Abstract: Protein kinase is the enzyme catalyzing protein phosphorylation, and involved in key processes like cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis etc. 518 kinases have been found in human body and formed complex regulatory network. Recent researches show protein kinase plays an important role in gene expression, DNA repair and tumor microenvironment remodeling. Mutation or deficiency of kinase can cause various diseases like inflammation, obesity, autoimmune disorders etc. Interaction between cytokine receptors, immune recognition receptors and kinases can regulate intracellular physiological activities like metabolism, cytoskeletal remodeling and movement etc.
Keywords: Protein Kinase, Cell Regulation, Gene Expression Regulation, DNA Repair, Tumor Microenvironment
1. Function of Protein Kinase
Protein kinase changes cell location, activity and interaction via transferring phosphate group on ATP terminal to tyrosine, serine or threonine on over 20% human proteins. Thus, cell characteristics are affected. According to features of hydroxyl group, kinases are divided into tyrosine kinases(90), tyrosine kinase-like enzyme(43) and serine/threonine kinases(385). Dual-specificity protein kinases like MEK1/2 can catalyze the phosphorylation of tyrosine and threonine residues on the target protein.
2. Functional Regulation of Non-canonical Kinase
2.1. Gene Expression Regulation
Phosphorylation changes chromatin structure and regulates gene transcription. E.g. The kinase activity of PKM2 regulates gene expression via phosphorylated histone H3. Besides, some metabolic enzymes can regulate chromatin conformation to further affect gene expression via methylation, acetylation, succinylation and glycosylation.
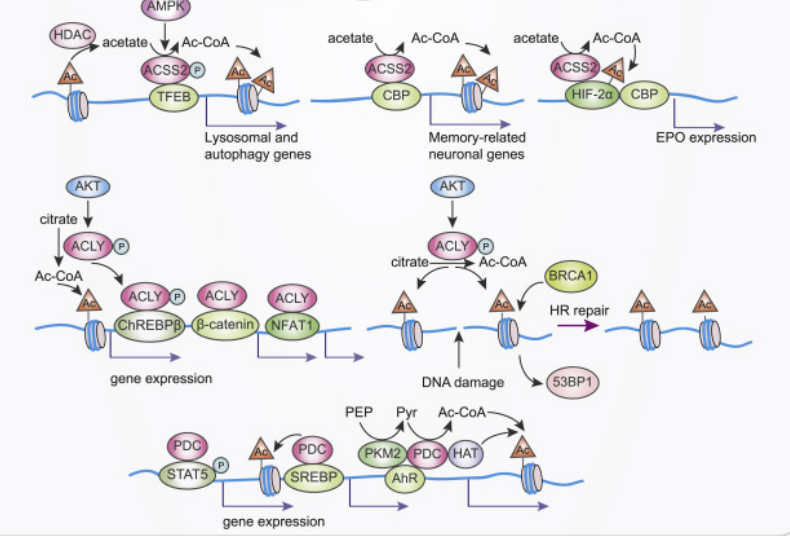
2.2. Cell Cycle Regulation and DNA Repair
PKM2 has protein kinase activity and can phosphorylate spindle histone Bub3 to further regulate chromosomal disjunction and mitosis checkpoint. Besides, PKM2 phosphorylates CtBP interacting protein(CtIP), increasing the recruitment of CtIP to promote the repair of broken DNA ends at DNA double strand break.
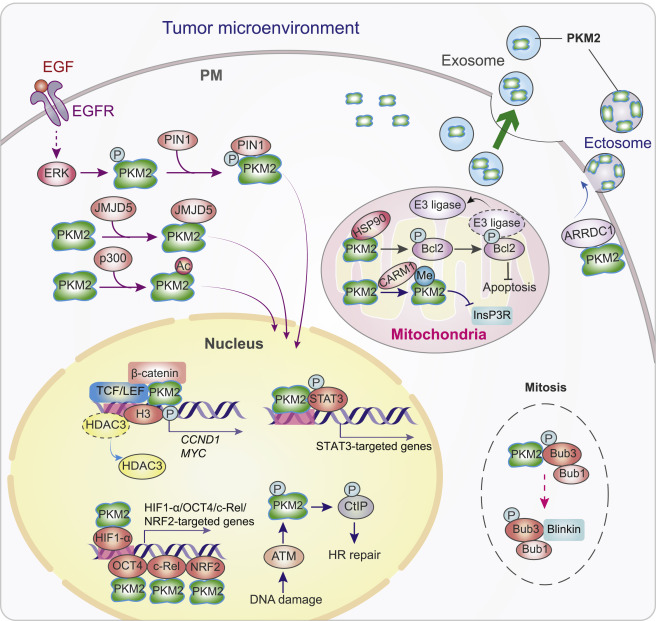
2.3. Protein Kinase in Signal Transduction
Key signaling pathways affecting cell proliferation and survival include PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway, Raf-MEK-ERK pathway, IKK-NF-κB pathway, and TGF-β pathway. These pathways play an important role in regulating cell function.
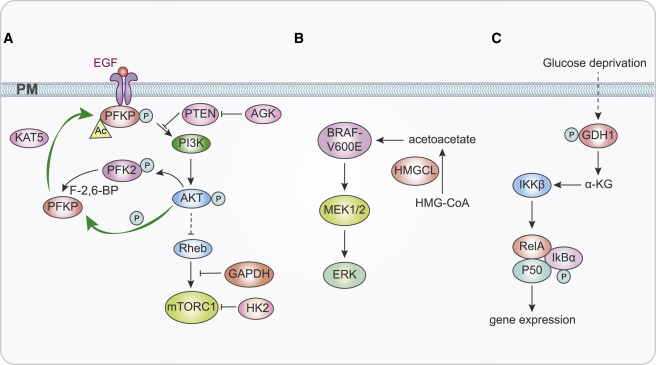
2.4. Regulation of Tumor Microenvironment
During tumor development, different phosphorylated protein substrates have great effects on tumor process. E.g. HK2 phosphorylates IκBα to promote the expression of PD-L1 and tumor immune escape. Besides, PKM2 is involved in tumor microenvironment remodeling via regulating exosome secretion of tumor cells. PKM2 also phosphorylates SNAP-23 to form complex and improve exosome release in tumor cells.
3. Kinase Drug Development for Clinical Research
In 2001, protein kinase inhibitor Gleevec(Imatinib) was first approved by FDA, showing the development of protein kinase inhibitors in tumor and other therapeutic fields. It's also the important milestone of targeted anti-tumor therapy. Currently, various kinase-related drugs have been in the clinical trial.
Although kinase researches obtain some achievements, regulation mechanism still requires for further discussion, including selection and interaction between kinases and substrates. Epigenetic modification is also important.

4. Recommended Products
|
Cat.No |
Product Name |
|
Recombinant Human AKT1 |
|
|
Recombinant Human AKT2 |
|
|
Recombinant Human AMPK1 |
|
|
Recombinant Human LAMTOR5 |
|
|
Recombinant Human LAMTOR4 |
|
|
Recombinant Human LAMTOR3 |
|
|
Recombinant Human LAMTOR2 |
|
|
Recombinant Human LAMTOR5 |
|
|
Recombinant Human ITPKA |
REFERENCES
[1]Impact of protein and small molecule interactions on kinase conformations, PMID: 39088265.
[2]Latent allosteric control of protein interactions by ATP-competitive kinase inhibitors, PMID: 39395271.
