Abstract: Three causes for background and non-specific reactions have been previously analyzed, including endogenous enzyme activity, activity of other endogenous substances, non-specific binding of antibodies etc. Now, another cause about intermolecular forces (ionic interaction and hydrophobic interaction) is specified below.
Keywords: Background, Ionic Interaction, Hydrophobic Interaction, Intermolecular Forces
1. Hydrophobic Interaction in Protein
Hydrophobic bonds play an important role in the antigen-antibody binding and can also result in background. After tissues are fixed by aldehyde fixatives, crosslinking reaction occurs between active ε- amino acid and α- amino acid in surrounding tissue protein. The reaction makes hydrophobic bonds of tissue protein and background staining during immunohistochemical process stronger. Hence, fixation time for other aldehyde fixatives or formalin-fixed tissues should not be too long. The background staining caused by excessive fixation can be solved by post fixation using Bouin's、Zenker's or B5 solution etc. Immunoglobulin is the protein with strong hydrophobicity as well, especially IgG1 and IgG3 antibodies. During the storage of antibodies, aggregation and polycondensation of immunoglobulin makes hydrophobicity stronger. Conjugates and protein-protein interaction of polar group in tissue slices can produce background.
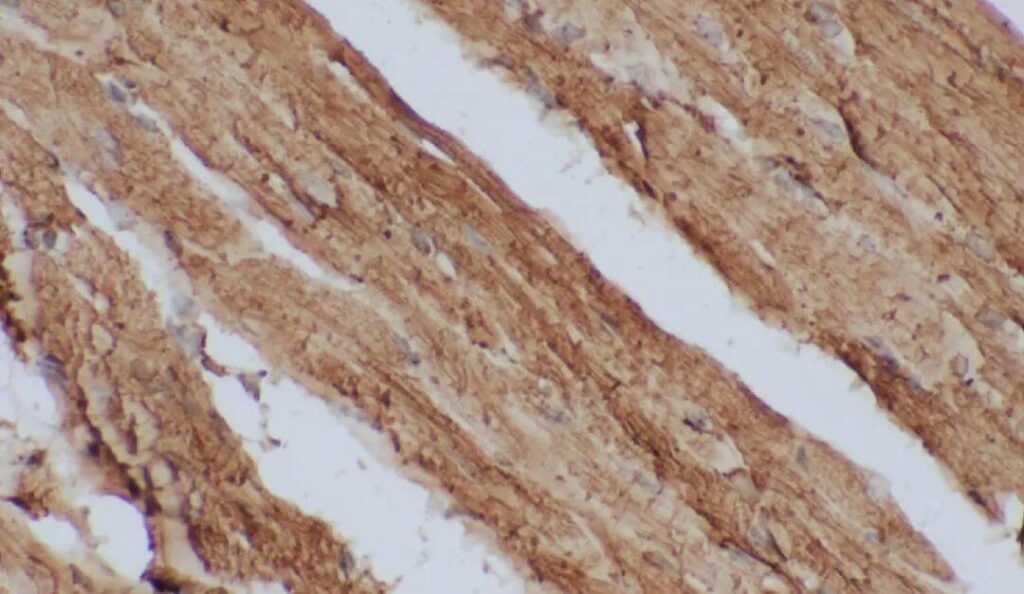
Figure 1. IHC Test for Rat Myocardial Tissue.
Currently, there are several methods for decreasing hydrophobic binding of immunoglobulin and tissue protein, such as dilution buffer with different pH and antibody isoelectric point(especially suitable for monoclonal antibodies), low ionic strength buffer(low ion concentration), nonionic detergent(e.g. Tween 20、Triton X or ethylene glycol) added in the buffer to improve pH(suitable for polyclonal antibodies). However, the most commonly used method for decreasing background staining caused by hydrophobic interaction is to use blocking protein to block slices before adding primary antibodies. The classical protein is the immunoglobulin having the same species of labeled second antibody used in immunostaining. Besides, bovine serum albumin, fish gelatin, fetal bovine serum, skimmed milk powder and casein are also applicable. Casein is more efficient than normal serum in blocking hydrophobic background staining.
2. Ionic Interaction
Ionic interaction is one of the main forces for antigen-antibody binding and also related to non-specific background staining. The isoelectric point of most antibodies is between 5.8-8.5. In the normal buffer pH condition, antibodies may carry net negative surface charges or net positive surface charges. If the tissue protein carries the opposite surface charge, ionic interaction will occur between immunoglobulin and tissue protein. It's important to balance dilution buffer to room temperature in order to prevent opposite net charge. The dilution buffer with high ionic strength can efficiently prevent non-immune binding between immunoglobulin with the tissue or cell(e.g. endothelium, collagen etc) with negative charge. People gradually realize non-specific staining is caused by combined effects of ionic interaction and hydrophobic interaction in many cases. There is a restrictive relation on modifications between different factors. Hence, it's complicated to solve this kind of non-specific background staining.
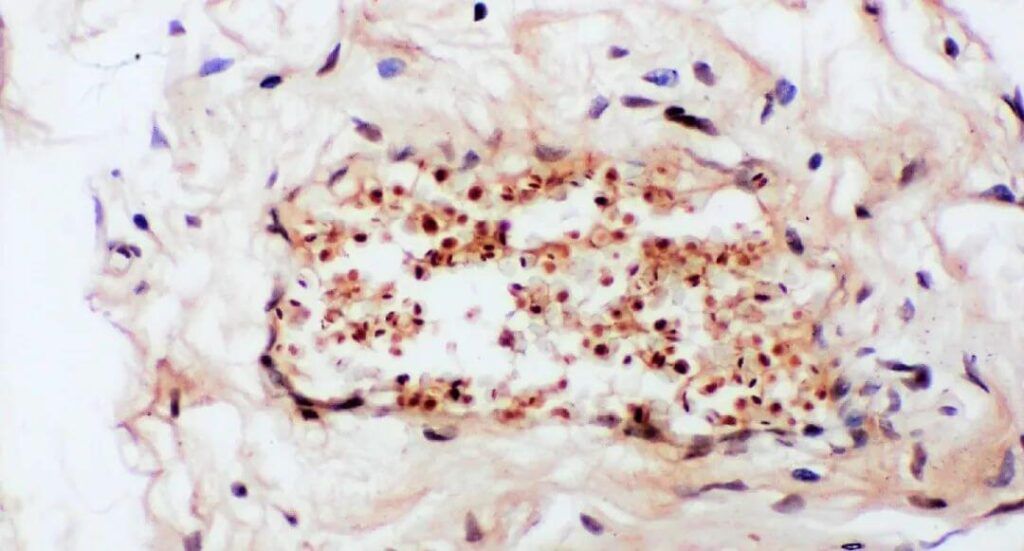
Figure 2. IHC Test for Human Cervical Cancer Tissue.
3. FineTest IHC Products
Browse a list of FineTest IHC products.
