Abstract: Plasmid miniprep is the commonly used experimental operation. Do you know the principle of the extraction method?
Keywords: Plasmid DNA, Plasmid Extraction, Plasmid Miniprep, Alkaline Lysis Method
1. Introduction of Plasmid Miniprep
First, plasmid is the circular DNA molecular separated from chromosome, which is capable of reproducing itself. Plasmid extraction is performed by the alkaline lysis method. Basic principle: bacteria suspension is exposed in the high PH strong linear alkylbezene sulfonates. Then, the cell wall is pyrolysed. Chromosome DNA denatures with protein. They intertwine to form large complex which is then coated by dodecyl dulfate. When potassium ion is replaced by sodium ion, the complex will deposit in the solution. After the centrifugation for complex, plasmid DNA exists in the supernatant. DNA is negatively charged, while plasmid extraction column is the equivalent of anion column and can adsorb DNA in the condition of high salt. After eluting the column by deionized water, the purified plasmid DNA is obtained.
2. Solution for Preparing Plasmid Using Alkaline Lysis Method
2.1. Solution P1: Consists of glucose, Tri-HCL and EDTA-Na2(Protection, Buffer)
Mainly aims to suspend bacteria. Tris-HCl is the buffer solution keeping pH of reaction system constant; EDTA-Na2 is the metal chelating agent, which acts on binding metal ions in microorganisms and inhibiting activity of DNAse; Glucose can improve the viscosity of the solution, maintain bacterial suspension and delay the sedimentation time. Whether RNAse A has been added should be validated during using Solution I. RNAse A aims to eliminate RNA. If bacteria are not completely mixed, the lysis will be influenced. Hence, concentration of the extracted plasmid is very low. Because RNA enzyme belongs to protein, Solution I containing RNase A should be stored at low temperature (4°C) due to the poor stability of the protein.
2.2. Solution P2: Consists of SDS and NaOH(Lysis, Denaturation)
Mainly aims to release contents by breaking cell wall of bacteria and denature protein along with DNA. After adding Solution P2, mix it well by slightly reversing. The action should be gentle. Don't strongly shake it. Otherwise, genomic DNA will be broken. The reaction time should not be too long. NaOH plays the significant role in cell lysis during the process. By breaking the structure of cell membrane, the phasic change from bilayer membranes to microencapsule occurs. As a result, the cell lysis happens. Binding with protein easily, SDS can denature it to form polypeptide complex soluble in solution. Then, polypeptide chain can intertwine with genomic DNA better.
2.3. Solution N3: Consists of Gu-HCl and KAC (Refolding, Separation)
As a part of the alkaline solution in Solution II, NaOH can break structure of DNA exposed in the solution for a long time. Thus, neutralization is required. After adding Solution III, potassium acetate interacts with SDS in Solution II. The reaction generates potassium dodecyl sulfate(PDS) insoluble in water. Thus, network macromolecule condensed by denatured chromosomal DNA, protein and cell debris will rapidly subside. However, plasmid DNA recovers the natural structure and is soluble in supernatant. To avoid partial sediment, rapid mixture is compulsory after adding Solution III.
2.4. Solution PB: Consists of Gu-HCl and 30% Isopropyl Alcohol (Wash Buffer)
After plasmid is absorbed by silica column, the isopropyl alcohol is added to precipitate the protein. If white flocculent precipitate appears, the purity of extracted plasmid is insufficient. Namely, protein contamination exists. Thus, after the centrifugation by adding Solution III, it is particularly noticed to avoid to pour precipitate along with supernatant into plasmid extraction column.
2.5. Solution PE: Consists of Tris-HCl and 80% Ethanol (Wash Buffer)
Mainly aims to wash residual salt ion. Wash buffer contains high concentration ethanol. Ethanol will influence subsequent digestion or sequencing reaction. To completely remove ethanol, the column should be spun in the centrifugal machine before eluting plasmid.
Elution buffer: aims to elute plasmid DNA sample on silica adsorption column. Before centrifugation, keep aqueous solution stay on the membrane for a long time. It is beneficial to elute plasmid DNA better. To improve the recovery rate of plasmid, aqueous solution can be refilled into adsorption column for centrifugal collection again.
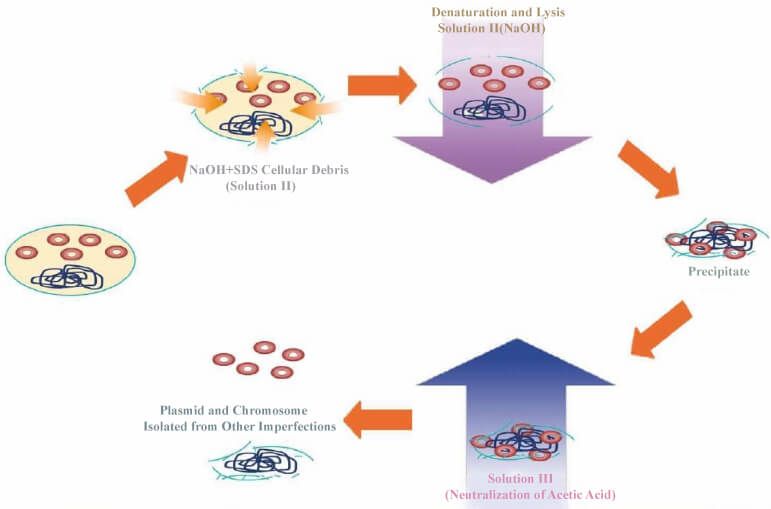
Figure 1. Schematic Diagram for Principle of Preparing plasmid DNA Using Alkaline Lysis Method.
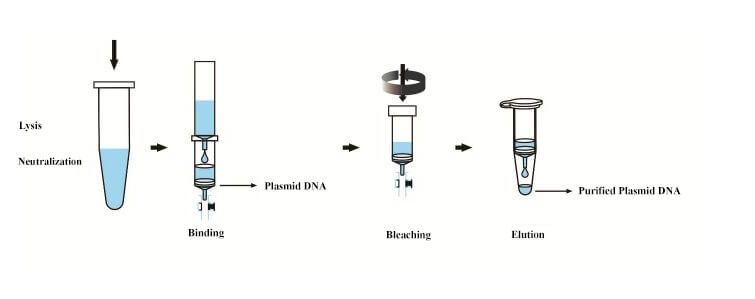
Figure 2. Schematic Diagram for Plasmid Extraction Steps.
