Abstract: Role of Tnf Alpha in cancer can kill and inhibit cytokines of tumor cells. As the important inflammatory mediator, it’s involved in pathologic injury of some autoimmune diseases and promotions for neutrophil phagocytosis, anti-infection against fever, hepatic acute phase protein synthesis, differentiation of myeloid leukemia cell into macrophage, cell proliferation and differentiation etc.
Keywords: Tnf Alpha, Cytokine, Inflammation, Cancer Research
1. Function of Tnf Alpha
1.1. Tnf Alpha Inhibitors Cancer
TNF-α can kill some tumor cells in vivo and in vitro or inhibit proliferative effect. Tumor cell lines have great sensitive differences on TNF-α. TNF-α even stimulates a very few tumor cells. The killing efficacy of TNF-α against cellular activity can be obviously improved when tumor cells(e.g. mouse fibroblast cell line) are treated by dactinomycin and mitomycin C. Tumors in vivo also have different effects on TNF-α and are not parallelled with the sensitivity of cells in vitro to TNF-α. The same cell line may contain sensitive and drug-resistant strains(e.g. L929-S and L929-R). Besides, the expression of endogenous TNF-α in target cells may resist the cytotoxicity of exogenous TNF. Thus, the sensitivity of cells to exogenous TNF can be changed by inducing or inhibiting the expression of exogenous TNF. Macrophage membrane-bound TNF may be involved in killing target cells.
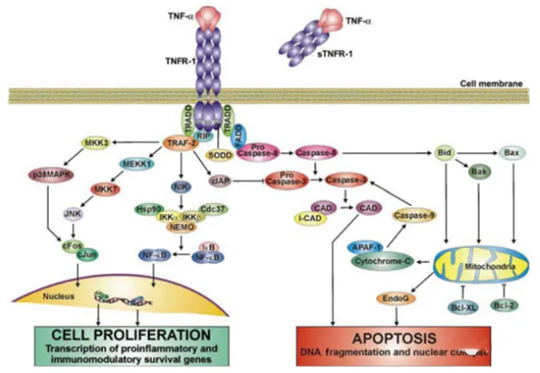
1.2. Anti-infection
TNF-α can kill virus-infected cells via increasing neutrophil phagocytosis, inhibiting influenza virus replication and protein synthesis, and fever against anti-infection.
1.3. Regulation of Immune Function
TNF-α can regulate some functions of immune cells. When patients suffer from some autoimmune diseases(e.g. lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome, nephritis etc.), the level of TNF-α increases.
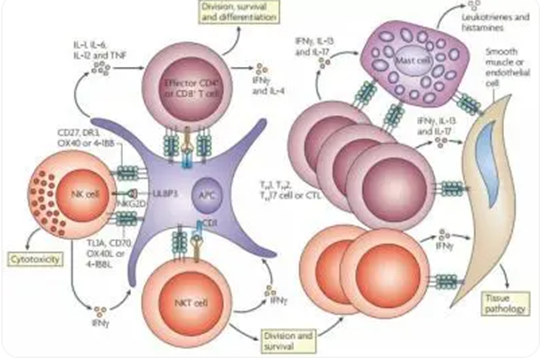
2. Tnf Alpha and Inflammation
2.1. Septic Shock
Disseminated intravascular coagulation and toxic shock caused by Gram-negative bacilli or meningococcus is stimulated by bacterial endotoxin to produce excessive TNF-α, resulting in fever, severe cardiac and adrenal damage, respiratory circulation failure and even death. The TNF level is positively correlated to case fatality rate. The possible pathogeny may be the tnf-stimulated endothelial cell resulting in inflammation, tissue damage and coagulation. TNF is also the important factor of acute hepatic necrosis. Viral fulminant hepatic failure peripheral blood cells induce TNF. The activity of IL-1 increases and is related to illness severity. Currently, the mechanism of TNF mediated endotoxic shock remains unclear. It's reported that TNF can promote the formation of prothrombin active substance, and inhibit the regulation of toxin shock by endothelial cell thrombin. TNF antibody (anti-serum or monoclonal antibody) effectively prevents fatal endotoxic shock in the body of mice, rabbits, and baboons.
2.2. Dyscrasia
TNF-α is also called cachectin and can induce the production of dyscrasia in the organism.
2.3. Relationship between TNF and Virus Replication
TNF also has the antivirus effect similar to IFN and inhibits virus replication via preventing the synthesis of early viral protein. TNF works together with TNF-α and TNF-γ to fight against virus. In the other hand, TNF induces the expression of HIV-Ⅰ gene in T cell. Activate or induce NF-κB in TNF and HIV infected CD4+ cells. NF-κB binds with the enhancer site of HIV LTR. The activated HIV gene may be related to HIV incidence. The production of TNF-α in the monocyte of AIDS patients increases. The level of TNF-α in the serum increases. Besides, TNF also has the antibacterial and antimalarial effect.
3. Recommended ELISA Kits
- [EH1488]Human ADAM17(Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 17) ELISA Kit
- [EH4080]Human anti-TNF-α Antibody(Anti Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Antibody) ELISA Kit
- [EM0183-HS]Mouse TNF-α(High sensitive Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha)ELISA Kit
- [EH0302-HS]Human HS-TNF-α(High sensitive Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit
- [EH0302]Human TNF-α(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit
- [ER1393]Rat TNF-α(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit
- [EM0183]Mouse TNF-α(Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha) ELISA Kit
REFERENCES
[1]The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) Polymorphisms in Gastric Cancer: a Meta-Analysis, PMID: 34478034.
[2]Investigation of TNF-α and IL-6 Levels in the Sera of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer Patients, PMID: 33461943.
