Abstract: In immunohistochemistry test, the most common questions are influences of background and how to explain experimental result. There are many reasons for background staining. Two main reasons are specified in this article: endogenous enzyme activity and activity of other endogenous substances.
Keywords: Immunohistochemistry Test, Immunostaining, Enzymology
1. Endogenous Enzyme Activity
1.1. Endogenous Peroxidase Activity
Endogenous peroxidase activity naturally exists in in erythrocytes(pseudoperoxidase), granulocytes(myeloperoxidase) and neurons. It can react with DAB to produce brown products and are hard to be distinguished from specific immunostaining. Pretreatment with H2O2 dilution(0.03%-3%, including 0.1% sodium azide) can reduce or remove pseudoperoxidase activity of frozen sections of erythrocytes and peroxidase activity of myeloid cells. Regular paraffin-embedded tissue slices and hemin slices with massive haemorrhage or acidity require higher concentration H2O2(3% H2O2 solution and 0.1% sodium azide). Alternatively, the endogenous enzyme activity can be removed by extending incubation time in lower concentration solution. H2O2-methanol is not recommended for regular use, especially for testing cell surface antigens.
Methanol has a bad influence on antigenicity and immunoreactivity. We should avoid to use it. However, when using H2O2-methanol, the incubation time should be within 15min.
1.2. Endogenous Alkaline Phosphatase(AP)
Alkaline phosphatase in mammalian tissues has intestinal or non-intestinal isozyme. The background staining will happen in the alkaline phosphatase method. 1mmol/L levamisole can inhibit non-intestinal alkaline phosphatase isozyme. However, isoenzyms of bovine intestinal alkaline phosphatase is unaffected as a reporter in alkaline phosphatase immunostaining method. 1% acetic acid can block the isozyme but destroy some antigens at the same time.
2. Activity of Other Endogenous Substances
2.1. Endogenous Avidin/Biotin Activity
Endogenous biotin widely exists in mammalian tissues and especially is rich in tissues like liver, lung, spleen, adipose tissue, kidney, brain etc. After the fixation of the tissue by formalin, background caused by endogenous biotin greatly decreases but increases in frozen sections. Strong ionic strength of alkaline avidin has high adsorption capacity for cellular molecules with opposite charges and non specific binding occurs, E.g.: glycosaminoglycans(GAGs) in nucleic acids, phospholipids, mast cell cytoplasm. The isoelectric point of avidin is 10. Avidin is alkaline in immunostaining buffer with pH close to neutrality and carries a positive charge. The strong heat-induced antigen retrieval will get endogenous biotin in the formalin-fixed tissue exposed. However, avidin in the detection system can bind with it and present strong background required for inhibition. Preparing avidin-biotin complex (ABC) by pH9.4 biotinylated solution can prevent the non-immune binding.
2.2. Endogenous Immunoglobulin Activity
In immunohistochemistry, the binding between the primary antibody and immunoglobulin on the tissue surface can cause background. Before the incubation of the primary antibody, the non-specific blocking reagent should be used, E.g.: 5% bovine serum albumin(BSA) can block the binding between the primary antibody and non-specific antigen in the tissue.
3. IHC Test Results by FineTest Products
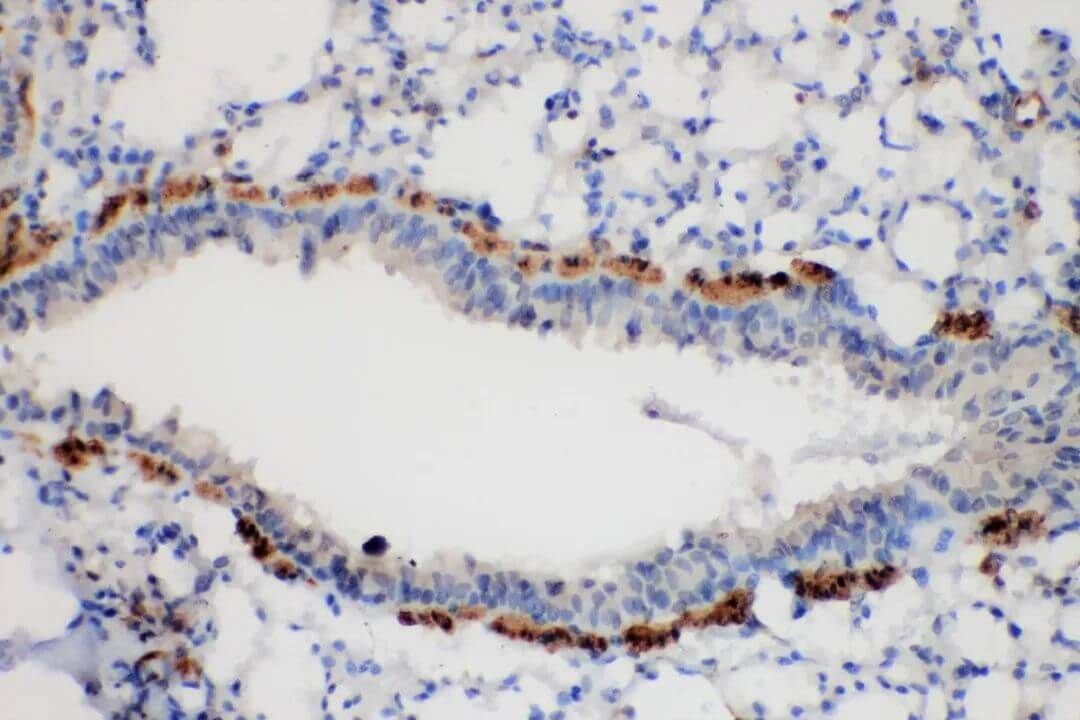
Figure 1. lung cancer 20x cyt+++.
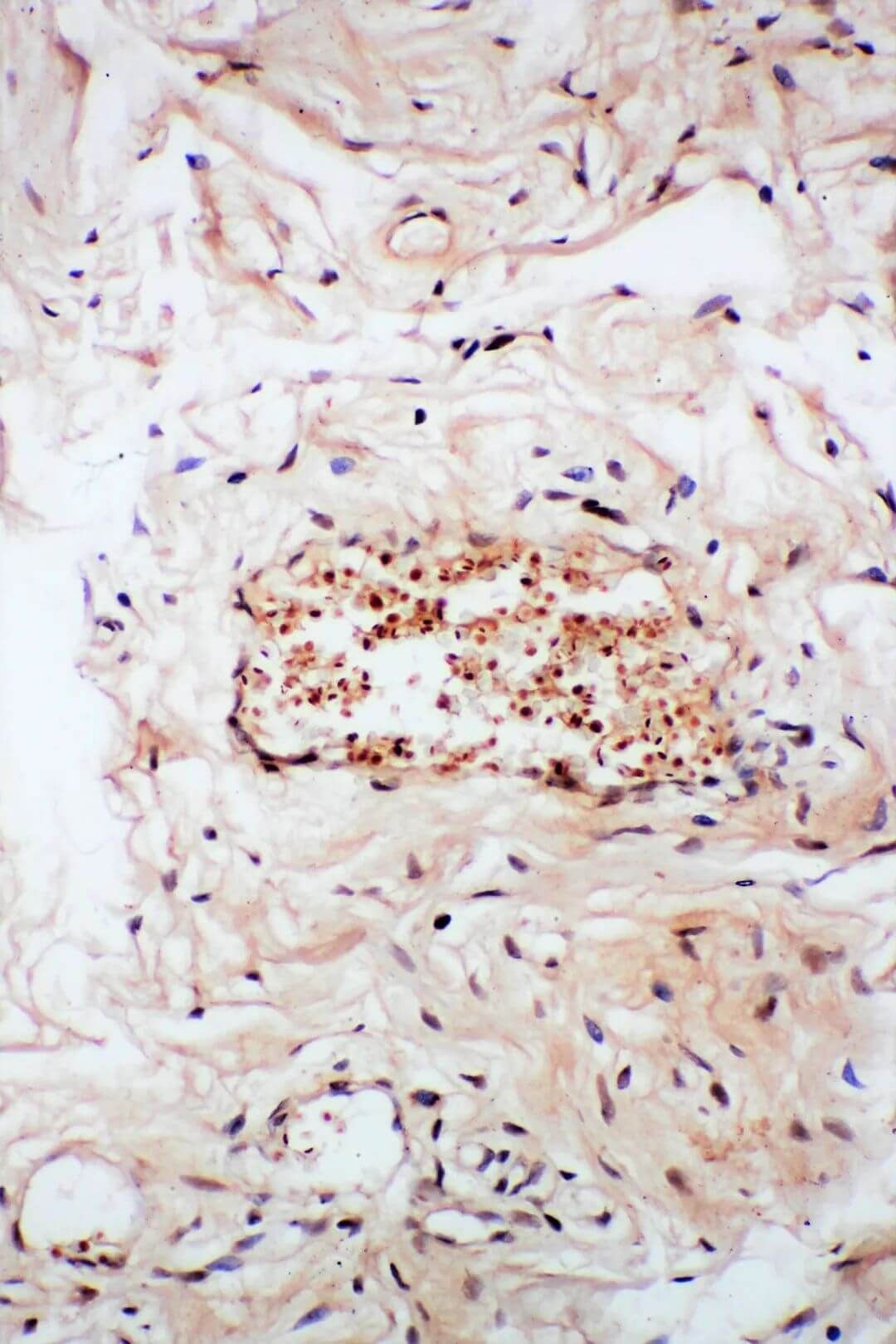
Figure 2. cervical carcinoma 20x.
Browse a list of FineTest IHC Products.
