Abstract: Hyperuricemia is the excessive uric acid or decreased excretion induced metabolic disease, showing increased uric acid level in the blood. It's the important pathogenic factor of arthrolithiasis, and closely relevant to hypertension, diabetes and cardio-cerebrovascular diseases. Deeper investigation on uric acid metabolism can help to explore its role in various diseases, providing new targeted therapy for disease prevention.
Keywords: Hyperuricemia, Uric Acid Metabolism, Targeted Therapy, Metabolic Disease
1. Pathologic Features
Increase of uric acid concentration level in the blood easily produces urate crystal in tissues(e.g. joint, kidney etc), resulting in a series of diseases. Crystals can cause acute gouty arthritis. Recurrent seizure may also cause chronic joint injury. Besides, deposition of urate crystal can cause renal calculi and chronic renal function failure, affecting patients’ quality of life and health.
2. Pathological Mechanism
Antioxidant roles of uric acid in normal level include removal of free radical and protection for nerve cells and blood vessel. Uric acid is converted into prooxidant and pro-inflammatory factor, when its concentration is higher than physiological range. High uric acid activates MAPK p38 and ERK pathway, induces activation of transcription factors(e.g. NF-κB and AP-1), and promotes maturation and release of IL-1β and IL-18, resulting in inflammatory response. In arthrolithiasis, phagocytosis of monosodium urate crystal by macrophage induces mitochondrial stress and increased ROS, activating NLRP3 further. Activation of rennin-angiotensin system and injury of vascular endothelium by high uric acid are involved in hypertension, atherosclerosis and T2DM. Besides, proteomics researches show hyperuricemia is associated with activation of complement system, increase of C3 and C4, and changes in HDL components. Thus, roles in inflammation and metabolic disorder are very important.
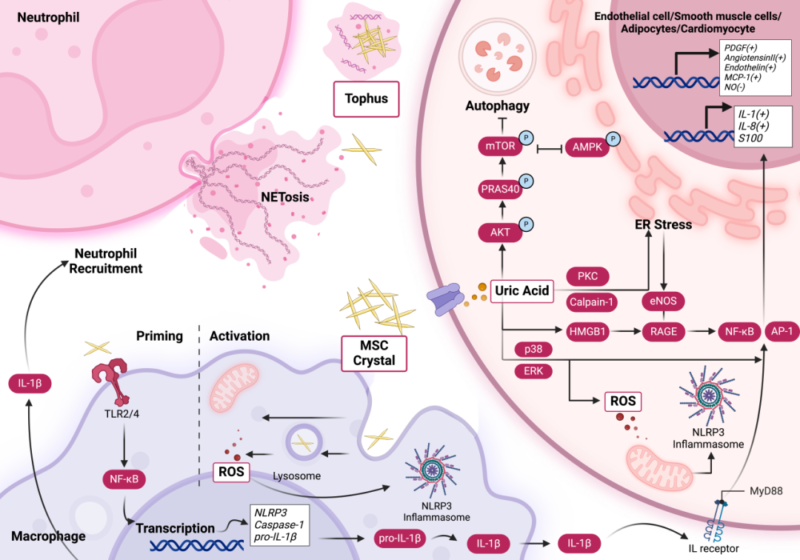
3. Treatments of Hyperuricemia
3.1. Non-Drug Treatments
Diet regulations can help to reduce blood uric acid level, including decreased high purine food, increased water intake for facilitating uric acid excretion, control of body weight with proper exercise.
3.2. Drug Therapies
Drug therapies for hyperuricemia include inhibitors for uric acid production(e.g. allopurinol, febuxostat tablets). Inhibition of xanthine oxidase(XO) activity reduces uric acid production in human body; Uricosuric agents(e.g. Benzbromarone, Probenecid) can improve uric acid excretion through kidney, and decrease concentration of blood uric acid; Biological reagents like recombinant uricases(e.g. rasburicase, pegloticase) can decompose uric acid to allantoin, which is easier for excretion. Selection of these drugs depends on patients’ diseases. Thus, effective control of uric acid level can prevent related complications.
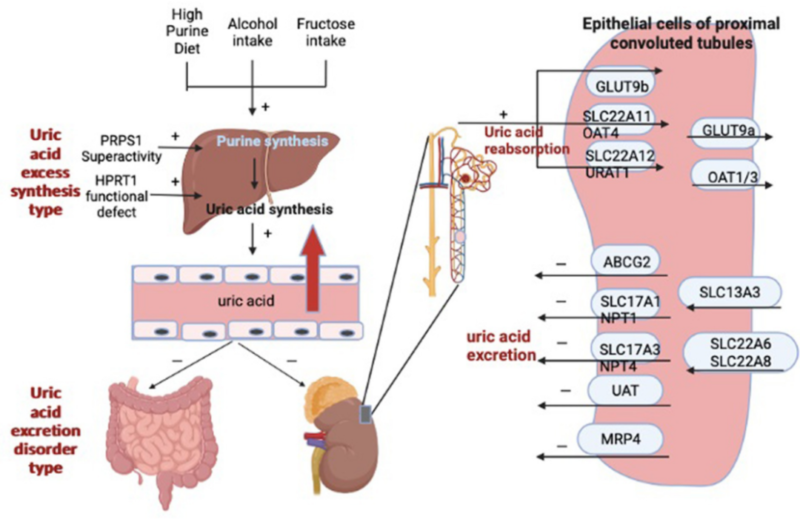
3.3. Hyperuricemia Management
Hyperuricemia management requires for lifestyle intervention, drug therapies and attention on new drugs. In recent years, new xanthine oxidase inhibitors(e.g. topiroxostat) show better curative effects and safety. Besides, inhibitors for uric acid transporters(e.g. URAT1, GLUT9) have been in the clinical research. New strategies for anti-inflammatory therapy and regulation of intestinal flora are also explored.
| Target | Antibodies | Recombinant Proteins | ELISA Kits |
| IL-1β | IL-1β antibody | IL-1β recombinant protein | IL-1β ELISA Kit |
| IL-6 | IL-6 antibody | IL-6 recombinant protein | IL-6 ELISA Kit |
| TNF-α | TNF-α antibody | TNF-α recombinant protein | TNF-α ELISA Kit |
| IL-18 | IL-18 antibody | IL-18 recombinant protein | IL-18 ELISA Kit |
| CRP | CRP antibody | CRP recombinant protein | CRP ELISA Kit |
| XOD | XOD antibody | XOD recombinant protein | XOD ELISA Kit |
| URAT1 | URAT1 antibody | URAT1 recombinant protein | URAT1 ELISA Kit |
| ABCG2 | ABCG2 antibody | ABCG2 recombinant protein | ABCG2 ELISA Kit |
| SOD | SOD antibody | SOD recombinant protein | SOD ELISA Kit |
| MDA | MDA antibody | MDA recombinant protein | MDA ELISA Kit |
| Insulin | Insulin antibody | Insulin recombinant protein | Insulin ELISA Kit |
| ADP | ADP antibody | ADP recombinant protein | ADP ELISA Kit |
REFERENCES
[1]Hyperuricemia-induced complications: dysfunctional macrophages serve as a potential bridge, PMID: 39935474.
[2]Hyperuricemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: Emerging Pathophysiology and a Novel Therapeutic Strategy, PMID: 41009566.
