FineTest ELISA kit contributes to the research on oxidative stress and osteoporosis. The immunoassay is designed to measure 4-HNE level in supernatant.
Article Title: Regulation of enzymatic lipid peroxidation in osteoblasts protects against postmenopausal osteoporosis
Journal Title: Nature Communications
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-55929-4
IF: 14.7
PMID: 39824794
Abstract: Oxidative stress plays a critical role in postmenopausal osteoporosis, yet its impact on osteoblasts remains underexplored, limiting therapeutic advances. Our study identifies phospholipid peroxidation in osteoblasts as a key feature of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Estrogen regulates the transcription of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), an enzyme crucial for reducing phospholipid peroxides in osteoblasts. The deficiency of estrogen reduces GPX4 expression and increases phospholipid peroxidation in osteoblasts. Inhibition or knockout of GPX4 impairs osteoblastogenesis, while the elimination of phospholipid peroxides rescues bone formation and mitigates osteoporosis. Mechanistically, 4-hydroxynonenal, an end-product of phospholipid peroxidation, binds to integrin-linked kinase and triggers its protein degradation, disrupting RUNX2 signaling and inhibiting osteoblastogenesis. Importantly, we identified two natural allosteric activators of GPX4, 6- and 8-Gingerols, which promote osteoblastogenesis and demonstrate anti-osteoporotic effects. Our findings highlight the detrimental role of phospholipid peroxidation in osteoblastogenesis and underscore GPX4 as a promising therapeutic target for osteoporosis treatment.
Keywords: Lipid peroxides, Drug effects, Metabolism, Oxidative stress, Signal transduction
Immunoassay
| FineTest Product | Sample | Species | Detection Target |
| Mouse 4-HNE(4-Hydroxynonenal) ELISA Kit(EM1583) | supernatant | Mouse | 4-HNE |
Validated Image
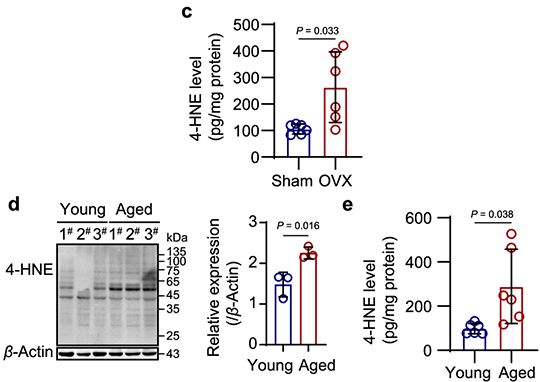
Figure Source: Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 17;16(1):758. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-55929-4.
