Products
IVNS1ABP antibody
Category:
Research Area:
| Synonyms: | Influenza virus NS1A-binding protein (NS1-BP antibody, NS1-binding protein)|Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-associated protein 3|Kelch-like protein 39|IVNS1ABP|ARA3|FLARA3|KIAA0850|KLHL39|NS1|NS1BP antibody | ||
| Catalogue No.: | FNab04428 | Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host: | Rabbit | Tested Application: | ELISA, WB, IHC |
| Clonality: | polyclonal | Isotype: | IgG |
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- IVNS1ABP antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab04428
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Immunogen affinity purified
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Isotype
- IgG
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- influenza virus NS1A binding protein
- Alternative Names
- Influenza virus NS1A-binding protein (NS1-BP antibody, NS1-binding protein)|Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-associated protein 3|Kelch-like protein 39|IVNS1ABP|ARA3|FLARA3|KIAA0850|KLHL39|NS1|NS1BP antibody
- UniProt ID
- Q9Y6Y0
- Observed MW
- 70 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500-1:2000; IHC: 1:20-1:200
Validated Images
 mouse heart tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab04428(IVNS1ABP antibody) at dilution of 1:800
mouse heart tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab04428(IVNS1ABP antibody) at dilution of 1:800
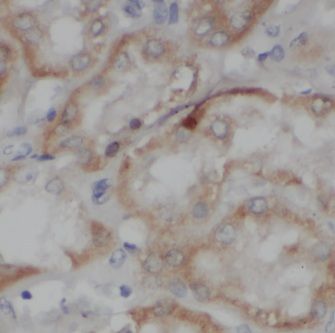 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human kidney using FNab04428(IVNS1ABP antibody) at dilution of 1:100
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human kidney using FNab04428(IVNS1ABP antibody) at dilution of 1:100
- Background
- Plays a role in cell division and in the dynamic organization of the actin skeleton as a stabilizer of actin filaments by association with F-actin through Kelch repeats. Protects cells from cell death induced by actin destabilization; Protects neurons from dendritic spines and actin filaments damage induced by the actin-destabilizing cytochalasin B when overexpressed. Activates Erk signaling pathway when overexpressed in cultured cell lines(By similarity). May be a component of the cellular splicing machinery with a role in pre-mRNA splicing; may mediate the inhibition of splicing by NS/influenza virus NS1A protein. Functions as modifier of the AHR/Aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway increasing the concentration of AHR available to activate transcription.



