Abstract: Hypertension refers to long-term higher arterial blood pressure. The consistent blood pressure reading of 130/80 or 140/90 mmHg may be hypertension. Essential and secondary hypertension are the two types, 90%-95% of which is essential hypertension with unknown etiology, possibly induced by the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. Secondary hypertension(5%-10%) is caused by some determined diseases(e.g. kidney disease) and can be treated for improvement or cure.
Keywords: Hypertension, Angiotensin, Cardiovascular Health, High Blood Pressure
1. Signs and Symptoms of Hypertension
Symptoms of early hypertension are not obvious. With the development of the disease, possible symptoms appear, e.g. headache, dizziness, cardiopalmus, blurred vision, tinnitus etc. Some people may feel tachypnea or chest pain, especially after strenuous exercise. Hypertension patients are difficultly aware of these symptoms possibly related to other diseases. Regular monitoring of blood pressure is very important for early detection and management of hypertension, and can avoid great damage to health.
2. Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis of hypertension is very complicated, involving the interaction of several factors. Change of mechanical stress and increase of Angiotensin II, sodium and catecholamine promote the production of reactive oxygen species(ROS) via cells. NADPH oxidase and mitochondria are the main source of ROS. The increase of ROS can exacerbate inflammatory response and activate redox sensitive transcription factor(e.g. NFκB). Immunocytes play an important role in inflammatory response(e.g. macrophages, dendritic cells, monocytes etc), including release of antibacterial substance, ROS and nitric oxide, activation of adaptive immunity, and promotion of hypertension and organ injury.
2.1. Angiotensin System
Angiotensin II is one of the key factor for hypertension, and can result in the rise of blood pressure via vasoconstriction, increased reabsorption of sodium, stimulated secretion of aldosterone.
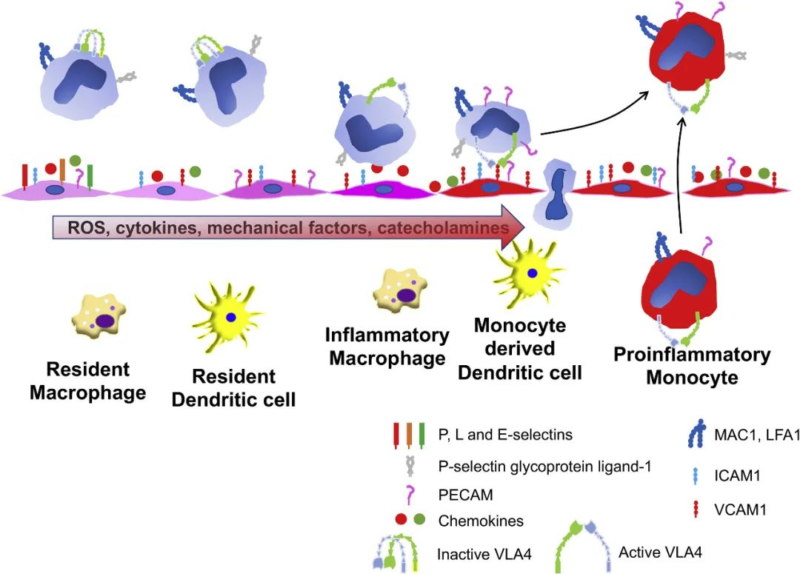
2.2. Interaction of Endothelial Leukocyte
Stimulated endothelial cells increase the expression of chemokines, selectin and adhesion molecules to promote rolling, adhesion and migration of monocytes. Transformation change happens in VLA4, enhancing the interaction between VLA4 and VCAM-1. Migrated monocytes can be transformed to inflammatory macrophages and monocyte-derived dendritic cells, or reappear as activated circulating monocytes.
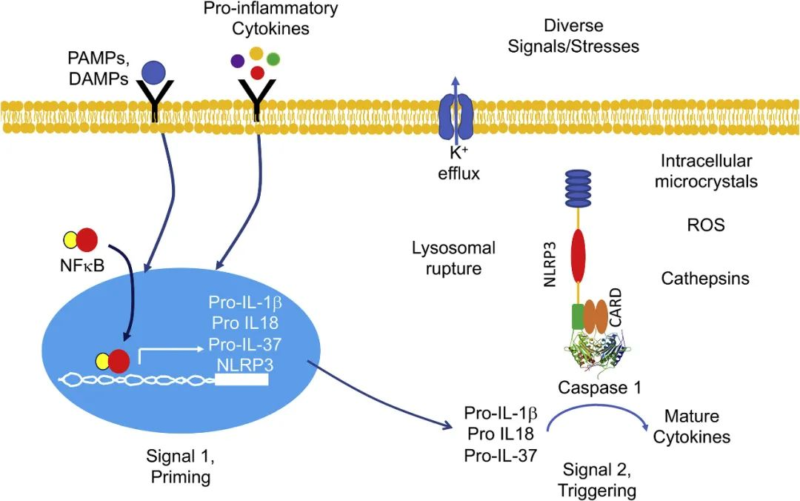
2.3. Activation of Inflammasome
IL-1α and IL-1β transfer signal via IL1R1. Activated IL1R1 can inhibit maturation of macrophages in the kidney, and further prevent the production of nitric oxide(NO) to help the increase of blood pressure.
2.4. Other Factors
High-sodium diet causes sodium retention to increase blood volume and blood pressure. Over-activation of sympathetic nerves can enhance cardiac contraction and heart rate. Besides, vasoconstriction further increase blood pressure. Renal dysfunction also promotes elevated blood pressure.(e.g. increased reabsorption of sodium or reduced perfusion)
3. Drugs to Lower Blood Pressure
Antihypertensive drugs mainly focus on the development of various drugs, such as diuretics, ACE inhibitors, Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker(ARBs), calcium channel blocker, β-receptor blocker and α-receptor blocker etc. These drugs decrease blood pressure via different mechanisms. In recent years, SGLT2 inhibitors and other new drugs against complications like diabetes also show potentiality. With the advancement of individual treatment, the integration of combined drug therapy and lifestyle intervention becomes key research, providing more effective and safer treatment options to different patients.
4. Preventative Measures for Hypertension
Hypertension prevention includes healthy diet(low-salt, higher intake of vegetable and fruit), maintenance of healthy weight, regular exercises(150 minutes of moderate exercise per week), stop smoking, de-stress(e.g. deep breathing, meditation), regular monitoring of blood pressure, physical examination, and limited intake of alcohol.
These measures can help to decrease blood pressure and prevent hypertension to keep cardiovascular health and improve quality of life. Detection of hypertension includes blood pressure measurement, family monitoring, 24h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring(ABPM) and blood and urine examination etc. Regular monitoring helps early detection of hypertension, so that timely treatment and interventions can be taken, especially for high-risk group.
5. Recommended Products
| Target | Antibodies | Recombinant Proteins | ELISA Kits |
| IL-6 | IL-6 antibody | IL-6 recombinant protein | IL-6 ELISA Kit |
| IL-1β | IL-1β antibody | IL-1β recombinant protein | IL-1β ELISA Kit |
| Angiotensin II | Angiotensin II antibody | Angiotensin II recombinant protein | Angiotensin II ELISA Kit |
| Endothelin-1 | Endothelin-1 antibody | Endothelin-1 recombinant protein | Endothelin-1 ELISA Kit |
| CRP | CRP antibody | CRP recombinant protein | CRP ELISA Kit |
| 8-iso-PGF2α | 8-iso-PGF2α antibody | 8-iso-PGF2α recombinant protein | 8-iso-PGF2α ELISA Kit |
| SOD | SOD antibody | SOD recombinant protein | SOD ELISA Kit |
| iNOS | iNOS antibody | iNOS recombinant protein | iNOS ELISA Kit |
| Aldosterone | Aldosterone antibody | Aldosterone recombinant protein | Aldosterone ELISA Kit |
| NA/NE | NA/NE antibody | NA/NE recombinant protein | NA/NE ELISA Kit |
REFERENCES
[1]Effects of beetroot juice on blood pressure in hypertension according to European Society of Hypertension Guidelines: A systematic review and meta-analysis, PMID: 39069465.
[2]Risk factors for chronic hypertension 5 years after a pregnancy complicated by preeclampsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis, PMID: 40079836.
