Abstract: Activity of some endogenous enzyme and other endogenous substances plays an important role in immunohistochemistry. Then, what are causes of background staining or non-specific binding of primary antibody?
Keywords: Immunohistochemical Staining, Non-specific Binding of Antibodies, Immunologic Test
1. Antibody Titration
Higher titer of primary antibody is one of the reasons for background staining. Reasonable antibody titer can produce strong specific signal with low or none background staining. Each kind of antibody should carry out standard titer by chessboard titration. At least, several titer tests are required. Many variables can influence the best primary antibody titer, including incubation time and temperature, antibody retrieval parameters (method, time, temperature, pH, chemical components), buffer (PBS or TBS, pH) and detection method (sensitivity, specificity, time, temperature).
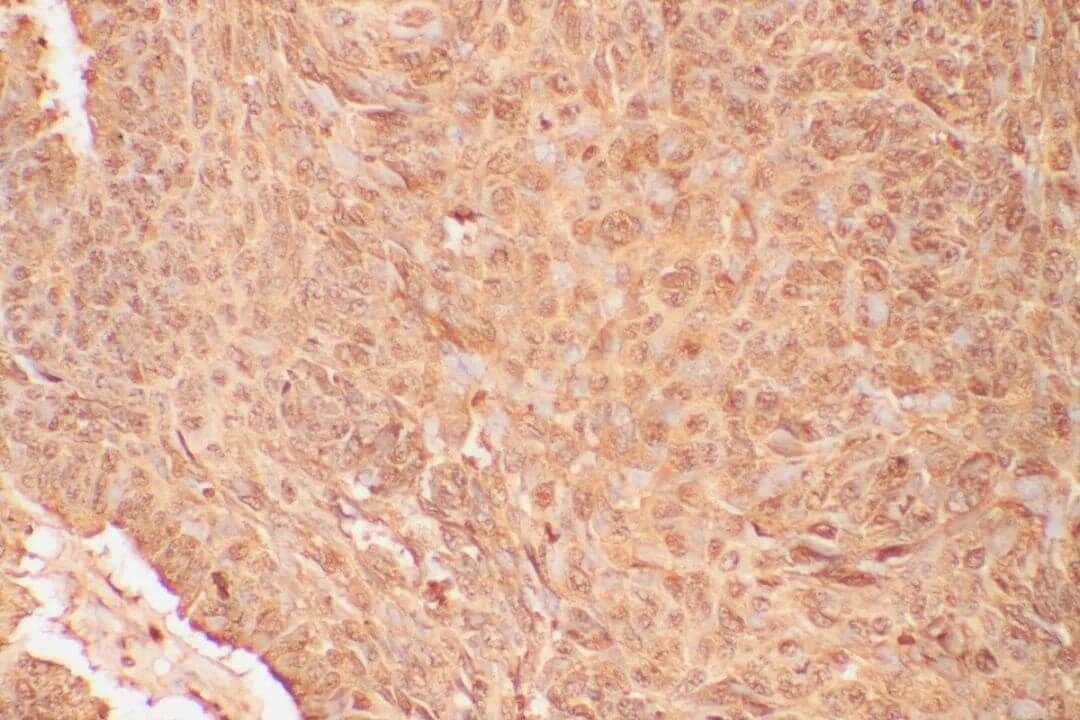
Figure 1. IHC Test for Liver Cancer.
2. Specific Cross Reaction of Antigen
This term defines the specific binding between antibodies with other antigens existing in histiocyte in addition to target antigen. Different cell or tissue has the same antigenic epitope of the antibody. E.g. CD79a monoclonal antibody can not only bind with CD79a molecule on B lymphocyte, but also strongly label smooth muscle cell. CD15 is applied for staining Hodgkin's lymphoma Reed-Sternberg cells. However, there is cross reaction between CD15 antibody and macrophages. A special specific cross reaction is called cross-species reaction. The same antigen (epitope) existing in the cytokeratin or vimentin of multiple species(e.g. dog, cat, horse, anti porcine coronavirus monoclonal antibody can react with ferret/dog/cat/pig coronavirus.) Secondary antibodies in immunohistochemistry may also react with tissue antigen (E.g. Rabbit anti rat second antibody may react with mouse tissue antigen). Using immunoglobulin for the same species of the tissue to be tested adsorbs the second antibody in order to remove the reaction. (E.g. if the rat secondary antibody is used in immunohistochemical staining of mouse tissue, mouse immunoglobulin or serum protein is required for removing the cross-species reaction.)
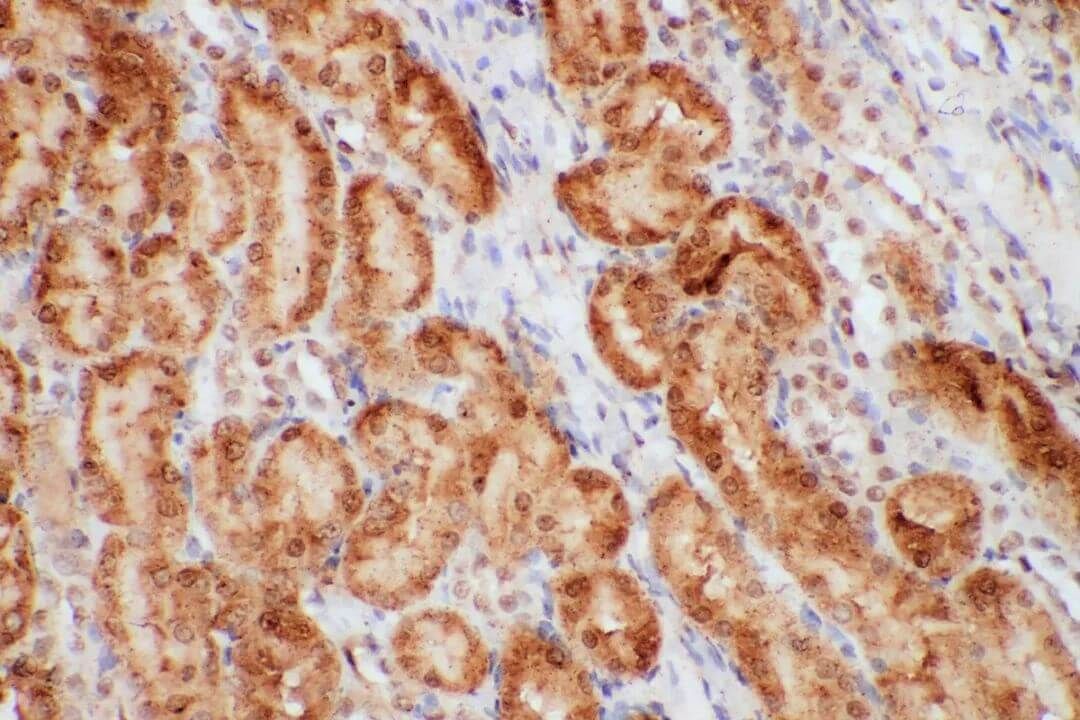
Figure 2. IHC Test for Kidney Cancer(20X).
3. Non-specific Cross Reaction of Antibody
The primary or secondary antibody binds with the irrelevant protein by non immune mechanism. Background can occur by tissue fixation or antigen retrieval resulting in conformational changes of protein.
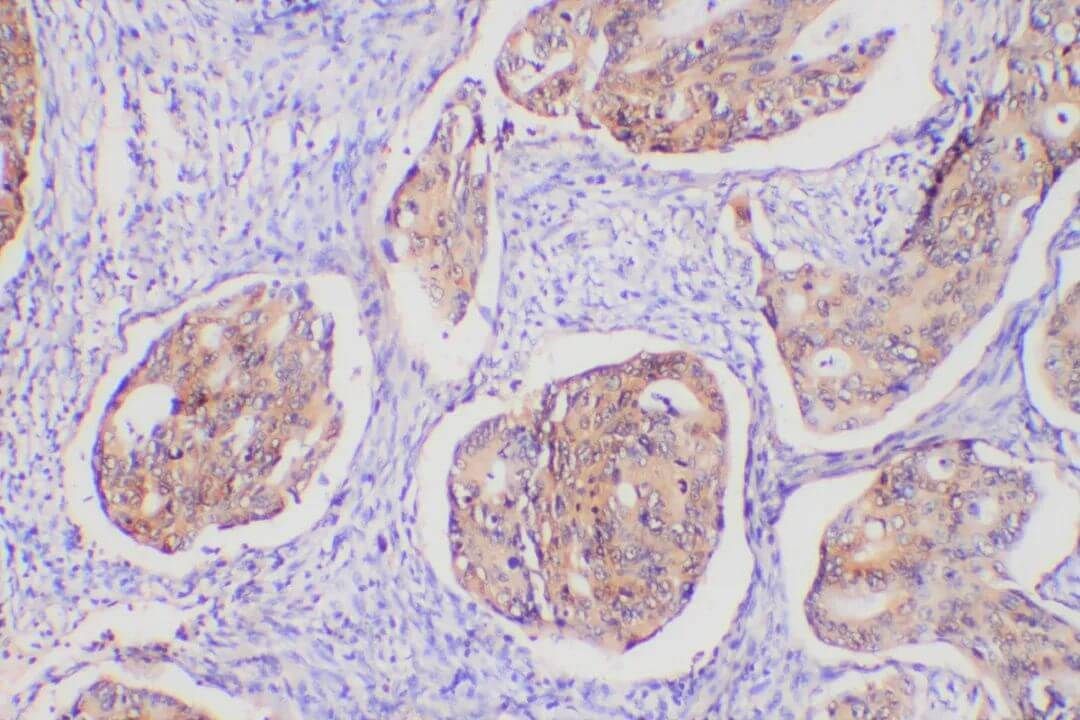
Figure 3. IHC Test for Colon Cancer.
Browse a list of FineTest IHC antibodies.
REFERENCES
Non-specific binding of antibodies in immunohistochemistry: fallacies and facts.
