Products
ATP5C1 antibody
Category:
Research Area:
- SPECIFICATIONS
- Product Name
- ATP5C1 antibody
- Catalogue No.
- FNab00705
- Size
- 100μg
- Form
- liquid
- Purification
- Protein A+G purification
- Purity
- ≥95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Clonality
- monoclonal
- Isotype
- IgG1
- Clone ID
- 8H11
- Storage
- PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3, -20℃ for 12 months(Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.)
Immunogen
- Immunogen
- ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F1 complex, gamma polypeptide 1
- Alternative Names
- ATP5C antibody, ATP5C1 antibody, ATP5CL1 antibody, F ATPase gamma subunit antibody
- UniProt ID
- P36542
- Observed MW
- 33 kDa
Application
- Tested Applications
- ELISA, WB, IHC
- Recommended dilution
- WB: 1:500-1:2000; IHC: 1:100-1:500
Validated Images
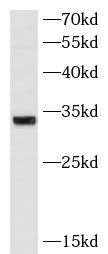 human heart tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab00705( ATP5C1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
human heart tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with FNab00705( ATP5C1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:1000
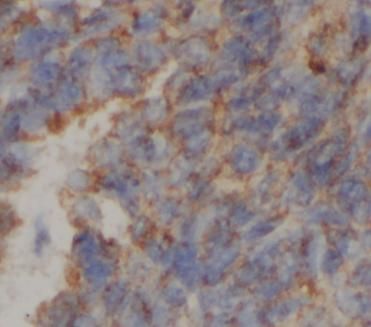 Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver cancer tissue slide using FNab00705( ATP5C1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:200 heat mediated antigen retrieved with Tris-EDTA buffer(pH9)
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human liver cancer tissue slide using FNab00705( ATP5C1 Antibody) at dilution of 1:200 heat mediated antigen retrieved with Tris-EDTA buffer(pH9)
- Background
- Mitochondrial membrane ATP synthase(F(1)F(0) ATP synthase or Complex V) produces ATP from ADP in the presence of a proton gradient across the membrane which is generated by electron transport complexes of the respiratory chain. F-type ATPases consist of two structural domains, F(1)-containing the extramembraneous catalytic core, and F(0)-containing the membrane proton channel, linked together by a central stalk and a peripheral stalk. During catalysis, ATP synthesis in the catalytic domain of F(1) is coupled via a rotary mechanism of the central stalk subunits to proton translocation. Part of the complex F(1) domain and the central stalk which is part of the complex rotary element. The gamma subunit protrudes into the catalytic domain formed of alpha(3)beta(3). Rotation of the central stalk against the surrounding alpha(3)beta(3) subunits leads to hydrolysis of ATP in three separate catalytic sites on the beta subunits.



