Abstract: Cardio-cerebrovascular diseases(CVD Diseases) refer to ischemic or hemorrhagic diseases of heart, brain and all tissues, induced by dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis and hypertension etc. People over 50 years old often suffer from these diseases, featured with high incidence, disability and mortality etc. The quality of life of many patients is still restricted. If these symptoms appear(e.g. headache and dizziness, chest distress and asthma, unable to sleep on your back, limb numbness, dyspnea etc), beware of cardio-cerebrovascular diseases. Early interventions are very important.
Keywords: Cardio-cerebrovascular Diseases, Ischemic Diseases, Hemorrhagic Diseases, Drug Treatment
1. Features of CVD Diseases
CVD diseases are featured with concealment, accident, hazard and urgency. Symptoms of most patients are not obvious before onset. But cardiac infarction, cerebral infarction and cerebral hemorrhage usually happen without any sign, easily threatening life. These diseases blocks blood flow, and may cause death or severe disabilities. Patients need first aid treatment within 3h of the attack. Otherwise, mortality rate is very high. Thus, early prevention and vigilance are very important.
2. Pathogenesis of CVD Diseases
Various pathogenic factors are specified below:
Endothelial Dysfunction: Endothelial cells are monolayer cells on the inner wall of blood vessels. Their functions include regulation of blood vessel tension, anti-inflammation and anti-coagulation etc. Some factors(e.g. hypertension, hyperglycemia, smoking etc) can cause damaged endothelial cells, reduced synthesis of nitric oxide, vasoconstriction, inflammatory response and thrombosis etc.
Lipid deposition and atherosclerosis: Atherosclerosis is the key cause of CVD diseases. The pathology is primarily induced by lipid and sugar accumulation in endarterium. Gradually formed fibroplasia and calcification cause artery wall thickening and stenosis. Myocardial ischemia or necrosis may happen. The pro- and anti-inflammatory balance determines the process of inflammatory reaction. Low density lipoprotein is phagocytized by macrophages and forms foam cells. If pro-inflammatory reaction is predominant, broken plaque may cause thrombus. If pro-resolving mediator is predominant, inhibited inflammation can promote the formation of stable plaque.
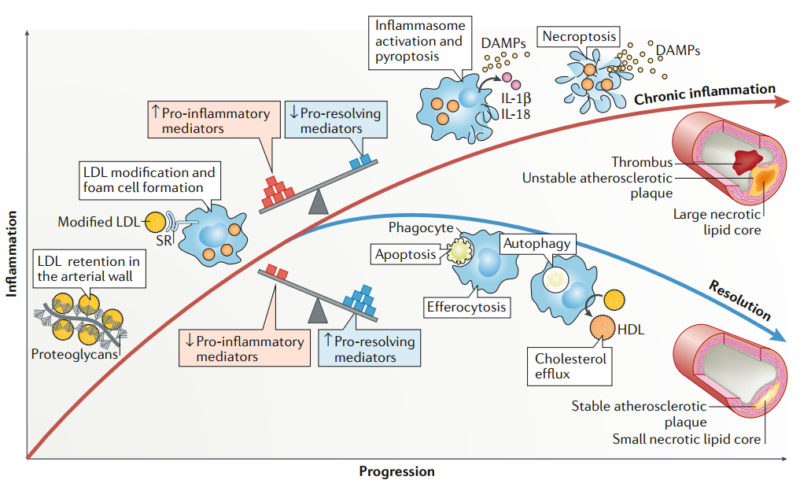
Chronic inflammation: Lipoprotein oxidation causes inflammation. Promoted platelet aggregation forms thrombus.
Thrombosis: Broken endothelium exposes basal membrane. Activated platelet and coagulation factor cause myocardial or cerebral infarction.
Hypertension: Persistent hypertension can damage blood vessel, and promote atherosclerosis.
3. Drug Treatment for CVD Diseases
In recent years, inflammatory signaling mechanism of CVD diseases is further investigated. But, clinical applications are still insufficient. Anti-inflammatory treatment becomes the standard therapy of coronary artery diseases. However, treatment for residual inflammation is still unresolved. Targeted anti-inflammatory drugs are still developed.
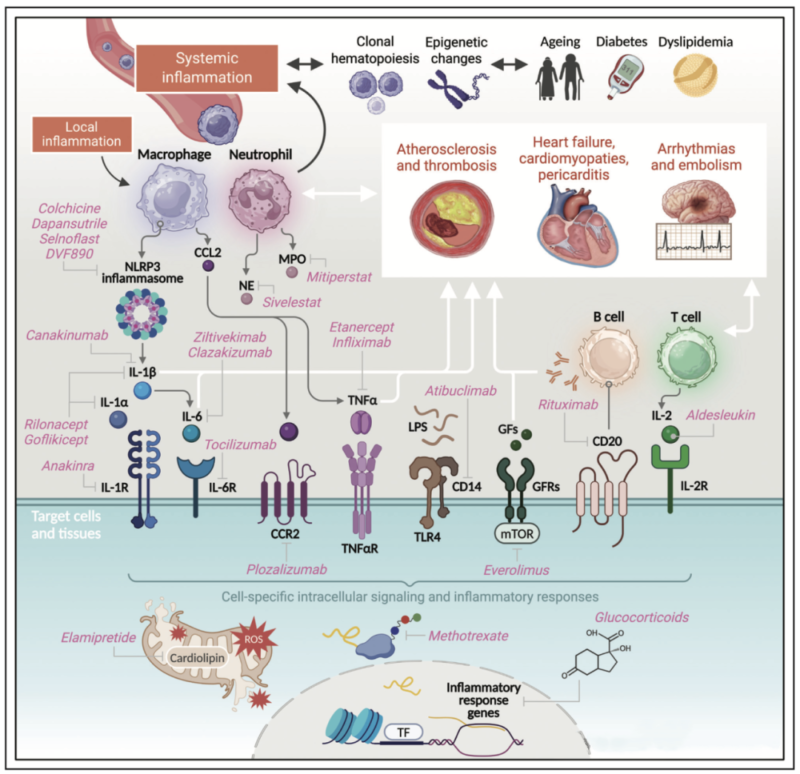
Atherosclerosis is caused by some factors(e.g. hypertension, dyslipidemia, smoking, diabetes, obesity, inheritance etc). Treatments include regulation of lifestyle and drug administration, e.g. statins, fibrates on blood lipid, antihypertensive drugs(β-blocker, ACEI/ARB), hypoglycemic agents(e.g. metformin), antiplatelet drugs(e.g. Aspirin). Hypertension therapy mainly relies on hypoglycemic agents, including diuretics, β-blocker etc. Arrhythmia requires for drug regulation. Angina pectoris can be relieved via antiplatelet drugs, β-blocker and statins.
4. Hot Markers
CVD diseases are mainly caused by hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes etc. Pathogenesis includes vascular endothelial injury, lipid deposition and thrombosis. Treatment methods include regulation of drug and lifestyle, and take a jump forward. Curative effects and drug resistance still persist. Further investigation on pathogenesis and drug resistance can solve some medical challenge.
|
Diseases |
Hot Topics |
Hot Targets |
|
Coronary Heart Disease |
Extremely High |
IL-6, TNF-a, CRP, MMP-9, sVCAM-1, sICAM-1, PAI-1, IL-1β, IL-18, IL-33 |
|
Heart Failure |
Extremely High |
BNP, NTProBNP, IL-6, TNF-a, CRP, IL-1β, IL-18, GDF-15 |
|
Hypertension |
High |
Ang II, ET-1, IL-6, TNF-a, CRP, TGF-β, IL-1β,IL-10 |
|
Atherosclerosis |
High |
ADPN, YKL40, IL6, IL-1β, TNF-a, MCP1 |
|
Myocardiopathy |
High |
IL-6, TNF-a, CRP, TGF-β, MMP-9, sVCAM-1, sICAM-1, IL-1β, IL-18, GDF-15 |
|
Pulmonary Hypertension |
High |
ET-1, IL-6, TNF-a, CRP, VEGF, TGF-β, IL-1β, IL-8,PDGF-BB, sST2 |
|
Arrhythmia |
Medium |
IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-a, CRP, TGF-β, CXCL12, CXCR4, VEGF, FGF-2, HGF |
|
Valvular Heart Disease |
Medium |
IL-6, TNF-a, CRP, MMP-2, MMP-9, IL-1β, IL-17,IL-22, IL-23 |
|
Pericarditis |
Medium |
IL-6, TNF-a, CRP, IL-1β, IL-18, MMP-9, sVCAM-1, sICAM-1, PAI-1, IL-33 |
|
Peripheral Arterial Disease |
Medium |
IL-6, TNF-a, CRP, MMP-9, sVCAM-1, sICAM-1, PAI-1, IL-1β, IL-18, IL-33 |
5. Recommended Products
REFERENCES
[1]Burden of Cardio-Cerebrovascular and Renal Diseases Attributable to Systolic Hypertension in France in 2021, PMID: 39648886.
[2]Glucokinase activator, circulating metabolites, and cardio-cerebrovascular diseases: a Mendelian randomization study, PMID: 40739561.
