Abstract: Vesicle plays an important role in intracellular substance transport between different membrane-bound organelles, known as vesicular transport. Vesicle-transported substances mainly contain membrane protein or lipid on the vesicular membrane, and inclusions on vesicles (e.g. neurotransmitters, hormones, various enzymes and cytokines etc).
Keywords: Vesicular Transport Protein, Membrane Protein, Intracellular Membrane Traffic
1. Vesicular Transport Process
The vesicle usually transports proteins between organelles, e.g. translocation of proteins from ER to Golgi apparatus or from Golgi apparatus to lysosome, secretory vesicles and cytoplasmic membrane etc. Transport vesicle is formed by budding from a organelle and encapsulates transported proteins. Through fusing with the target organelle, the vesicle transports the protein from an organelle to another one.
2. SNARE Proteins Vesicle Fusion
2.1. SNARE Protein Complex
Key fusion mechanism model of vesicular transport process is SNARE hypothesis at the molecular level. The hypothesis shows different v-SNARE proteins are found in each type of vesicles and can recognize and pair for specific t-SNARE on the relevant target membrane where the vesicle is anchored to form trans-SNARE complex through the specific interaction. With the help of α-SNAP protein, the ATPase activity of NSF protein reversibly dissociates SNARE protein complex and drives membrane fusion to form cis-SNARE complex.
The hypothesis also shows vesicular transport is specific due to the specific interaction of SNARE proteins mediating vesicle fusion. Although SNARE proteins are initially found on synaptic vesicle and plasma membrane, the homologue also exists in other intercellular transport processes. Nearly each step of membrane transport is implemented by a pair of different SNARE proteins(v-SNARE and t-SNARE).
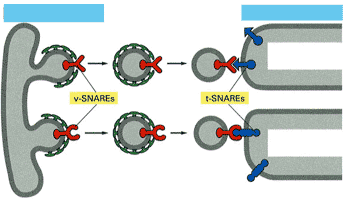
2.2.SNARE Protein Type
SNARE proteins still play a key role in intracellular transport pathway. Syntaxin, SNAP25 and VAMP/synaptobrevin are firstly found and exhaustively studied SNARE proteins. A minimum of three proteins are involved in the vesicle fusion, such as v-SNARE, t-SNARE and SNAP25, also called anchored fusion proteins. SNAP25 consists of two α-helix peptide chains. It's usually accompanied by t-SNAREs and acts as the v-SNAREs receptor. When the liposome containing v-SNAREs contacts with the liposome containing t-SNAREs/SNAP25, SNAP25 coils around v-SNAREs and t-SNAREs. NSF protein is also involved in vesicle fusion. Besides, α-, β- and γ-SNAPs are also involved in vesicle fusion process.
SNARE is the small protein with molecular weight 18-42KD. All SNARE protein markers contain about 60 conserved amino acid residues(seven repetitive sequences, called SNARE motif.) The coiled-coil structure can connect two relative membranes for fusion. SNAP25 protein is the exception. It contains two SNARE motifs and binds with the membrane by palmitoyl group. Most SNARE proteins are C-terminal anchored transmembrane proteins(Type II integral membrane protein) with/without the short extracellular domains. However, many SNARE proteins without transmembrane domain are anchored on the membrane by palmitoylation or isoprenylation.
3. Rab Protein Vesicle Trafficking
Besides anchored proteins, some proteins like Rab are also involved in regulating vesicular transport. Rab belongs to GTP-binding family and contains 200 amino acids. The protein structure is very similar to Ras. Rab regulates fusion speed of vesicle by continuous binding and ATP hydrolysis cycle. GDI as the heterologous protein in the cytoplasm inhibits dissociation between Rab and GDP. (A large amount of GTP exists in the cytoplasm. If GDP drops, Rab may bind with GTP on incorrect location.) After Rab is transported to the specific location, GEF can specifically catalyze dissociation of Rab and bind with GTP to change the Rab molecular conformation and rapidly bind with vesicle membrane proteins. During vesicle fusion, GTP is hydrolyzed into GDP and separated from Rab.
4. Recommended FineTest Antibodies
| Catalogue No. | Detection Target | Product Name |
| FNab07002 | RAB2 | anti- RAB2 antibody |
| FNab07013 | anti- RAB2B antibody | |
| FNab07048 | RAB9 | anti- RAB9A antibody |
| FNab07050 | anti- RAB9B antibody | |
| FNab07038 | RAB5 | anti- RAB5A antibody |
| FNab07040 | anti- RAB5B antibody | |
| FNab06988 | RAB11A | anti- RAB11 antibody |
| FNab07009 | RAB27A | anti- RAB27A antibody |
| FNab07010 | anti- RAB27A antibody | |
| FNab07011 | anti- RAB27A-specific antibody | |
| FNab07045 | RAB8A | anti- RAB8A antibody |
| FNab07024 | RAB3A | anti- RAB3A antibody |
| FNab07025 | anti- RAB3A-specific antibody | |
| FNab08055 | SNAP | anti- SNAP25 antibody |
| FNab08056 | anti- SNAP25 antibody | |
| FNab08057 | anti- SNAP25 antibody |
REFERENCES
Vesicular transport as a new paradigm in short-term regulation of transepithelial transport, PMID: 10803686.
