Products
PPP1CC antibody
Category:
Research Area:
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- PPP1CC antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab06697
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Immunogen affinity purified
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Isotype
- IgG
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- protein phosphatase 1, catalytic subunit, gamma isoform
- UniProt ID
- P36873
- Observed MW
- 35 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, IP
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500-1:2000; IP: 1:200-1:1000; IHC: 1:20-1:200; IF: 1:20-1:200
Validated Images
 MCF7 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab06697(PPP1CC antibody) at dilution of 1:300
MCF7 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab06697(PPP1CC antibody) at dilution of 1:300
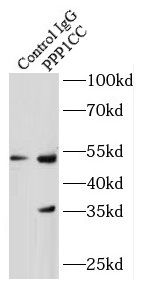 IP Result of anti-PPP1CC (IP:FNab06697, 4ug; Detection:FNab06697 1:500) with HEK-293 cells lysate 2000ug.
IP Result of anti-PPP1CC (IP:FNab06697, 4ug; Detection:FNab06697 1:500) with HEK-293 cells lysate 2000ug.
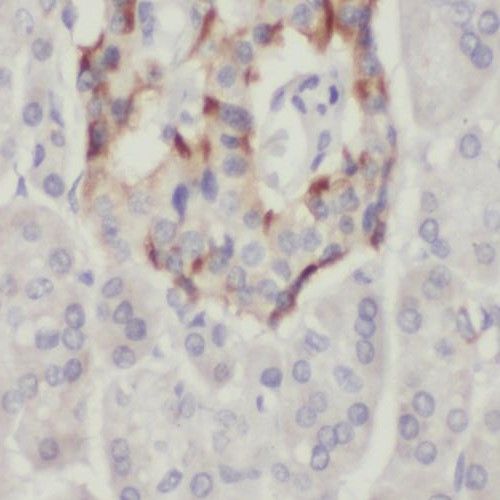 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human pancreas cancer using FNab06697(PPP1CC antibody) at dilution of 1:100
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human pancreas cancer using FNab06697(PPP1CC antibody) at dilution of 1:100
- Background
- Protein phosphatase that associates with over 200 regulatory proteins to form highly specific holoenzymes which dephosphorylate hundreds of biological targets. Protein phosphatase 1(PP1) is essential for cell division, and participates in the regulation of glycogen metabolism, muscle contractility and protein synthesis. Dephosphorylates RPS6KB1. Involved in regulation of ionic conductances and long-term synaptic plasticity. May play an important role in dephosphorylating substrates such as the postsynaptic density-associated Ca(2+)/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II. Component of the PTW/PP1 phosphatase complex, which plays a role in the control of chromatin structure and cell cycle progression during the transition from mitosis into interphase. In balance with CSNK1D and CSNK1E, determines the circadian period length, through the regulation of the speed and rhythmicity of PER1 and PER2 phosphorylation. May dephosphorylate CSNK1D and CSNK1E. Dephosphorylates the 'Ser-418' residue of FOXP3 in regulatory T-cells(Treg) from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, thereby inactivating FOXP3 and rendering Treg cells functionally defective(PubMed:23396208).



