Abstract: Macrophages are immune cells widely distributed in various human tissues, and play an important role in tumor immunity and critical illness. As the component of mononuclear phagocyte system, macrophages are mainly responsible for phagocytizing dead cells, cell debris, pathogen and other foreign substances. Besides, roles of macrophage markers in signal transduction and regulation are involved in various biological processes, such as immune response, growth, tissue repair, homeostasis maintenance and cancer development.
Keywords: Macrophage Markers, Macrophage Polarization Assay, Immunity
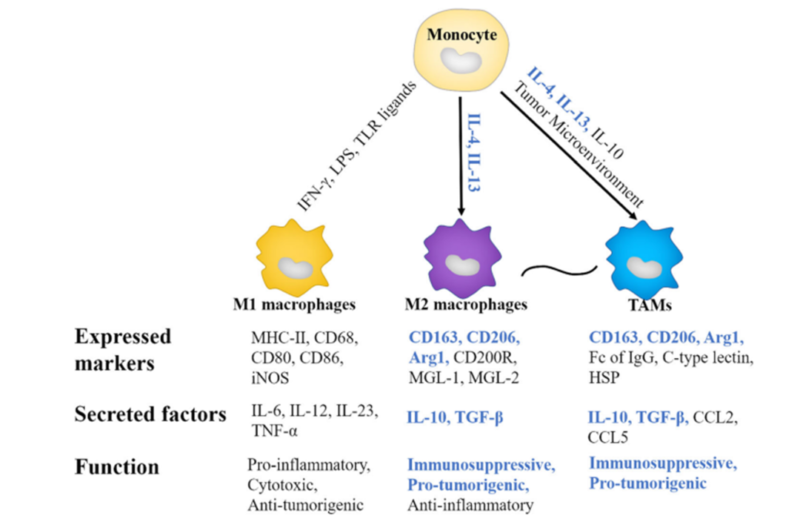
1. In Vitro Macrophage Polarization
Except M1 and M2 macrophages, tumor-associated macrophages(TAM) in tumor microenvironment mainly express markers(e.g. CD163, CD206 and Arg etc ) to promote tumor growth and metastasis. TAM secretes growth factors(e.g. VEGF) and stimulate angiogenesis to promote proliferation of tumor cells. Besides, they produce immunity to inhibit cytokines(e.g. IL-10) and activity of anti-cancer immunocytes(e.g. T cell). Besides, TAM provides nutrition and energy required by growth of tumor cells via changing metabolism. They are also important subgroups in tumor research.
In vitro polarization of macrophage is the important experiment where peripheral blood monocytes are employed, investigating the function and differentiation. However, research work is limited to insufficient primary cells and difficult separation. Thus, inducing differentiation of THP-1 cell is the alternative method. THP-1 is derived from patients with acute myeloid leukemia, and can highly express CD14 as the monocyte cell line. THP-1 is widely applied in macrophage related research.
2. Macrophage Polarization Assay
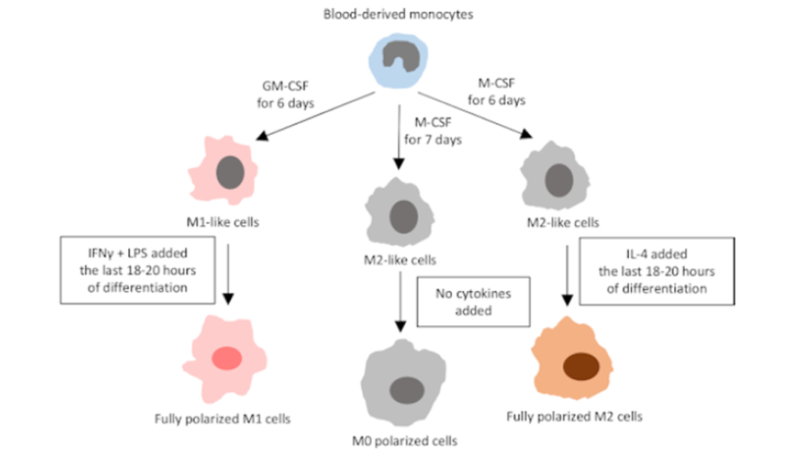
2.1. Polarization of Human Peripheral Blood Monocyte M1/M2(For Reference)
Experimental Solution:
❶ Separate PBMCs from peripheral blood with Ficoll
❷ Sort monocytes enriched by CD14 magnetic beads, alternatively seed 10-20 x 10⁶ PBMC in 2ml serum-free medium. Wash off non-adhered cells after 2-3h to obtain 1 x 10⁶ monocytes.
❸ Add culture medium containing about 50 ng/ml M-CSF into 6 well plate. Regulate the concentration of monocyte to 1-2 x 10⁶/ml. Induce and differentiate into macrophage.
❹ Suck 1ml culture medium after three days. Add 1ml fresh culture medium.
❺ Induce polarization of M1 and M2 after 6 days. Add LPS(10 ng/ml) and IFN-γ(50 ng/ml) or IL-4(20 ng/ml). Stimulate 18-20h.
❻ Finally, detect the expression of Marker related to M1 and M2 with flow cytometry.
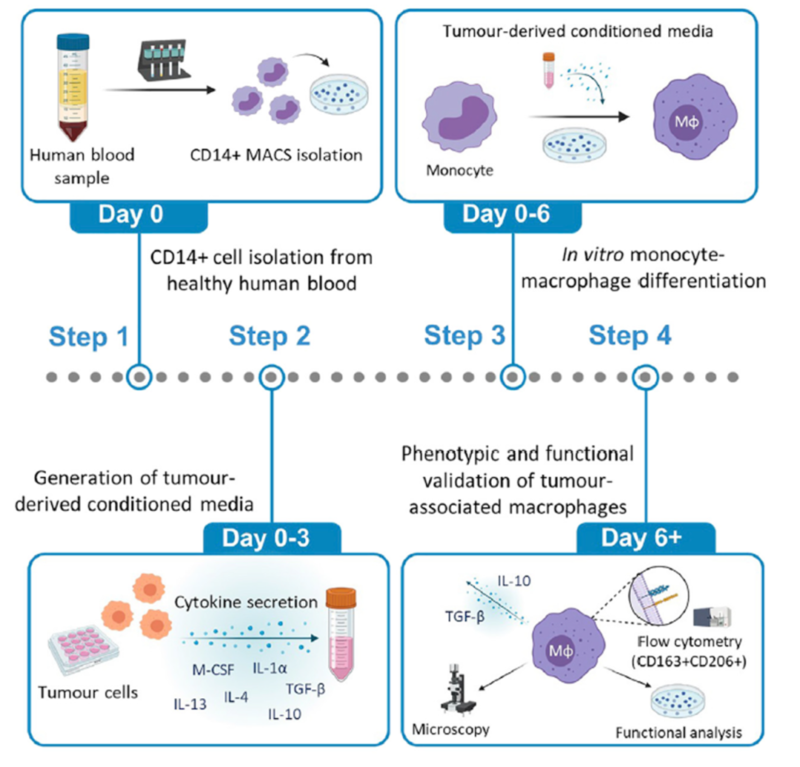
2.2. Polarization of Human Peripheral Blood Monocyte TAM(For Reference)
Tumor-associated macrophages play an important role in tumor growth and metastasis. The experimental method below induces the differentiation of human monocytes into tumor-associated macrophages via the conditioned medium derived from tumor cells.
Experimental Solution:
❶ Separate PBMCs from peripheral blood with Ficoll
❷ Sort monocytes enriched by CD14 magnetic beads
❸ Detect the purity of monocytes with flow cytometry, and ensure over 95% purity
❹ Resuspend 1 x 10⁶ CD14+ monocyte with 1ml complete medium, and seed into 24 well plate
❺ Prepare tumor derived conditioned medium: seed 2.5 x 10⁵ melanoma cells on 6 well plate and culture overnight. Wash and add 1ml serum-free medium to culture for 48h. Centrifuge to remove debris and filter. Quantify to 70 µg/ml.
❻ Take 500 µl culture medium out of 24 well plate. Add 500 µl tumor derived conditioned medium. Induce the differentiation of monocytes into tumor-associated macrophages.
❼ Culture for 72h. Detect tumor-associated macrophages via flow cytometry.
2.3. Polarization of THP-1 Cell to M1/M2(For Reference)
Directional differentiation of human monocyte cell line THP-1 is the important in vitro model for macrophage research. THP-1 cell is usually activated by phorbol ester(PMA) or cytokines(e.g. GM-CSF, M-CSF).
Experimental Solution:
Cell Culture: Culture THP-1 cell in RPMI-1640 culture medium, add 10% FBS.
Induced Differentiation: Process cells for 48h with 25 nM Vitamin D3 or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate(PMA).
Polarization of M1 and M2 Macrophage Markers:
M1 Polarization: add IFN-γ and LPS, culture 24-48h.
M2 Polarization: add IL-4 and IL-13, culture 24-48h.
Detection: Analyse polarized cell markers via flow cytometry or qPCR.
3. M1 M2 Macrophage Polarization
Macrophage polarization markers include M1 and M2. M1 is stimulated by IFN-γ and LPS, and has pro-inflammatory effects. M2 is induced by IL-4 and IL-13, and has anti-inflammatory and tissue repair effects. They play different roles in immune response and tumor microenvironment. In polarization assay, design and select polarizing factors properly. Distinguish M1/M2 group via blank, single staining and biological control. Ensure data accuracy and detect markers via flow cytometry.
4. Recommended Products
REFERENCES
[1]Targeting SRSF10 might inhibit M2 macrophage polarization and potentiate anti-PD-1 therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma, PMID: 39223929.
[2]Targeting macrophage polarization by inhibiting Pim2 alleviates inflammatory arthritis via metabolic reprogramming, PMID: 40000906.
