Products
TNFSF11 antibody
Category:
Research Area:
| Synonyms: | Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11|Osteoclast differentiation factor (ODF)|Osteoprotegerin ligand (OPGL)|Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL)|TNF-related activation-induced cytokine (TRANCE)|Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11 antibody, membrane form|Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11 antibody, soluble form|TNFSF11|OPGL|RANKL|TRANCE antibody | ||
| Catalogue No.: | FNab09838 | Reactivity: | Human |
| Host: | Mouse | Tested Application: | ELISA, WB |
| Clonality: | monoclonal | Isotype: | IgG1 |
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- TNFSF11 antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab09838
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Protein A+G purification
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- monoclonal
- Isotype
- IgG1
- Clone ID
- 4F11
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11
- Alternative Names
- Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11|Osteoclast differentiation factor (ODF)|Osteoprotegerin ligand (OPGL)|Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand (RANKL)|TNF-related activation-induced cytokine (TRANCE)|Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11 antibody, membrane form|Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11 antibody, soluble form|TNFSF11|OPGL|RANKL|TRANCE antibody
- UniProt ID
- O14788
- Observed MW
- 35 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:1000-1:5000
Validated Images
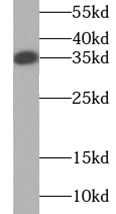 Hela cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab09838(RANKL antibody) at dilution of 1:3000
Hela cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab09838(RANKL antibody) at dilution of 1:3000
- Background
- TNFSF11 also known as RANKL, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) cytokine family which is a ligand for osteoprotegerin and functions as a key factor for osteoclast differentiation and activation. RANKL induces osteoclast formation through its receptor, RANK, which transduces signals by recruiting adaptor molecules, such as the TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF) family of proteins. RANKL was shown to be a dentritic cell survival factor and is involved in the regulation of T cell-dependent immune response. T cell activation was reported to induce expression of this gene and lead to an increase of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss. RANKL was shown to activate antiapoptotic kinase AKT/PKB through a signaling complex involving SRC kinase and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6, which indicated this protein may have a role in the regulation of cell apoptosis.



