Abstract: Chemokines consist of over 50 kinds of polypeptides. Their roles in immune response and cancer treatment are very important. They coordinate the recruitment of immune cells, spatial distribution in the tissue and interaction. Chemokines include four types: CXC(α subfamily), CC(β subfamily), XC(γ subfamily) and CX3C(δ subfamily). Multiple roles of chemokines and their pathways in tumor development become potential targets for immunotherapy.
Keywords: Chemokines, Cancer Treatment, Cancer Immunotherapy, Targeted Therapy
1. Types of Chemokines
C Chemokines: Only contains two conserved cysteine residues, connected by a disulfide bond.
CC Chemokines: Contains four conserved cysteine residues. Two of them are located on the N-terminal and closely adjacent to each other.
CXC Chemokines: Also contains four conserved cysteine residues. But the first two are separated by an arbitrary amino acid.
CX3C Chemokines: Also contains four conserved cysteine residues. But the first two are isolated via three arbitrary amino acids.
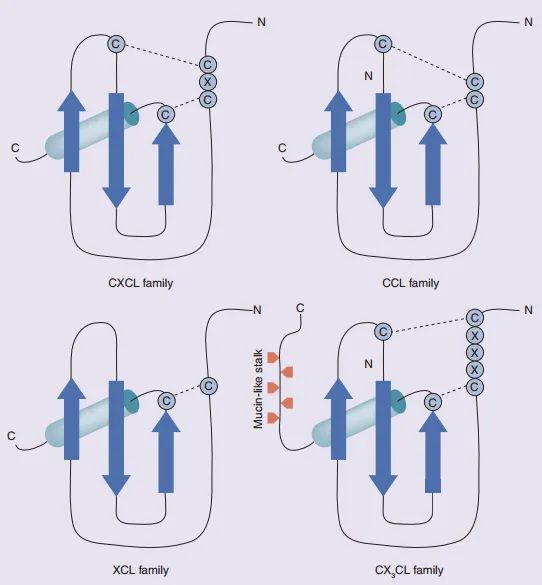
2. Chemokine Examples
2.1. CXCL6
CXCL6(also called GCP-2 or LIX) is the connective tissue derived CXC chemokine, and plays an important role in neutrophil chemotaxis. The anti-angiogenesis activity shows the anti-tumor potentiality. CXCL6 is widely involved in inflammation, immune regulation, angiogenesis and tissue repair etc.
2.2. CXCL9/CXCL10/CXCL11
CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11 are IFN-γ induced CXC chemokines, regulating activation and migration of immune cells as the ligand of CXCR3. They are also involved in immune response. Axis of CXCL9/10/11-CXCR3 provides new potential targets for cancer immunotherapy.
2.3. Eotaxin(CCL11)
This CC chemokine is produced by IFN-γ stimulated endothelial cells and TNF activated monocytes. Eotaxin plays its role of selective eosinophil chemotaxis through CCR3 receptor. Inflammatory regulation in asthma and allergic reactions is also very important, showing wide applications in immune and inflammatory research.
2.4. CXCL1
CXCL1(also called GRO-α/MGSA) is the splenocyte secreted CXC chemokine, promoting activation of neutrophils. It’s also involved in inflammatory response. Besides, CXCL1 plays a role in pathogenesis of melanoma via stimulating cell mitosis, including research areas immunity, inflammation and tumor etc.
2.5. RANTES (CCL5)
RANTES is the CC chemokine mediating the signal transduction via CCR1, CCR3, CCR5 and US28 receptor. It also participates in chemotaxis of various immune cells and inhibiting some HIV strains. RANTES is widely involved in immune regulation, inflammatory response and antiviral research.
2.6. Exodus-2 (CCL21)
Exodus-2 is the CC chemokine and acts via binding with CCR7 receptor. Key expressions are found in lymphatic endothelium, spleen and vermiform appendix, participating in T and B cell chemotaxis. Exodus-2 acts in inhibiting hematopoiesis, and is also widely involved in immune and inflammatory research.
2.7. TARC (CCL17)
This CC chemokine is produced by thymus dendritic cells, playing its signaling role via interacting with CCR4 receptor on NK cell, basophil and Th2 cell. TARC is also widely involved in biological processes like immune response and wound healing.
3. Role of Chemokines in Cancer Treatment
Chemokines play an important role in tumor immunity, attracting immune cells(T cells, NK cells etc) to enter tumor microenvironment to improve antitumor respone. They may also recruit immuno-suppressive cells(e.g. regulatory T cells etc) to help immune evasion. Besides, chemokines are involved in regulation of tumor-associated inflammation, promoted angiogenesis and tumor cell metastasis, e.g. axis of CXCL12/CXCR4 is closely related to organ-specific metastasis.
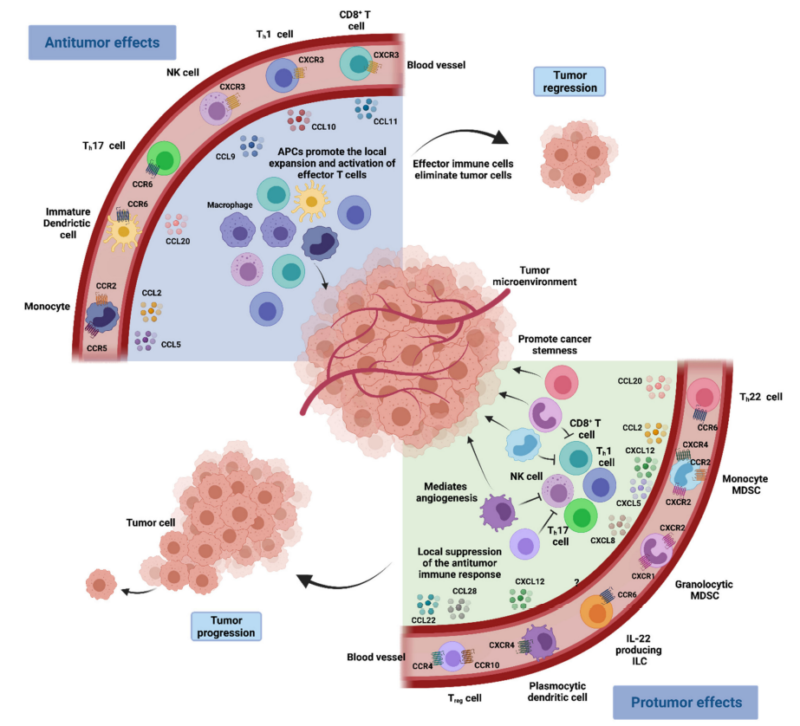
4. Targeted Therapy
Currently, some chemokine-targeted drugs have been approved for clinical treatment. E.g. Mogamulizumab(anti CCR4 Mab) and Plerixafor(AMD3100, CXCR4 antagonist) are mainly applied in the treatment of hematological malignancies. Besides, more therapeutic strategies for different chemokines and their receptors are being actively developed. These targets show bright prospect in various tumor treatments. Some therapies have been in the clinical trial and are expected for wide applications.
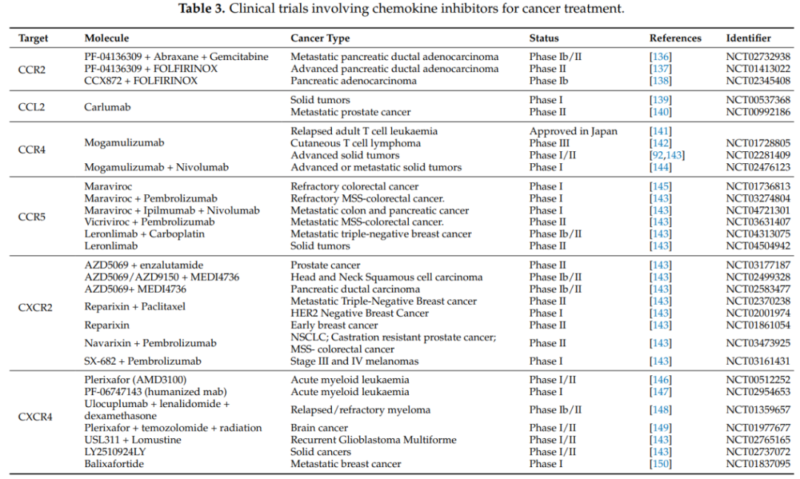
Important roles of chemokine network in tumor immune response show potential immunotherapeutic targets. More chemokine receptor inhibitors are subject to preclinical evaluation and clinical trial. Tumor immune response could be optimized through the combined routine therapy.
5. Recommended Products
REFERENCES
[1]An atypical atherogenic chemokine that promotes advanced atherosclerosis and hepatic lipogenesis, PMID: 40055309.
[2]Systemic chemokine-modulatory regimen combined with neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with triple-negative breast cancer, PMID: 39542655.
