Products
DYNLT1 antibody
Category:
Research Area:
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- DYNLT1 antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab02590
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Immunogen affinity purified
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Isotype
- IgG
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- dynein, light chain, Tctex-type 1
- Alternative Names
- TCTEL1 antibody, TCTEX-1 antibody, TCTEX1 antibody
- UniProt ID
- P63172
- Observed MW
- 12 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC, IP
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500-1:2000; IP: 1:200-1:1000; IHC: 1:20-1:200
Validated Images
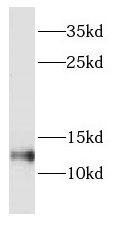 human brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab02590(DYNLT1 antibody) at dilution of 1:500
human brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab02590(DYNLT1 antibody) at dilution of 1:500
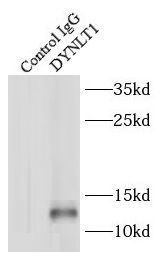 IP Result of anti-DYNLT1 (IP:FNab02590, 4ug; Detection:FNab02590 1:300) with mouse skeletal muscle tissue lysate 3600ug.
IP Result of anti-DYNLT1 (IP:FNab02590, 4ug; Detection:FNab02590 1:300) with mouse skeletal muscle tissue lysate 3600ug.
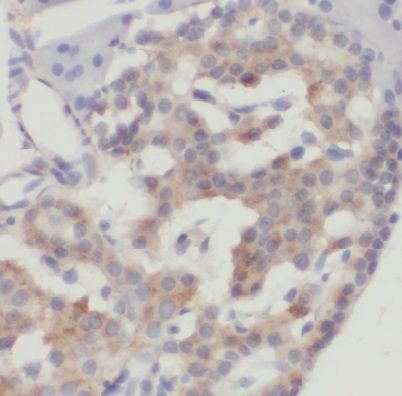 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human pancreas using FNab02590(DYNLT1 antibody) at dilution of 1:50
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human pancreas using FNab02590(DYNLT1 antibody) at dilution of 1:50
- Background
- Acts as one of several non-catalytic accessory components of the cytoplasmic dynein 1 complex that are thought to be involved in linking dynein to cargos and to adapter proteins that regulate dynein function. Cytoplasmic dynein 1 acts as a motor for the intracellular retrograde motility of vesicles and organelles along microtubules. Binds to transport cargos and is involved in apical cargo transport such as rhodopsin-bearing vesicles in polarized epithelia. Is involved in intracellular targeting of D-type retrovirus gag polyproteins to the cytoplasmic assembly site. May also be a accessory component of axonemal dynein. Plays a role in neuronal morphogenesis; the function is independent of cytoplasmic dynein and seems to be coupled to regulation of the actin cytoskeleton by enhancing Rac1 activity. The function in neurogenesis may be regulated by association with a G-protein beta-gamma dimer. May function as a receptor-independent activator of heterotrimeric G-protein signaling; the activation appears to be independent of a nucleotide exchange. Plays a role in regulating neurogenesis; inhibits the genesis of neurons from precursor cells during cortical development presumably by antagonizing ARHGEF2. Involved in the regulation of mitotic spindle orientation(By similarity).



