1. PGE2 Signaling Pathway
The synthesis and PGE2 signaling pathway is outlined as follows: First, phospholipase A2(PLA2) catalyzes the hydrolysis of cell membrane phospholipid, and releases Arachidonic acid(AA). Then, AA is converted to PGG2 and PGH2 by Cyclooxygenase(COX, including COX-1 and COX-2). Finally, the catalysis of PGG2 and PGH2 by PGE synthases(mPGES-1, mPGES-2 and cPGES) performs the conversion of PGE2. Current PGES include mPGES-1, mPGES-2 and cPGES. They mediate the biosynthesis of PGE2 by different COX coupling methods. cPGES is mainly coupled with COX-1, and controls the PGE2 production under physiological conditions. mPGES-1 is coupled with COX-2 as inducible synthase, and involved in the PGE2 synthesis caused by inflammation. mPGES-2 is coupled with COX-1 and COX-2. Its function is still unclear and gene knockout has no effect on PGE2 production. PGE2 binds with G-protein coupled receptor EP1-EP4 to produce the signal. The activation of EP1 receptor and EP3 receptor can increase the concentration of Ca2+ in the cell via phospholipase C(PLC). EP3 receptor also inhibits cAMP production via adenylate cyclase(AC). The activation of EP2 receptor or EP4 receptor stimulates the cAMP production via adenylate cyclase(AC). The activation of EP4 increases protein kinase B(AKT/PKB) via stimulating phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase(PI3K).
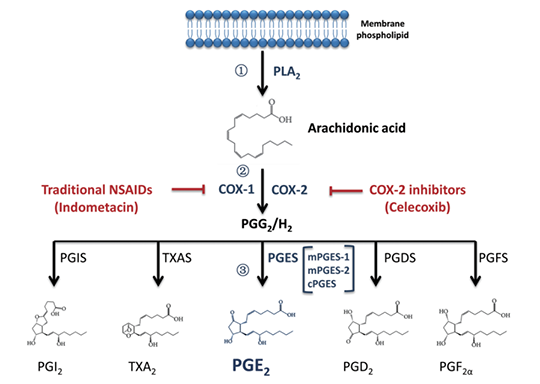
2. PGE2 Metabolism
PGE2 is a very important lipid metabolite, playing a key role in regulation of fever, inflammation, and blood pressure. When subject to physiological or pathological stimulation, PGE2 will release. Through 4 receptors(EP1, EP2, EP3 and EP4), PGE2 is widely involved in the metabolic process of organisms and cells, regulating vasodilation and vasoconstriction. Usually, PGE2 has an effect on EP1 and EP3 receptor, resulting in vasoconstriction and hypertension. The activation of EP2 and EP4 receptors can cause vasodilation and hypotension. The overall function of 4 receptors is vasoconstriction. Exogenously administering PGE2 and analogue can cause the decrease of arterial blood pressure.
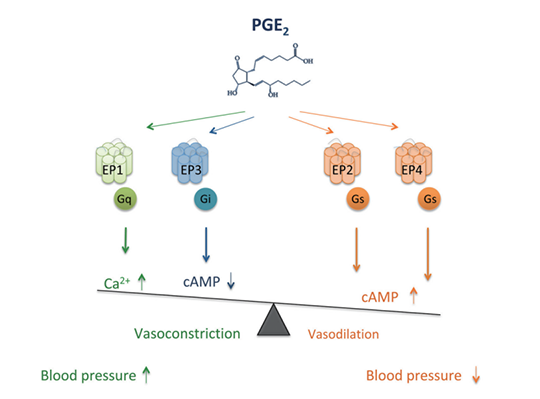
3. Role of PGE2 in Cardiovascular Diseases
PGE2 plays an important role in regulation of cardiovascular functions and maintenance of homeostasis. The knock-out of mPGES-1 can increase mitochondrial membrane potential by inhibiting PGE2-induced decrease of oxidase(NADPH) activity in smooth muscle cell, therefore causing the inhibition of vascular inflammation and oxidative stress response, as well as retardation of vasoconstriction and endothelial dysfunction. However, the animal experiment shows targeting inhibition of mPGES-1 has some protective effects on inflammatory vascular diseases like atherosclerosis. Its safety for cardiovascular diseases is still questionable. mPGES-1 derived from different tissues and cells producing PGE2 may have different and even opposite biological effects. Besides, EP receptors also play an important role in cardiovascular homeostasis and diseases. Many specific EP receptor agonists and antagonists have obvious effects on occurrence, development and prognosis of cardiovascular diseases.
4. Recommended Products
4.1. Antibodies
|
Cat.No |
Product Name |
MW(kDa) |
Antibody Type |
|
PTGER3 antibody |
55 kDa, 70 kDa |
pAb |
|
|
PTGER4 antibody |
50 kDa, 22 kDa |
pAb |
4.2. ELISA Kits
|
Cat.No |
Product Name |
Range |
Sensitivity |
|
PGE2(Prostaglandin E2) ELISA Kit |
31.25-2000pg/ml |
18.75pg/ml |
|
|
Human PGE2(Prostaglandin E2) ELISA Kit |
31.25-2000pg/ml |
18.75pg/ml |
|
|
Mouse PGE2(Prostaglandin E2) ELISA Kit |
31.25-2000pg/ml |
18.75pg/ml |
|
|
Rat PGE2(Prostaglandin E2) ELISA Kit |
31.25-2000pg/ml |
18.75pg/ml |
|
|
Sheep PGE2(Prostaglandin E2) ELISA Kit |
31.25-2000pg/ml |
18.75pg/ml |
|
|
Porcine PGE2 (Prostaglandin E2) ELISA Kit |
31.25-2000pg/ml |
18.75pg/ml |
