What is Matrix effect?
Matrix is the substance which is not the target analyte in the sample. Since the matrix components will disturb the analytic process significantly and affect the accuracy of analysis results, researchers called it as matrix effect. This is the problem that should be avoid in the development and use for Elisa kits.
How to estimate the matrix effect?
When a single sample or a small amount of sample value is below the blank value, the reason may be the experimental operation errors, and then the end user should repeat the experiments and improve his operating technique. When there is a lot of sample value that is below the blank value, the end user should consider the matrix effect and then constructing a calibration curve. The reason of matrix effect is complicated, it may be that matrix in the sample has led to the decline of the antigen and antibody combining capacity, and then end user may see that the sample value is below the blank value, and he cannot calculate the sample value or get a negative value.
Though the reason is complicated, we still have some methods to estimate the matrix effect.
The first method is to use the linear dilution. Generally speaking, the combination among antigen, capture antibody and detection antibody is very strong. The sample concentration is diluted and will not influence their combination, the nonspecific binding capacity that cause matrix effects are much weaker. If the end user continues to dilute the sample, the interference of non-specific binding will decrease gradually and the final testing data will be more close to the true value. When there is no matrix effect, no matter how the end user dilutes it, the testing data will be the same with the true value. When there is matrix effect, the dilution will lead to the decrease of non-specific binding, the testing data will also change a lot.
The second method is the incorporation of recovery experiment. The end user can add the low, medium and high concentration of analyte to the determined samples. The ratio of the measured increase in concentration before and after incorporation to the added concentration is the recovery rate, which is presented in the form of percentage.
The recovery rate is about 80-120% which is should meet the standards.
The matrix effect can be eliminated by optimization in the process of product development. Wuhan Fine Biotech Co.; Ltd has optimized its Elisa product R&D. During the ELISA kit development, for the standard, we do not choose human or animal serum and plasma as the diluent of the standard curve; we just use the product imitation. Our customized buffer system with its optimized buffer fluid can eliminate the matrix effect. When the end user tests a certain analyte, if non-specific binding exists in correlation factors or similar structure factors, it will also lead to matrix effect. So we have tested a lot of cross reactions to ensure there is no obvious cross reactions and interference. Our Elisa kits are qualified with strict matrix effect testing, it includes linear dilution, the incorporation of recovery experiment. We have recorded the testing results in the manuals. For more details, please inquire FineTest Company. The FineTest kit components are very stable; the operation is convenient and fast. In the following, it will introduce the FineTest kit features and different methods.
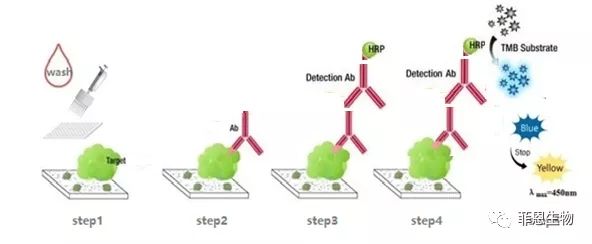
1.Sandwich ELISA, Double Antibody
The microplate in the kit is pre-coated with antibodies. We use the Biotin-coupled antibodies as detection antibody.
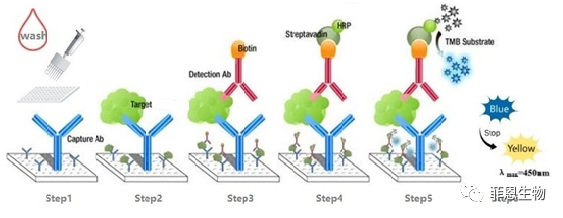
2.Sandwich ELISA, Double Antigen
The microplate in the kit is pre-coated with antigens. We use the Biotin-coupled antigens as detection antibody.
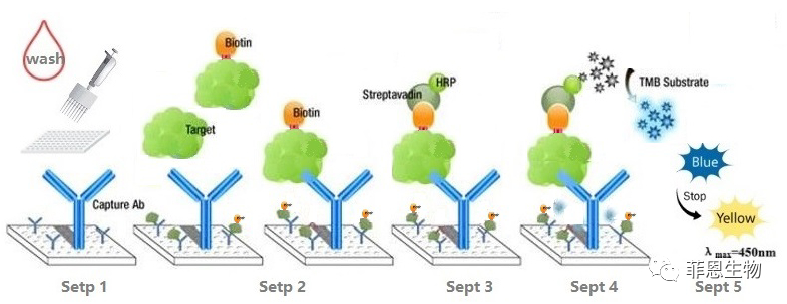
3.Competitive ELISA, Coated with Antibody
The microplate in the kit is pre-coated with antibodies. During the reaction, the target protein in the sample or standard will react with the fixed amount of biotin-labeled antigen to compete and bind with the antibody.
4.Competitive ELISA, Coated with Antigen
The microplate in the kit is pre-coated with antigens. During the reaction, the target antigen in the sample or standard will react with the fixed amount of biotin-labeled antibody to compete and bind with the antigen.
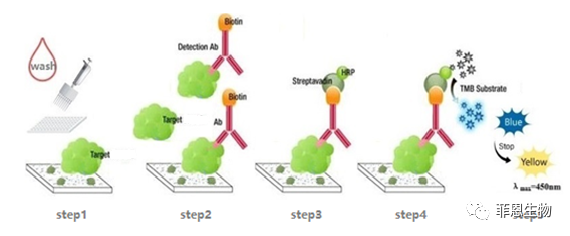
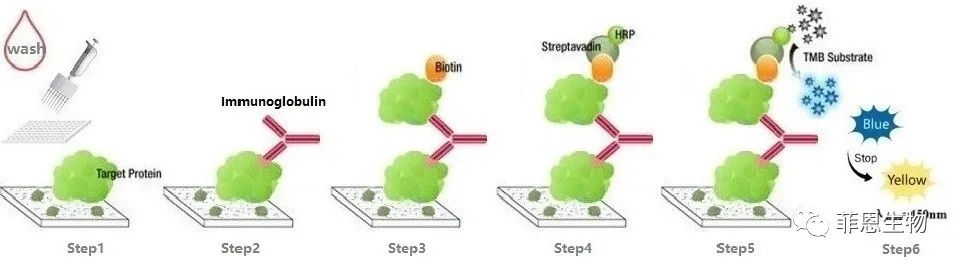
5.Indirect (SABC)
The microplate in the kit is pre-coated with antigens. We use the Biotin-coupled antibody as detection antibody.
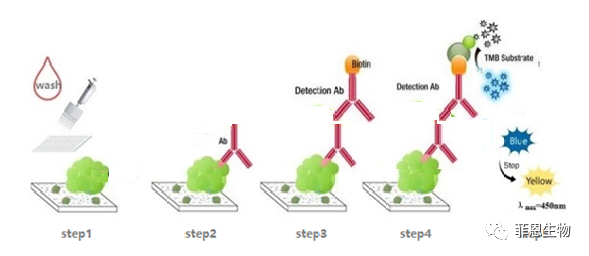
6.Indirect (HRP)
The microplate in the kit is pre-coated with antigens. We use the Biotin-coupled antibody as detection antibody.