Products
MUL1 antibody
Category:
Research Area:
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- MUL1 antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab05435
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Immunogen affinity purified
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Isotype
- IgG
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- mitochondrial E3 ubiquitin ligase 1
- Alternative Names
- C1orf166 antibody, GIDE antibody, MAPL antibody, MULAN antibody, RNF218 antibody
- UniProt ID
- Q969V5
- Observed MW
- 35 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, IHC, WB
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500-1:2000; IHC: 1:20-1:200
Validated Images
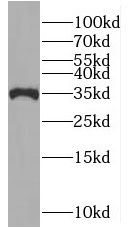 Transfected HEK-293 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab05435(MUL1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
Transfected HEK-293 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab05435(MUL1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
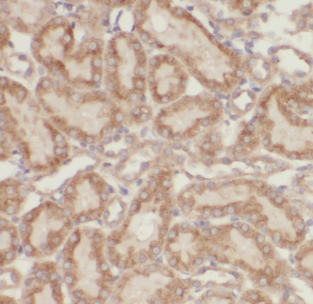 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human kidney using FNab05435(MUL1 antibody) at dilution of 1:50
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human kidney using FNab05435(MUL1 antibody) at dilution of 1:50
- Background
- Exhibits weak E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity. E3 ubiquitin ligases accept ubiquitin from an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in the form of a thioester and then directly transfer the ubiquitin to targeted substrates. Can ubiquitinate AKT1 preferentially at 'Lys-284' involving 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination and seems to be involved in regulation of Akt signaling by targeting phosphorylated Akt to proteosomal degradation. Proposed to preferentially act as a SUMO E3 ligase at physiological concentrations. Plays a role in the control of mitochondrial morphology. Promotes mitochondrial fragmentation and influences mitochondrial localization. The function may implicate its ability to sumoylate DNM1L. Inhibits cell growth. When overexpressed, activates JNK through MAP3K7/TAK1 and induces caspase-dependent apoptosis. Involved in the modulation of innate immune defense against viruses by inhibiting DDX58-dependent antiviral response. Can mediate DDX58 sumoylation and disrupt its polyubiquitination.



