Products
BLK antibody
Category:
Research Area:
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- BLK antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab00906
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Immunogen affinity purified
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- polyclonal
- Isotype
- IgG
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- B lymphoid tyrosine kinase
- UniProt ID
- P51451
- Observed MW
- 58 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC, IP
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500-1:2000; IP: 1:500-1:2000; IHC: 1:20-1:200
Validated Images
 SH-SY5Y cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab00906(BLK antibody) at dilution of 1:500
SH-SY5Y cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab00906(BLK antibody) at dilution of 1:500
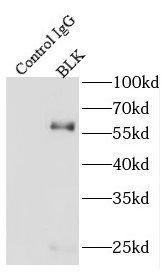 IP Result of anti-BLK (IP:FNab00906, 4ug; Detection:FNab00906 1:500) with SH-SY5Y cells lysate 1600ug.
IP Result of anti-BLK (IP:FNab00906, 4ug; Detection:FNab00906 1:500) with SH-SY5Y cells lysate 1600ug.
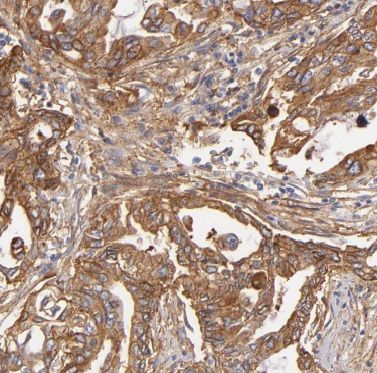 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human pancreas cancer using FNab00906(BLK antibody) at dilution of 1:10
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human pancreas cancer using FNab00906(BLK antibody) at dilution of 1:10
- Background
- Non-receptor tyrosine kinase involved in B-lymphocyte development, differentiation and signaling. B-cell receptor(BCR) signaling requires a tight regulation of several protein tyrosine kinases and phosphatases, and associated coreceptors. Binding of antigen to the B-cell antigen receptor(BCR) triggers signaling that ultimately leads to B-cell activation. Signaling through BLK plays an important role in transmitting signals through surface immunoglobulins and supports the pro-B to pre-B transition, as well as the signaling for growth arrest and apoptosis downstream of B-cell receptor. Specifically binds and phosphorylates CD79A at 'Tyr-188'and 'Tyr-199', as well as CD79B at 'Tyr-196' and 'Tyr-207'. Phosphorylates also the immunoglobulin G receptors FCGR2A, FCGR2B and FCGR2C. With FYN and LYN, plays an essential role in pre-B-cell receptor(pre-BCR)-mediated NF-kappa-B activation. Contributes also to BTK activation by indirectly stimulating BTK intramolecular autophosphorylation. In pancreatic islets, acts as a modulator of beta-cells function through the up-regulation of PDX1 and NKX6-1 and consequent stimulation of insulin secretion in response to glucose.



