Products
PKC gamma antibody
Category:
Research Area:
| Synonyms: | PKC gamma antibody, PKCC antibody, PKCG antibody, PRKCG antibody, Protein kinase C gamma type antibody, protein kinase C antibody, gamma antibody, SCA14 antibody | ||
| Catalogue No.: | FNab06485 | Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host: | Rabbit | Tested Application: | ELISA, WB, IHC, FC, IP |
| Clonality: | polyclonal | Isotype: | IgG |
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- PKC gamma antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab06485
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Immunogen affinity purified
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Isotype
- IgG
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- protein kinase C, gamma
- Alternative Names
- PKC gamma antibody, PKCC antibody, PKCG antibody, PRKCG antibody, Protein kinase C gamma type antibody, protein kinase C antibody, gamma antibody, SCA14 antibody
- UniProt ID
- P05129
- Observed MW
- 78 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC, FC, IP
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500-1:5000; IP: 1:200-1:2000; IHC: 1:20-1:200; IF: 1:50-1:500
Validated Images
 human brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab06485(PRKCG antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
human brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab06485(PRKCG antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
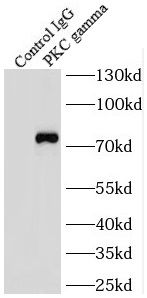 IP Result of anti-PKC gamma (IP:FNab06485, 4ug; Detection:FNab06485 1:500) with mouse brain tissue lysate 2640ug.
IP Result of anti-PKC gamma (IP:FNab06485, 4ug; Detection:FNab06485 1:500) with mouse brain tissue lysate 2640ug.
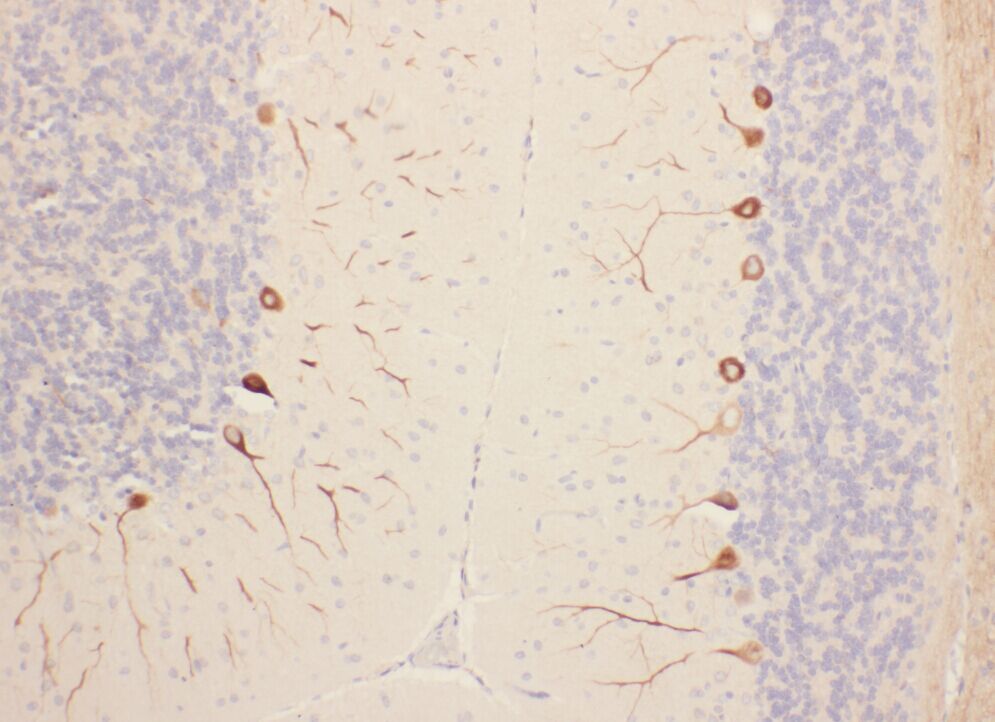 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human cerebellum tissue slide using FNab06485(PRKCG Antibody) at dilution of 1:200
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human cerebellum tissue slide using FNab06485(PRKCG Antibody) at dilution of 1:200
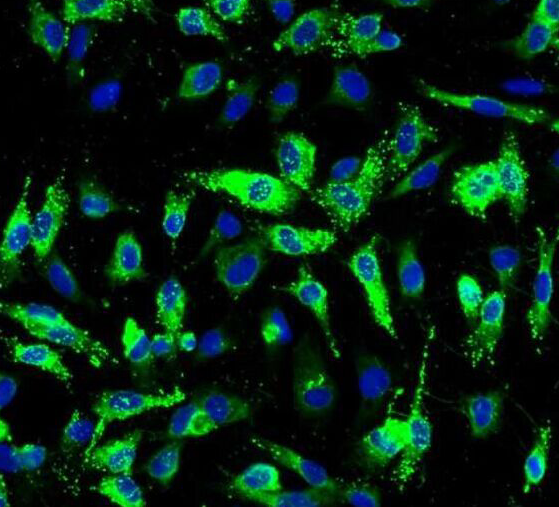 Immunofluorescent analysis of ( -20℃ Ethanol ) fixed HeLa cells using FNab06485( PRKCG Antibody) at dilution of 1:50 and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L)
Immunofluorescent analysis of ( -20℃ Ethanol ) fixed HeLa cells using FNab06485( PRKCG Antibody) at dilution of 1:50 and Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L)
- Background
- Protein kinase C(PKC) is a family of serine-and threonine-specific protein kinases that can be activated by calcium and second messenger diacylglycerol. PKC family members phosphorylate a wide variety of protein targets and are known to be involved in diverse cellular signaling pathways. PKC gamma is a neuron-specific member of the classical PKCs and is activated and translocated to subcellular regions as a result of various stimuli, including diacylglycerol synthesis, increased intracellular Ca(2+) and phorbol esters. Defects in this protein have been associated with spinocerebellar ataxia type 14(SCA14), an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease.



