Abstract: Non-specific antibody binding plays a key role in getting accurate results during flow cytometry. High non-specificity not only produces false positive signal, but also can conceal true biomarkers. Thus, it’s important to identify the source and effects of non-specificity. Optimization of experimental condition, proper antibody selection and strict control can effectively decrease non-specificity and improve data reliability, offering a solid foundation to biological research and clinical application.
Keywords: Non-specific Antibody Binding, Flow Cytometry, Antibodies with High Specificity
1. Binding Capacity
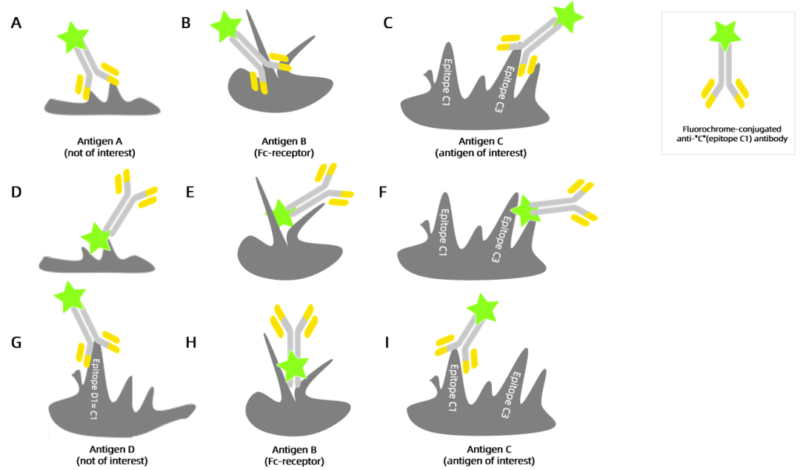
Before checking non-specific antibody binding, binding mode of antibody should be known(as shown in Figures A-F). A: bind with non-target antigen, B: bind with Fc receptor, C: bind with non-target antigen, incorrect epitope, D-F: binding situation among conjugated fluorescent dye, non-target antigen, Fc receptor and target antigen. G-I: G binds with shared antigenic epitope, H binds with Fc receptor, I binds with target antigen and its epitope, forming specific antibody.
2. Reasons for Non-specific Antibody Binding
2.1. Excessive Antibodies
Excessive antibodies bind to non-target marker with low affinity to decrease signal-to-noise ratio. It’s suggested to titrate and determine the best concentration following the manual. Besides, antibody incubation time should be suitable, and can be regulated according to vendor’s suggestion and experimental situation.
2.2. Non-specific Adhesion
All cells can adhere to proteins in different levels. Antibody(also a kind of protein) can bind with cells via non-specific interaction. Addition of appropriate amount of fetal bovine serum(FBS) or bovine serum albumin(BSA) into wash buffer and staining solution can decrease the binding.
2.3. Check Whether the Antibody Binds with Fc Receptor
Fc receptor is the protein bound with the antibody on the surface of immunocyte. The surface of some cells(e.g. monocyte, macrophage, neutrophil, B cell) expresses Fc receptor. Antibodies used in flow cytometry usually contain Fc segment. Thus, during antibody staining, the possible binding of Fc segment with Fc receptor on the cell surface can cause non-specific binding.
2.4. Select Antibodies with High Specificity
The cross-reaction of antibodies may recognize similar epitopes instead of target antigen epitopes. Flow cytometry antibodies developed by FineTest ensure the high performance and specificity. The FCM antibodies have highly recognizable ability on antigenic epitope, providing higher sensitivity for scientific and clinical research.
2.5. Reduce Background Signal
The binding between Fc receptor and antibodies is obvious. However, some fluorescence dyes can also bind with Fc receptor. E.g. PE dye can bind with mouse Fc-γ-RII(CD16) and Fc-γ-RIII(CD32). Besides, anthocyanidin dyes(e.g. Cy series) and related tandem dyes(e.g. PE-cy5, APC-cy7) also easily bind with Fc receptor, especially for FcR cell(e.g. monocyte). The binding can't be inhibited via Fc receptor inhibitor. It's suggested to avoid to use anthocyanidin dyes.
2.6. Insufficient Washing
Proper wash buffers and repeated washing can effectively remove unbound antibodies and decrease effects on non-specific binding.
2.7. Dead Cells
Dead cells are adhered and easily cause high non-specific binding due to exposed DNA. DNA binding dyes(e.g. 7-AAD or PI) can identify living or dead cell to remove dead cell. If viability dyes can't be added due to fluorescent combination, viable gating in FSC/SSC scatter diagram can help to distinguish living or dead cell.
3. Recommended Flow Cytometry Antibodies
| Species | Cell Populations | Flow Cytometry Antibody Combination | Cat.No |
| Human | T/B/NK cell populations detection | CD45-PerCP | PCP-30039 |
| CD3-FITC | FITC-30004 | ||
| CD16-PE | PE-30061 | ||
| CD56-PE | PE-30008 | ||
| CD19-APC | APC-30066 | ||
| Human | Thl/Th2 cell populations detection | CD3-PerCP/Cyanine5.5 | PCP55-30004 |
| CD4-FITC | FITC-30005 | ||
| IFN-γ-PE | PE-30053 | ||
| IL4-APC | APC-30043 | ||
| Mouse | Thl/Th2 cell populations detection | CD3-PerCP/Cyanine5.5 | PCP55-30002 |
| CD4-FITC | FITC-30001 | ||
| IFN-γ-PE | PE-30074 | ||
| IL4-APC | APC-30026 | ||
| Human | Treg cell populations detection | CD4-FITC | FITC-30005 |
| CD25-PE | PE-30035 | ||
| CD127-APC | APC-30033 | ||
| Mouse | Treg cell populations detection | CD4-FITC | FITC-30001 |
| CD25-PE | PE-30017 | ||
| FOXP3-APC | APC-30055 |
REFERENCES
[1] Reduced Non-Specific Binding of Super-Resolution DNA-PAINT Markers by Shielded DNA-PAINT Labeling Protocols, PMID: 39422065.
[2] BMP2 Binds Non-Specifically to PEG-Passivated Biomaterials and Induces pSMAD 1/5/9 Signalling, PMID: 39215622.
