Products
HNRNPK antibody
Category:
Research Area:
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- HNRNPK antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab03955
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Immunogen affinity purified
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Isotype
- IgG
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K
- Alternative Names
- Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K)|Transformation up-regulated nuclear protein (TUNP)|HNRNPK|HNRPK antibody
- UniProt ID
- P61978
- Observed MW
- 51 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500-1:2000; IHC: 1:50-1:200; IF: 1:10-1:100
Validated Images
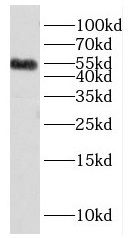 HeLa cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab03955(HNRNPK antibody) at dilution of 1:300
HeLa cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab03955(HNRNPK antibody) at dilution of 1:300
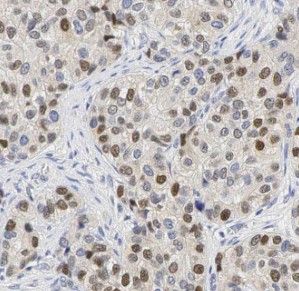 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer using FNab03955(HNRNPK antibody) at dilution of 1:50
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer using FNab03955(HNRNPK antibody) at dilution of 1:50
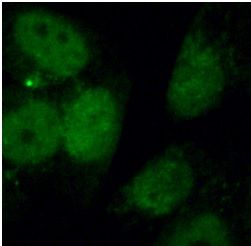 Immunofluorescent analysis of HepG2 cells using FNab03955(HNRNPK antibody) at dilution of 1:50 and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L)
Immunofluorescent analysis of HepG2 cells using FNab03955(HNRNPK antibody) at dilution of 1:50 and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L)
- Background
- One of the major pre-mRNA-binding proteins. Binds tenaciously to poly(C) sequences. Likely to play a role in the nuclear metabolism of hnRNAs, particularly for pre-mRNAs that contain cytidine-rich sequences. Can also bind poly(C) single-stranded DNA. Plays an important role in p53/TP53 response to DNA damage, acting at the level of both transcription activation and repression. When sumoylated, acts as a transcriptional coactivator of p53/TP53, playing a role in p21/CDKN1A and 14-3-3 sigma/SFN induction(By similarity). As far as transcription repression is concerned, acts by interacting with long intergenic RNA p21(lincRNA-p21), a non-coding RNA induced by p53/TP53. This interaction is necessary for the induction of apoptosis, but not cell cycle arrest.



