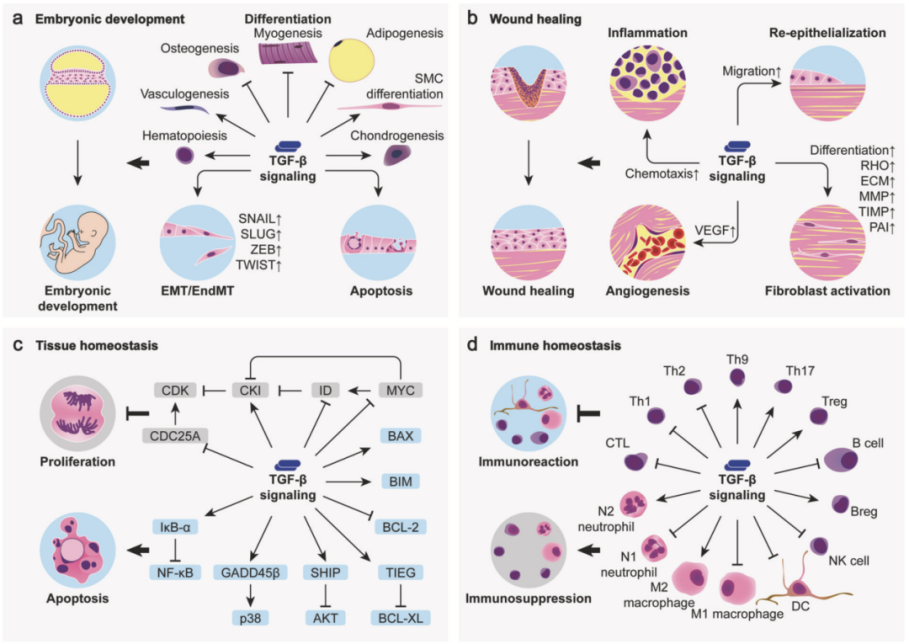
3.2. Immunosuppression
Roles of TGF Beta in immunosuppression are various. TGF Beta promotes differentiation of regulatory T cell via inducing the expression of Foxp3, and inhibit excessive immune response; Activation and proliferation of effector T cell are also inhibited. IL-6 promotes differentiation of Th17 cell, and grants the pro-inflammatory effect; Inhibition of B cell proliferation and antibody secretion restricts abnormal immune response; The activity of NK cell is also reduced; Inhibition of mature dendritic cell reduces antigen presenting ability. The transition to anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype is promoted via reducing the pro-inflammatory activity of macrophage.
3.3. Immunoenhancement
Roles of TGF Beta in tissue repair and immune regulation are very important. In damaged sites, TGF Beta promotes differentiation of macrophage to anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype. Inhibition of excessive inflammation promotes tissue repair. Besides, TGF Beta also induces the synthesis and deposition of extracellular matrix, and helps the reconstruction of damaged sites. In the specific environment(e.g. tumor microenvironment), TGF Beta can promote the differentiation of Th17 cell, and activate the pro-inflammatory response via regulating the balance of T cell.
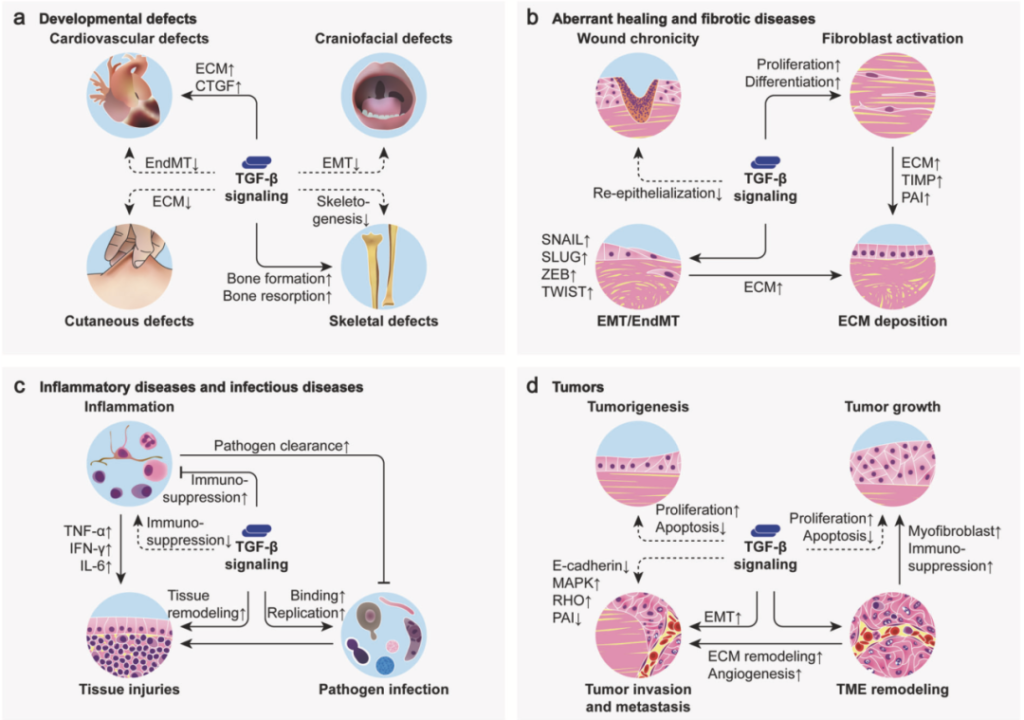
4. TGF Beta Related Diseases
Roles of TGF Beta in various diseases are crucial. In autoimmune diseases, dysfunction of TGF Beta can result in systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease etc. TGF Beta can regulate immune tolerance and inhibit autoimmune response. In tumor immunity, TGF Beta can inhibit immune response and promote tumor escape. In slow virus infection, TGF Beta aggravates the disease. In bacterial infection, TGF Beta assists to regulate immune response and prevent tissue damage.
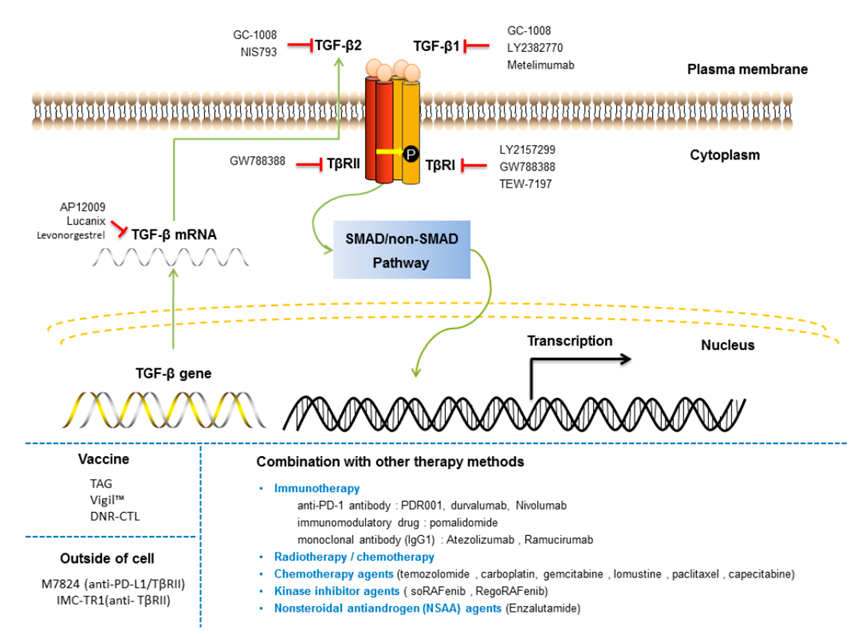
5. Targeted Therapy of TGF Beta Signaling Pathway
Roles of TGF Beta in diseases relevant to tumor, fibrosis and immunity are crucial. Drug development for TGF Beta signaling pathway has been the hot research, including ligand and neutralizing antibodies(e.g. Fresolimumab and Bintrafusp alfa), receptor and small molecule inhibitor(e.g. Galunisertib and Vactosertib), trap and fusion protein(e.g. AVID200). Besides, applications of TGF-β inhibitor and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor have shown the collaborative anti-tumor effect.
6. Recommended Products
|
Cat.No |
Product Name |
|
Recombinant Human TGFB1 |
|
|
Recombinant Human TGFB3 |
|
|
Recombinant Mouse/Rat TGF-beta 2 |
|
|
Recombinant Human TGF-beta 2 |
REFERENCES
[1] Disruption of TGF-β signaling pathway is required to mediate effective killing of hepatocellular carcinoma by human iPSC-derived NK cells, PMID: 38986609.
[2] PIEZO1 attenuates Marfan syndrome aneurysm development through TGF-β signaling pathway inhibition via TGFBR2, PMID: 39585648.
