FineTest Elisa kit contributes to the research on immunotherapy for breast cancer. The immunoassay is designed to measure C3a concentration in lung homogenate supernatant.
Publication Details
Article Title: Chemotherapy-induced complement signaling modulates immunosuppression and metastatic relapse in breast cancer
Journal Title: Nature Communications
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33598-x
IF: 17.694
PMID: 36184683
Abstract: Mortality from breast cancer is almost exclusively a result of tumor metastasis and resistance to therapy and therefore understanding the underlying mechanisms is an urgent challenge. Chemotherapy, routinely used to treat breast cancer, induces extensive tissue damage, eliciting an inflammatory response that may hinder efficacy and promote metastatic relapse. Here we show that systemic treatment with doxorubicin, but not cisplatin, following resection of a triple-negative breast tumor induces the expression of complement factors in lung fibroblasts and modulates an immunosuppressive metastatic niche that supports lung metastasis. Complement signaling derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) mediates the recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) to the metastatic niche, thus promoting T cell dysfunction. Pharmacological targeting of complement signaling in combination with chemotherapy alleviates immune dysregulation and attenuates lung metastasis. Our findings suggest that combining cytotoxic treatment with blockade of complement signaling in triple-negative breast cancer patients may attenuate the adverse effects of chemotherapy, thus offering a promising approach for clinical use.
Keywords: Chemotherapy, Breast Neoplasms, Immunosuppression Therapy, Lung Neoplasms, Tumor Microenvironment, Drug Safety
Immunoassay
| FineTest Product | Sample | Detection Target | Species |
| Mouse C3a(Complement Component 3a) ELISA Kit(EM0882) | lung homogenate supernatant | C3a | Mouse |
Validated Image
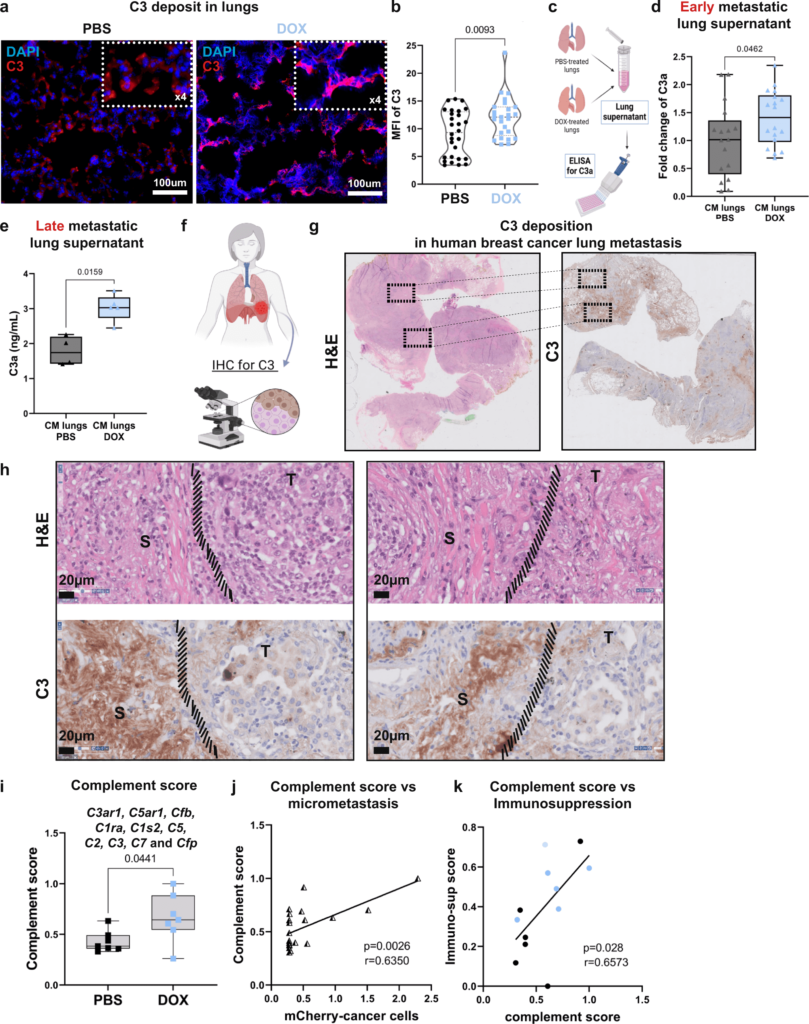
Figure Source: Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 2;13(1):5797. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33598-x.
Fig. 6: Activation of complement signaling in lungs is associated with infiltration of C3aR and C5aR1 expressing MDSCs.
