Abstract: Autophagy is the process during which cells transferred damaged, denatured or aging proteins to lysosomes. It removes these substances by the digestion and degradation of lysosomes. As the self-degradation mechanism, Autophagy widely exists in cells and plays an important role especially in removing metabolized waste and providing energy required for normal cell functions.
Keywords: Autophagy Process, Types of Autophagy, Autophagy Mechanism, Autophagy and Disease, Autophagy Detection
1. Different Types of Autophagy
There are three types of autophagy, including macroautophagy, microautophagy and chaperone-mediated autophagy(CMA). They conduct protein degradation for cytoplasmic components. Macroautophagy transferred cytoplasmic substance to lysosomes via double-membrane autophagosome. Autophagosome fuses with lysosome to form autolysosome. Microautophagy directly absorbs cytoplasmic components via membrane invagination of lysosome. Both macroautophagy and microautophagy can deal with larger structure via selective or non-selective method. Chaperone-mediated autophagy(CMA) guides the target protein(e.g. Hsc-70) to lysosome membrane, and finally causes protein unfolding and degradation via the transfer of lysosomal membrane receptor.
According to the selectivity for different substrates, autophagy can be further divided into mitophagy, ribophagy, pexophagy and reticulophagy etc. Recent research focus more on mitophagy.
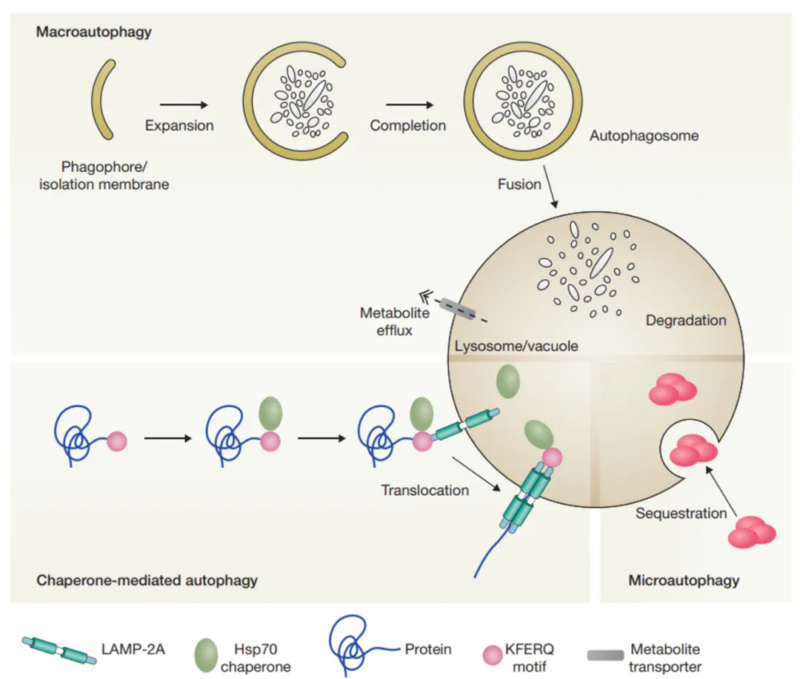
2. Molecular Mechanism of Autophagy
Autophagy initiates from separation membrane(phagocytic vacuoles), and may be derived from endoplasmic reticulum or lipid bilayer of Golgi apparatus and endosome. Swelling of phagocytic vacuoles enwraps intracellular substances to form autophagosome. After fusing with lysosome, autophagosome degrades inclusion to products like amino acid.
Autophagy is the complex degradation process and involved in many key steps: first, Beclin-1/VPS34 is regulated by stress signalling to promote formation of phagocytic vacuoles. Then, Atg5-Atg12 complex interacts with Atg16L, and is involved in aggregation of phagocytic vacuoles. LC3 protein processes and inserts phagocytic vacuole membrane, and then captures the target for degradation. Autophagy is regulated by various signaling pathways, and especially affected by mTOR kinase. During sufficient nutrition, mTOR inhibits autophagy. During low ATP level or hypoxia, REDD1 and AMP kinase active autophagy via inhibiting mTOR. Besides, growth factor actives mTOR to inhibit autophagy via PI3K/Akt pathway.
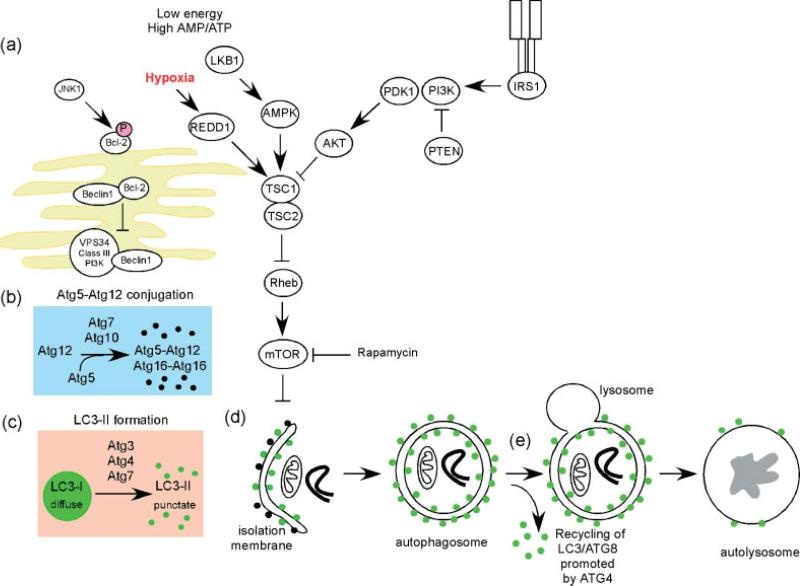
3. Autophagy and Disease
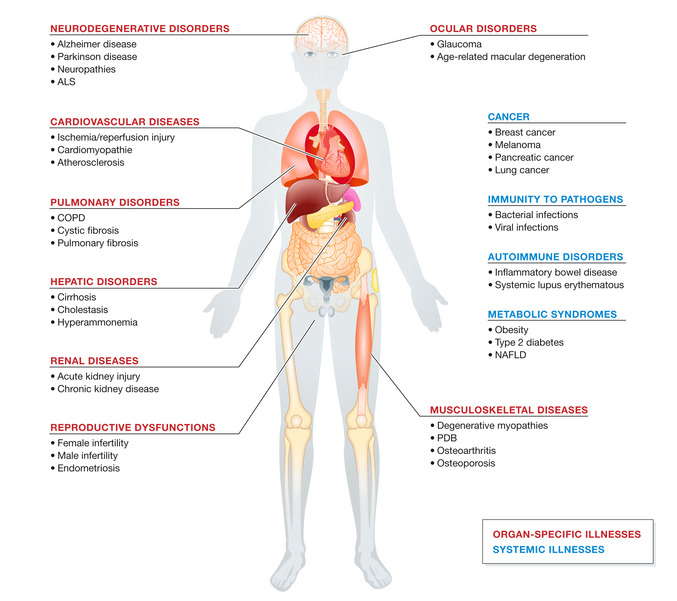
Autophagy is the core mechanism for maintaining homeostasis of cells and organisms, and is also widely involved in development of various diseases. Researches show the intervention of drugs or genes damages autophagic function, and accelerates the development of diseases. Autophagy associated gene mutation is closely related to various severe pathological states(especially for neurodegenerative diseases). Autophagy deficiency can cause tangle and accumulation of amyloid beta plaques and tau, or aggregation of α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease, thus aggravating neuronal damage. Besides, autophagy dysfunction in diseases like neuropathy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis(ALS) can cause protein damage and organelle accumulation. In cancer, autophagy can inhibit tumorigenesis and support the survival of tumor cells(especially for hypoxia and nutritional deficiency). Autophagy becomes the potential target due to its dual effects in cancer treatment. Autophagy also plays an important role in various diseases like cardiovascular, lung and liver diseases etc. The dysfunction is closely related to multiple organ dysfunction. Its key role in cell health is obvious.
4. Autophagy Detection Methods
Autophagy is the multi-step dynamic process. Traditionally, electron microscope is applied in observing autophagy. The finding of ATG protein promotes the development of molecular tools to quantify autophagy. Homeostatic evaluation usually detect LC3-II level to measure number of autophagosomes and LC3 conversion via ICC/IHC/IF/WB. Number of LC3-II spots, LC3 conversion rate and autophagic flow are common indicators. Besides, measurement for p62/SQSTM1 degradation is inversely proportional to autophagic activity. Lower p62/SQSTM1 level shows higher autophagic activity.
5. Recommended Products
|
Target |
Antibody |
Recombinant Protein |
ELISA Kit |
|
ATG3 antibody |
ATG3 recombinant protein |
ATG3 ELISA Kit |
|
|
ATG5 antibody |
ATG5 recombinant protein |
ATG5 ELISA Kit |
|
|
ATG7 antibody |
ATG7 recombinant protein |
ATG7 ELISA Kit |
|
|
ATG12 antibody |
ATG12 recombinant protein |
ATG12 ELISA Kit |
|
|
ATG13 antibody |
ATG13 recombinant protein |
ATG13 ELISA Kit |
|
|
ULK1 antibody |
ULK1 recombinant protein |
ULK1 ELISA Kit |
|
|
ATG14 antibody |
ATG14 recombinant protein |
ATG14 ELISA Kit |
|
|
ATG16L antibody |
ATG16L recombinant protein |
ATG16L ELISA Kit |
|
|
Beclin 1 antibody |
Beclin 1 recombinant protein |
Beclin 1 ELISA Kit |
|
|
BCL2 antibody |
BCL2 recombinant protein |
BCL2 ELISA Kit |
|
|
AMPK antibody |
AMPK recombinant protein |
AMPK ELISA Kit |
|
|
SQSTM1 antibody |
SQSTM1 recombinant protein |
SQSTM1 ELISA Kit |
|
|
PIK3C3 antibody |
PIK3C3 recombinant protein |
PIK3C3 ELISA Kit |
|
|
PIK3R4 antibody |
PIK3R4 recombinant protein |
PIK3R4 ELISA Kit |
|
|
MAP1LC3A antibody |
MAP1LC3A recombinant protein |
MAP1LC3A ELISA Kit |
REFERENCES
[1]LYC inhibits the AKT signaling pathway to activate autophagy and ameliorate TGFB-induced renal fibrosis, PMID: 38037248.
[2]Astrocytic autophagy plasticity modulates Aβ clearance and cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease, PMID: 39044253.
