Abstract: FADD protein is involved in the pathogenesis and progression of various diseases, including virus infection, bacterial infection, cardiovascular disease, ischemic injury, atherosclerosis, chronic enteritis, pancreatitis, liver injury etc.
Keywords: FADD protein, FADD in apoptosis, programmed cell death
1. FADD in Apoptosis
FADD (also called Mort1) is a kind of FAS-associated death domain protein and specifically binds with FAS cytoplasmic domain. FADD is a 25 kDa adaptor protein. After FAS binds with the relevant ligand FasL(CD95L), FAS receptor is activated by trimerization. The activated receptor binds with FADD, and then activates caspase-8 by the interaction to form death-inducing signalling complex. Later, caspase-1, 3, or 7 is activated to promote the apoptosis of cell where FAS protein is found.
2. Role of FADD Protein
It's also found that FADD is involved in regulating PKC function and various non-apoptotic intracellular processes. Usually, newly synthesized PKC tends to be mature and get the activated function after programmed phosphorylation process, including activation-loop, turn motif and hydrophobic motif. In this research, Prof. Zi-Chun Hua and his team find FADD is involved in regulating inactivation of protein kinase C.
The mutation(S191D) simulated by a FADD phosphoryl group promotes dephosphorylation of turn motif and hydrophobic motif. The phosphorylation of S191 negatively regulates FADD.
PP2A is the phosphatase related to the dephosphorylation of cPKC. FADD can interact with PP2A. The deficiency of FADD destroys PP2A mediated dephosphorylation of cPKC and improve the stability and activity of cPKC, resulting in the promotion of cytoskeleton remodeling, motility and chemotaxis.
These results show the new function of FADD. During non-apoptotic process, FADD can regulate dephosphorylation, stability and signal termination of cPKC.
3. Cited FineTest Product
| Product Name | Sample | Detection Target | Application |
| anti- FADD antibody (FNab02941) | rat brain tissue | FADD | western blot |
Publication Details
Article Title: Edaravone attenuates neuronal apoptosis in hypoxic-ischemic brain damage rat model via suppression of TRAIL signaling pathway
Journal Title: The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology
DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.03.020
IF: 5.652
PMID: 29635023
Validated Image
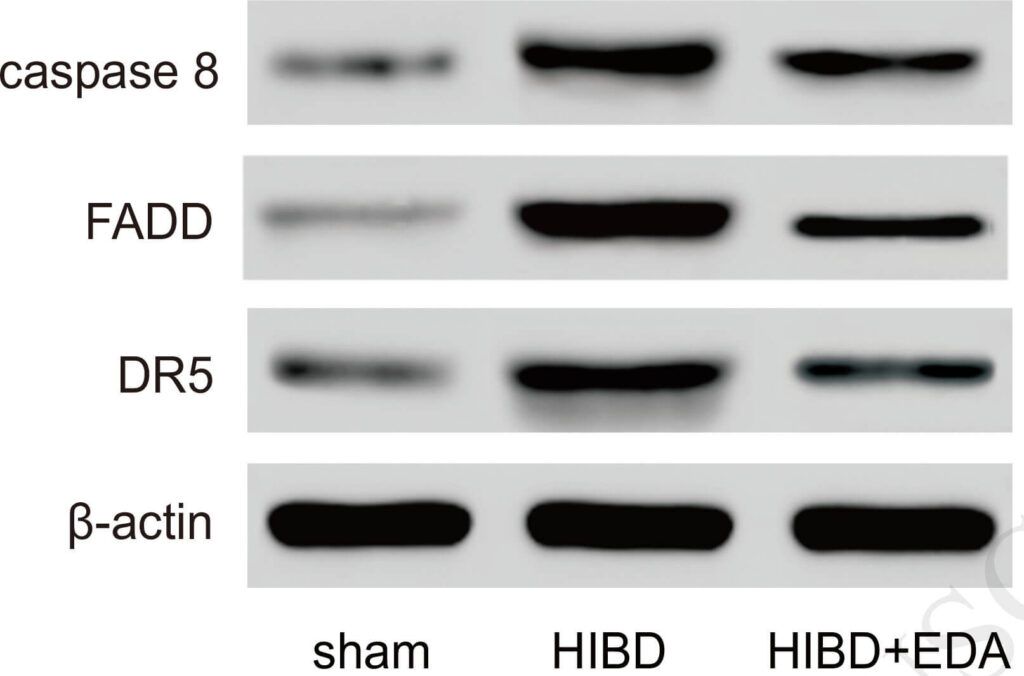
Figure Source: Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018 Jun;99:169-177. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.03.020. Epub 2018 Apr 7.
Figure 5. Western blot of key proteins on TRAIL pathway (A-B): Western blot analysis determined the expressions of FADD, caspase 8 and death receptor DR5 in TRAIL pathway. FADD, caspase 8 and DR5 were all up-regulated in HIBD group compared with sham group. They were down-regulated in HIBD+EDA group, compared with HIBD group.
Supplementary Materials
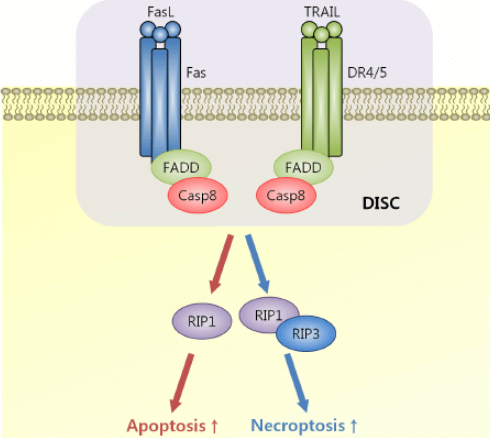
Figure 1s. FADD in Apoptosis.
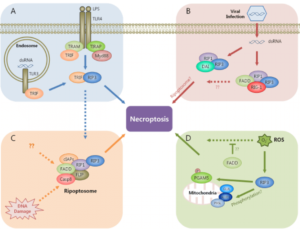
Figure 2s. Role of FADD in programmed death caused by different stimulation.
