Abstract: Collagen protein is the main structural component of extracellular matrix and plays an important role in mechanical stability of various tissues, tissue structure and morphology. One-third of total proteins in human body are collagen proteins. There are 28 kinds of collagen proteins with different advanced tissue structure. The most common one can form fibre. These proteins are assembled with unique hierarchical structure. Collagen molecules are paralleled and cross-linked, forming long fiber nanostructure and more advanced structure.
Keywords: Collagen Proteins, Protein Synthesis, Collagen Types and Functions, Collagen Applications
1. Collagen Protein Structure
Collagen protein family members are trimer, consisting of 3 α chains. Each chain has the repetitive sequence (Gly-X-Y)n. X and Y are usually proline and hydroxyproline. Collagen proteins are synthesized by coded gene, and become mature protein by post-translational modification and processing. Collagen proteins forming fibre are procollagen during synthesis, and has one collagen or COL structural domain at least, as well as non-collagen or NC structural domain. Collagen molecules produced by processed procollagen assemble striped fibers. Each fibrous collagen molecule is about 300 nanometers in length and 1.5 nanometers in diameter. In the fibre, collagen molecules are interlaced from N to C, forming D cycle repetition mode.
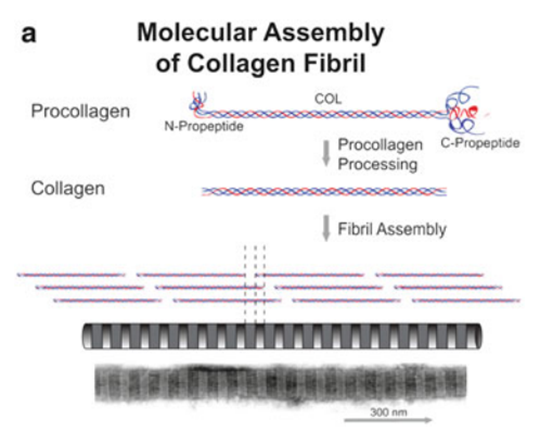
2. Collagen Types and Functions
Collagen proteins code 45 genes at least and 28 different kinds of collagen glycoprotein in the genome of vertebrates and more advanced invertebrates. These collagen proteins are assigned to roman numerals(I-XXVIII) according to discovery time. There are four types of collagen proteins based on the structure and function, including fibrous collagens(e.g. Ⅰ, Ⅱ, Ⅲ, Ⅴ, Ⅺ, ⅩⅣ and ⅩⅩⅦ, the most common types are Ⅰ, Ⅱ and Ⅲ. ), fibril-associated collagen with interrupted triple-helices(FACIT, e.g. Ⅸ, Ⅻ, ⅩⅣ, ⅩⅥ, ⅩⅨ and ⅩⅫ, these collagens don’t form fibres, but regulate the assembly and size of fibre via the interaction with other collagens), reticular collagens(e.g. Ⅳ, Ⅶ and ⅩⅩⅧ), membrane-associated collagens with interrupted triple-helices(MACITs, e.g. ⅩⅢ, ⅩⅩⅢ and ⅩⅩⅤ, these collagens have specific structural domains which play an important role in biological function).
3. Collagen Protein Synthesis
The biosynthesis of collagen protein includes intracellular and extracellular stages. In nucleus, genetic information of collagen molecules is transcribed to ribosome by mRNA, synthesizing peptide chains containing over 1,000 amino acid residues. These peptide chains enter endoplasmic reticulum(ER) for hydroxylation and glycosylation modification. The modified dissolved collagen proteins form triple helix procollagen and are secreted to outside the cells. Then, they hydrolyze peptide chain on N and C terminal to form protocollagen. Under neutral pH conditions, attraction of charges between molecules automatically polymerize protocollagen to collagenous fiber. The polymerization is unstable and requires for the convention of lysine to allysine, depending on the catalysis of lysine oxidase. Allysine further reacts with histidine to form aldehyde histidine, and finally aldimine condensation with 5-hydroxylysine happens to form schiff base structure. Then, tension and toughness of collagen microfibrils increase. The solubility decreases and insoluble collagen fibers form.
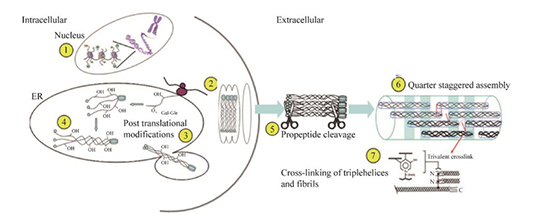
4. Collagen For Medical Applications
Collagen proteins are widely applied in biomedicine, tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Collagen proteins are used as scaffold materials to promote the regeneration of damaged tissue, e.g. repair of skin, cartilage, and skeletal tissue. In beauty products and skin care, collagen proteins can improve the elasticity and tightness of the skin, and decrease wrinkles and fine lines. As the carrier or package of drugs, collagen proteins can control drug release, improving bioavailability, stability, efficacy and safety of drugs. It's reported that overexpression of ECM gene is related to poor prognosis of cancer patients. The TCGA data analysis shows mutation rate of somatic cell in gastric cancer collagen gene is higher than background mutation rate. The mutation of somatic cell in COL7A1 gene can predict survival benefits. Collagen proteins may be effective targets for anti-tumor therapy. The fusion between anti-tumor cytokines(e.g. IL-2, IL-12) and collagen-binding protein lumican can extend the tumor retention time, improving the efficacy of immunotherapy.
5. Recommended Products
5.1. Recombinant Proteins
|
Cat.No |
Product Name |
MW(kDa) |
Host |
|
Recombinant Human COL1A1 |
34.9 kDa |
E.Coli |
|
|
Recombinant Human COL1A2 |
40.3 kDa |
E.Coli |
|
|
Recombinant Human COL2A1 |
48.0 kDa |
E.Coli |
|
|
Recombinant Human COL3A1 |
40.6 kDa |
E.Coli |
|
|
Recombinant Human COL6A1 |
33.2 kDa |
E.Coli |
|
|
Recombinant Human COL6A2 |
44.9 kDa |
E.Coli |
|
|
Recombinant Human COL8A1 |
43.2 kDa |
E.Coli |
|
|
Recombinant Human COL15A1 |
21.7 kDa |
E.Coli |
5.2.Antibodies
|
Cat.No |
Product Name |
MW(kDa) |
Type |
|
Collagen Type I antibody |
|
pAb |
|
|
Collagen Type I antibody |
118 kDa |
pAb |
|
|
Collagen Type II antibody |
141 kDa |
pAb |
|
|
Collagen Type III(N-Terminal) antibody |
140-150 kDa |
pAb |
|
|
Collagen Type III antibody |
140-150 kDa |
pAb |
|
|
Collagen Type IV antibody |
200 kDa |
pAb |
|
|
COL6A1 antibody |
140 kDa |
pAb |
|
|
COL6A2 antibody |
140 kDa |
pAb |
|
|
COL8A1 antibody |
73 kDa |
pAb |
|
|
COL14A1 antibody |
|
pAb |
|
|
COL10A1 antibody |
30 kDa |
pAb |
|
|
COL16A1 antibody |
158 kDa |
pAb |
|
|
COL18A1 antibody |
19 kDa, 27 kDa |
pAb |
|
|
COL23A1 antibody |
70 kDa |
pAb |
5.3. ELISA Kits
|
Cat.No |
Product Name |
Range |
Sensitivity |
|
Human COLI ELISA Kit |
0.313-20ng/ml |
0.188ng/ml |
|
|
Human PINP ELISA Kit |
0.156-10ng/ml |
0.094ng/ml |
|
|
Human COL4 ELISA Kit |
0.781-50ng/ml |
0.469ng/ml |
|
|
Human COL1A1 ELISA Kit |
0.313-20ng/ml |
0.188ng/ml |
|
|
Human COL3 ELISA Kit |
0.625-40ng/ml |
0.375ng/ml |
|
|
Human COL7A1 ELISA Kit |
0.156-10ng/ml |
0.094ng/ml |
|
|
Human PIIINP ELISA Kit |
0.156-10ng/ml |
0.094ng/ml |
|
|
Human COL2 ELISA Kit |
46.875-3000pg/ml |
28.125pg/ml |
|
|
Human ICTP ELISA Kit |
78.125-5000pg/ml |
46.875pg/ml |
|
|
Human COL4 ELISA Kit |
0.156-10ng/ml |
0.094ng/ml |
|
|
Human PICP ELISA Kit |
62.5-4000pg/ml |
37.5pg/ml |
|
|
Human COL2A1 ELISA Kit |
0.625-40ng/ml |
0.375ng/ml |
|
|
Human COL6α1 ELISA Kit |
0.156-10ng/ml |
0.094ng/ml |
|
|
Human COL3A1 ELISA Kit |
31.25-2000pg/ml |
18.75pg/ml |
|
|
Human CTXI ELISA Kit |
0.156-10ng/ml |
0.094ng/ml |
|
|
Human PIVNP ELISA Kit |
0.156-10ng/ml |
0.094ng/ml |
|
|
Human PIICP ELISA Kit |
31.25-2000pg/ml |
18.75pg/ml |
|
|
Human PCOL-I ELISA Kit |
62.5-4000pg/ml |
37.5pg/ml |
|
|
Human COL15A1 ELISA Kit |
0.156-10ng/ml |
0.094ng/ml |
|
|
Human COL28A1 ELISA Kit |
0.156-10pmol/ml |
0.094pmol/ml |
|
|
Human CTXII ELISA Kit |
0.156-10ng/ml |
0.094ng/ml |
|
|
Human COL9A3 ELISA Kit |
31.25-2000pg/ml |
18.75pg/ml |
|
|
Human COL10A1 ELISA Kit |
0.313-20ng/ml |
0.188ng/ml |
|
|
Human PIINP ELISA Kit |
93.75-6000pg/ml |
56.25pg/ml |
|
|
Human COL11α1 ELISA Kit |
39.063-2500pg/ml |
23.438pg/ml |
|
|
Human COL15 ELISA Kit |
0.313-20ng/ml |
0.188ng/ml |
|
|
Human COL6 ELISA Kit |
3.125-200ng/ml |
1.875ng/ml |
|
|
Human PCII ELISA Kit |
0.156-10ng/ml |
0.094ng/ml |
REFERENCES
[1]Collagen type XIV is proportionally lower in the lung tissue of patients with IPF, PMID: 37938243.
[2]Effects of empagliflozin on collagen biomarkers in patients with heart failure: Findings from the EMPEROR trials, PMID: 38037709.
