Products
Creatine Kinase MM-Specific antibody
Category:
Research Area:
| Synonyms: | CKMM antibody, Creatine Kinase MM antibody, Creatine Kinase M-Specific antibody, Creatine kinase M chain antibody, Creatine kinase M type antibody, creatine kinase antibody, muscle antibody, M CK antibody | ||
| Catalogue No.: | FNab01957 | Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host: | Rabbit | Tested Application: | ELISA, WB, IHC |
| Clonality: | polyclonal | Isotype: | IgG |
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- Creatine Kinase MM-Specific antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab01957
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Immunogen affinity purified
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Isotype
- IgG
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- creatine kinase, muscle
- Alternative Names
- CKMM antibody, Creatine Kinase MM antibody, Creatine Kinase M-Specific antibody, Creatine kinase M chain antibody, Creatine kinase M type antibody, creatine kinase antibody, muscle antibody, M CK antibody
- UniProt ID
- P06732
- Observed MW
- 43 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:1000-1:10000; IHC: 1:20-1:200
Validated Images
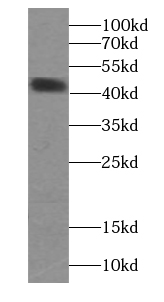 mouse heart tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab01957(CKM-Specific antibody) at dilution of 1:2000
mouse heart tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab01957(CKM-Specific antibody) at dilution of 1:2000
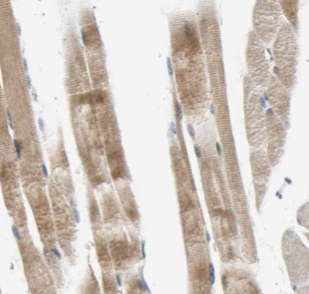 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human skeletal muscle using FNab01957(CKM-Specific antibody) at dilution of 1:100
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human skeletal muscle using FNab01957(CKM-Specific antibody) at dilution of 1:100
- Background
- CKM, also named as CKMM and M-CK, is a member of the ATP:guanido phosphotransferase protein family. It is a cytoplasmic enzyme involved in energy homeostasis and is an important serum marker for myocardial infarction. CKM reversibly catalyzes the transfer of phosphate between ATP and various phosphogens such as creatine phosphate. It acts as a homodimer in striated muscle as well as in other tissus,and as a heterodimer with a similar brain isozyme in heart. CK isoenzymes play a central role in energy transduction in tissues with large, fluctuating energy demands, such as skeletal muscle, heart, brain and spermatozoa. CK MB consists of a dimer of nonidentical chains. With MM being the major form in skeletal muscle and myocardium, MB existing in myocardium, and BB existing in many tissues, esp



