Abstract: Insulin resistance refers to reduced cell response to insulin, leading to inefficient entrance of glucose into cells and more insulins secreted by pancreas. Long-term insulin resistance can increase the risk of Type 2 Diabetes and obesity due to heredity, improper diet and insufficient exercise etc. Treatments include improved diet, increased exercise, weight loss and drugs(e.g. metformin). Insulin dose-response curve can show decrease of insulin sensitivity or weaker reaction. Only in extremity, insulin response is lost.
Keywords: Insulin Resistance, Blood Sugar Regulation, Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity, Insulin Sensitivity
1. Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome
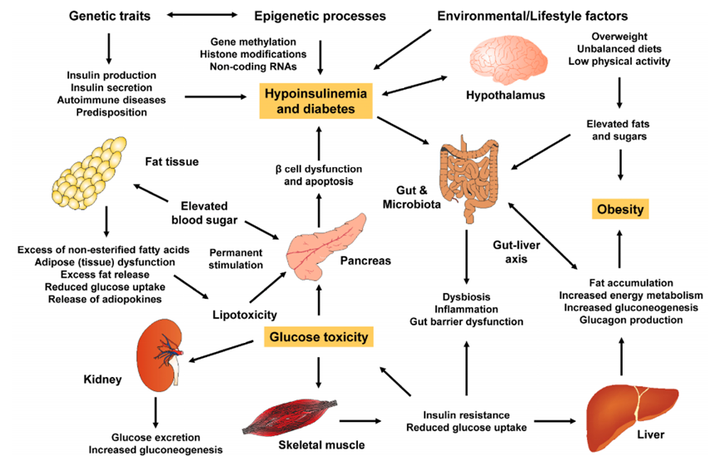
Causes of insulin resistance include genetic and acquired factors(obesity, aging, insufficient exercise, drug etc). Serious syndromes are usually induced by gene mutation or chromosome abnormality(e.g. Down syndromes). Insulin metabolic syndromes are caused by genetic predisposition and unhealthy lifestyle(e.g. obesity). Gene mutation includes insulin pathway genes and lipid deposition.
2. Insulin Resistance Mechanism
Insulin resistance mechanisms are very complex, covering various physiological and pathological processes. First, one of the main reasons is the abnormal insulin pathway. Insulin activates downstream pathways(e.g. PI3K/AKT) to promote the entrance of glucose into cells via binding with insulin receptors. Dysfunction in any stage can cause the resistance as well. Second, release of massive free fatty acid and inflammatory factors by obesity (especially visceral fat accumulation) inhibits insulin effects. Free fatty acid interferes with insulin signal transduction via molecular approaches(e.g. diacylglycerol, ceramide), resulting in insulin resistance in muscle and liver. Besides, oxidative stress and low-grade chronic inflammation also activate various pathways to inhibit insulin effects. ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction are also important mechanisms, affecting function of insulin receptors and intensifying insulin resistance via fatty acid accumulation respectively. Other factors can also enhance insulin resistance to form vicious circle, e.g. hormonal imbalance, insulin antibody production, hyperinsulinemia.
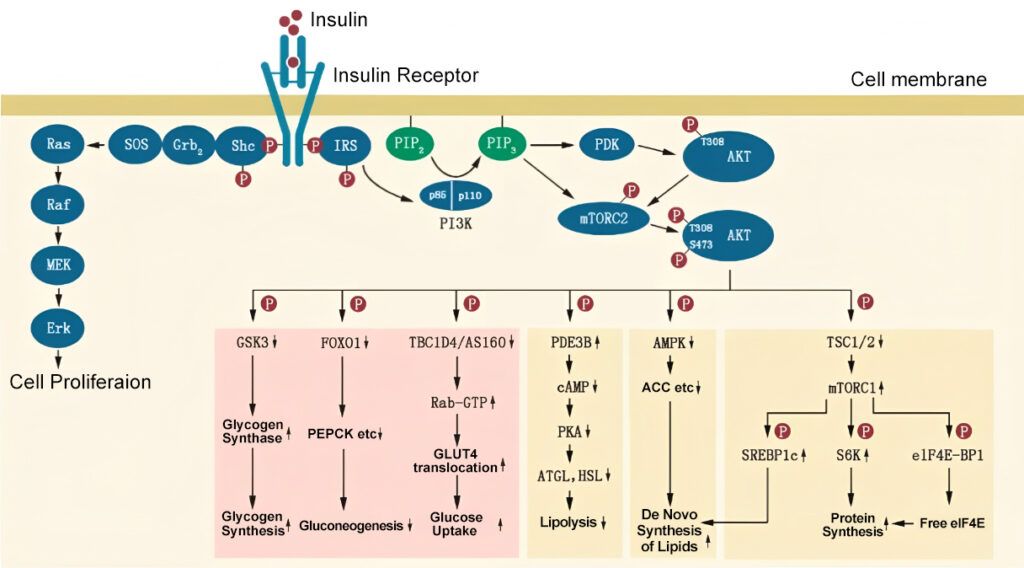
3. Insulin Resistance Disease
As a common metabolic disorder, reduced cell response to insulin decreases insulin effects in regulating blood sugar. This situation usually increase blood sugar level and suffering of Type 2 diabetes.
Decreased sensitivity of the liver to insulin in T2DM patients induces increased liver glyconeogenesis. Glucose uptake ability in muscle tissue weakens. Insulin in liver reduces glucose production via inhibiting expression of PEPCK and G6Pase. Damaged insulin signal in T2DM increases enzymatic activity and continuous release of glucose in liver. Insulin in muscle increases glucose uptake via promoting GLUT4 transfer. Insulin signal dysfunction in T2DM decreases GLUT4 translocation, resulting in the increase of blood sugar.
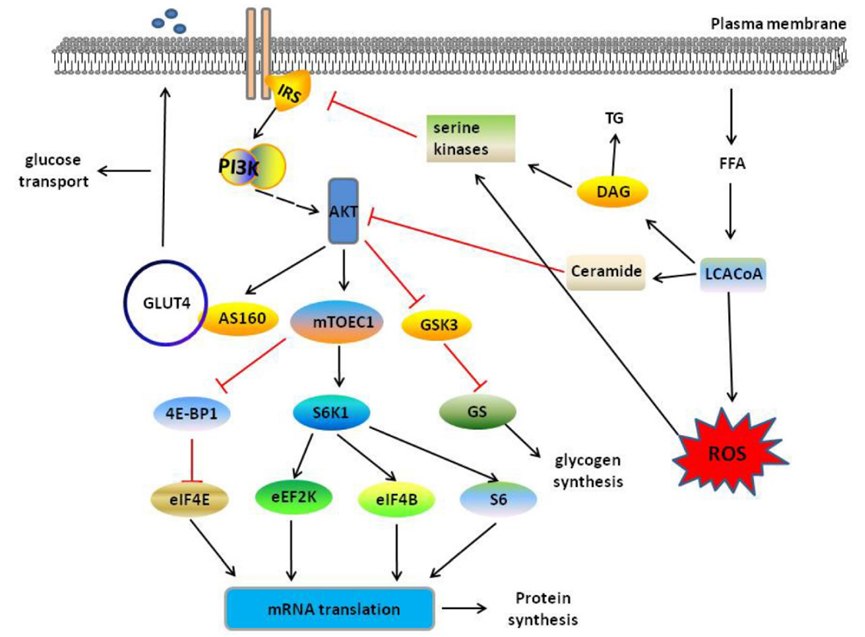
Insulin resistance weakens the inhibition of liver to insulin, increasing fat mobilization and release of free fat acid(FFA). High level of FFA in the liver can be converted into triacylglycerol and stored as lipid droplet, forming NAFLD. Besides, excessive FFA produces reactive oxygen to increase oxidative stress and liver injury via β-oxidation pathway.
4. Insulin Resistance Pathway
Based on metabolic mechanism of T2DM, several signaling pathways become potential therapeutic targets. AMPK is the key factor regulating cellular energy metabolism. It can promote glucose uptake, lipid oxidation and inhibit liver glyconeogenesis. Metformin decreases blood sugar via activating AMPK. SIRT1 takes effects via improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammatory response. GLP-1 receptor agonist regulates blood sugar via increasing insulin secretion and decreasing appetite.
5. Insulin Resistance Treatment Drugs
T2DM drugs regulate blood sugar via improving insulin sensitivity, promoting insulin secretion or reducing glucose production. Common drugs include metformin, sulphonylurea, GLP-1 receptor agonist, DPP-4 inhibitor, SGLT-2 inhibitor and insulin. The best blood sugar regulation for individual treatment requires for drugs and lifestyle management.
6. Recommended Products
| Target | Antibody | Recombinant Protein | ELISA Kit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cortisol | Cortisol antibody | Cortisol recombinant protein | Cortisol ELISA Kit |
| DPP4 | DPP4 antibody | DPP4 recombinant protein | DPP4 ELISA Kit |
| GLP-1R | GLP-1R antibody | GLP-1R recombinant protein | GLP-1R ELISA Kit |
| INSR | INSR antibody | INSR recombinant protein | INSR ELISA Kit |
| SGLT2 | SGLT2 antibody | SGLT2 recombinant protein | SGLT2 ELISA Kit |
| Adiponectin | Adiponectin antibody | Adiponectin recombinant protein | Adiponectin ELISA Kit |
REFERENCES
[1] The insulin resistant brain: impact on whole-body metabolism and body fat distribution, PMID: 38363340.
[2] Iron homeostasis and insulin sensitivity: unraveling the complex interactions, PMID: 39287729.
