Products
CTNNA1 antibody
Category:
Research Area:
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- CTNNA1 antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab02056
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Protein A+G purification
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- monoclonal
- Isotype
- IgG1
- Clone ID
- 0A11
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- catenin(cadherin-associated protein), alpha 1, 102kDa
- Alternative Names
- Alpha E catenin antibody, Cadherin associated protein antibody, CAP102 antibody, Catenin alpha 1 antibody, CTNNA1 antibody
- UniProt ID
- P35221
- Observed MW
- 95-100 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500-1:2000; IHC: 1:50-1:1000
Validated Images
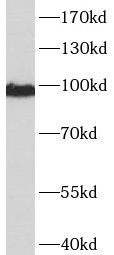 NIH/3T3 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab02056(CTNNA1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
NIH/3T3 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab02056(CTNNA1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
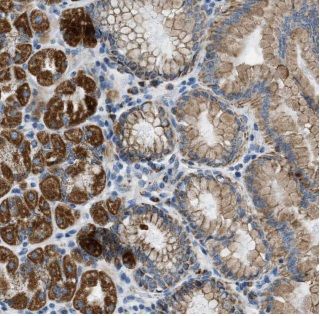 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human stomach tissue slide using FNab02056(CTNNA1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:200
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human stomach tissue slide using FNab02056(CTNNA1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:200
- Background
- Associates with the cytoplasmic domain of a variety of cadherins. The association of catenins to cadherins produces a complex which is linked to the actin filament network, and which seems to be of primary importance for cadherins cell-adhesion properties. Can associate with both E-and N-cadherins. Originally believed to be a stable component of E-cadherin/catenin adhesion complexes and to mediate the linkage of cadherins to the actin cytoskeleton at adherens junctions. In contrast, cortical actin was found to be much more dynamic than E-cadherin/catenin complexes and CTNNA1 was shown not to bind to F-actin when assembled in the complex suggesting a different linkage between actin and adherens junctions components. The homodimeric form may regulate actin filament assembly and inhibit actin branching by competing with the Arp2/3 complex for binding to actin filaments. May play a crucial role in cell differentiation.



