Products
PSMA7 antibody
Category:
Research Area:
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- PSMA7 antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab06866
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Immunogen affinity purified
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Isotype
- IgG
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- proteasome(prosome, macropain) subunit, alpha type, 7
- Alternative Names
- HSPC antibody
- UniProt ID
- O14818
- Observed MW
- 28-30 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC, FC, IP
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500-1:2000; IP: 1:200-1:1000; IHC: 1:20-1:200
Validated Images
 HeLa cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab06866(PSMA7 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
HeLa cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab06866(PSMA7 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
 IP Result of anti-PSMA7 (IP:FNab06866, 4ug; Detection:FNab06866 1:500) with mouse brain tissue lysate 4000ug.
IP Result of anti-PSMA7 (IP:FNab06866, 4ug; Detection:FNab06866 1:500) with mouse brain tissue lysate 4000ug.
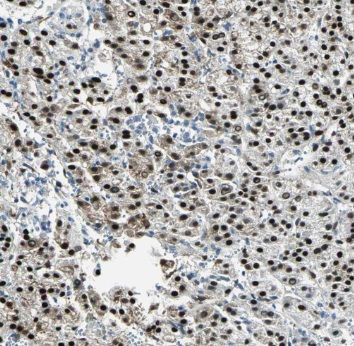 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver cancer using FNab06866(PSMA7 antibody) at dilution of 1:50
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver cancer using FNab06866(PSMA7 antibody) at dilution of 1:50
- Background
- The proteasome is a multicatalytic proteinase complex which is characterized by its ability to cleave peptides with Arg, Phe, Tyr, Leu, and Glu adjacent to the leaving group at neutral or slightly basic pH. The proteasome has an ATP-dependent proteolytic activity. Plays an important role in the regulation of cell proliferation or cell cycle control, transcriptional regulation, immune and stress response, cell differentiation, and apoptosis. Interacts with some important proteins involved in transcription factor regulation, cell cycle transition, viral replication and even tumor initiation and progression. Inhibits the transactivation function of HIF-1A under both normoxic and hypoxia-mimicking conditions. The interaction with EMAP2 increases the proteasome-mediated HIF-1A degradation under the hypoxic conditions. Plays a role in hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation. Mediates nuclear translocation of the androgen receptor(AR) and thereby enhances androgen-mediated transactivation. Promotes MAVS degradation and thereby negatively regulates MAVS-mediated innate immune response.



