Abstract: Immunoprecipitation technique(IP) can purify and enrich the target protein. In the proteomics research, the protein-protein interaction can be recognized. Immunoprecipitation is applied in the protein research on relative abundance, size, up/down-regulation, stability, PTMs and interaction etc.
Keywords: Immunoprecipitation Assay, Immunoprecipitation Technique, Proteomics
1. High Background
- Insoluble protein: Residual insoluble proteins are in the sample. Remove the supernatant immediately after centrifugation.
- Insufficient washing: Optimize washing buffer, improve washing efficiency by adding detergent(0.5-1%NP-40/Triton X-100/Tween-20), and increasing saline ion concentration(250mM NaCl/1-2mM DTT/β-ME), washing time as well as frequency.
- Non-specific binding: Non-specific protein binds with the magnetic bead. Magnetic bead is insufficiently pre-blocked with BSA. Check whether the BSA is fresh. Incubate magnetic bead and 1%BSA for 1h. Wash with PBS 3-4 times before use.
- Low specificity: use antibodies with high specificity and affinity purify.
- Non-specific binding caused by overused antibody: try to use less antibody.
- Overused protein in the lysate: Too many false positive proteins appear in the washing buffer. Use less sample.
- Non-specific binding between proteins and antibodies: incubate the magnetic bead and sample before immunoprecipitation. Remove the components which can bind with the magnetic bead. Some researchers also use isotype control in lysate treatment.
- Degradation of target protein in the sample: Perform the sample lysate at low temperature. Add excessive protease inhibitor.
- Contamination: The high-intensity elution buffer(e.g. SDS-PAGE loading buffer) can result in the elution of various non-specific proteins and antigen. Gentle buffer(e.g. 0.1M glycine, pH2.5) can avoid the contamination.
2. Elution of Excessive Antibodies
Higher volume of antibodies, try to decrease the volume.
3. Undetected Elution of Target Protein
- Protein expression level: The target protein in the sample is unexpressed or expressed in a low level. For low expression, use more lysate. But the non-specific binding may increase. Thus, remove the lysate before immunoprecipitation.
- Insufficient antibody: The antibody volume is insufficient. Check and increase the volume.
- Uneluted protein: The target protein is not eluted from the magnetic bead. Check whether the elution buffer is suitable.
- The antibody doesn't bind with the magnetic bead: Check whether the magnetic bead matches with antibody subtype. Store the magnetic bead properly. Avoid deterioration or drying.
- Higher alkalinity in the lysate: Use lower alkalinity lysate. Usually, NP-40, RIPA, western or IP cellular lysate can be used.
4. Effect of Sampling Loading Order on the Recovery of Target Protein
Mixed incubation for magnetic bead, antibody and antigen sample is faster. But the purity and recovery of target protein are lower.
Indirect method: antibody binds with antigen sample first. Then add magnetic bead for incubation. The recovery of target protein is the highest; Direct method: magnetic bead binds with antibody first. Then, add antigen for incubation; For highly expressed protein, differences between the two methods are less. For lowly expressed protein, indirect method can get higher recovery of target protein.
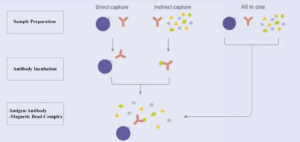
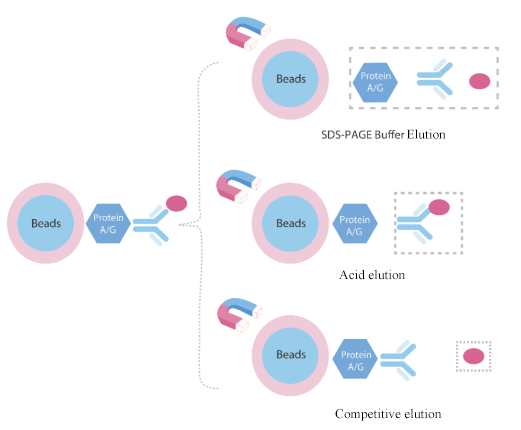
5. Antigen Elution Method
Denaturing elution method: This method is very efficient for WB analysis. But the eluted protein lacks of biological activity.
Acid elution method: Suitable for functional analysis of eluted protein. 0.1M-0.15 glycine (pH2.5-3) is the most efficient non-denaturing elution buffer.
Competitive elution method: For tagged target proteins, use high concentration of tag or ligand for competitive elution. The eluted protein has biological activity and antigenic fragments are not contaminated.
6. Positive and Negative Control Setting
Positive Control: Also known as input. Directly use cellular lysate or extracted protein for WB to determine whether the target protein exists in the sample.
Negative Control: Use isotype control as negative control to eliminate non-specific binding.
7. Secondary Antibody Selection
|
IP Capture Antibody |
WB for Primary Antibody |
WB for Secondary Antibody |
Notes |
|
Mouse |
Mouse pAb |
HRP-protein A or HRP-anti mouse IgG |
If the primary antibody belongs to mouse lgG1/lgG3 subtype, the affinity of HRP-conjugated Protein A is very low. Properly decrease the dilution ratio(try to use HRP-anti mouse IgG as well); If the primary antibody belongs to mouse lgM/lgA subtype, avoid to choose HRP-Protein A due to the unconjugated feature. |
|
Rabbit pAb |
HRP-anti rabbit IgG |
|
|
|
Rabbit |
Mouse pAb |
HRP-anti mouse IgG |
|
|
Rabbit pAb |
HRP-protein A or HRP-anti rabbit IgG light chain specific antibody |
HRP-Protein A can effectively decrease heavy chain signal and the effect of light chain signal. The background is clean. Suitable for detecting most target proteins except 45-55kDa. For target proteins between 45-55kDa, HRP-anti rabbit IgG light chain specific antibody is recommended. |
REFERENCES
[1]Visualization of Protein-protein Interaction in Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Fractions by Co-immunoprecipitation and In Situ Proximity Ligation Assay, PMID: 28117799.
[2]Immunoprecipitation and Western blot-based detection of protein O-GlcNAcylation in cells, PMID: 35106498.
