FineTest ELISA kit contributes to the research on hydrocephalus and brain damage. The immunoassay is designed to measure VEGFC and FOXC2 concentration in meninges.
Publication Details
Article Title: Neutrophil extracellular trap-mediated impairment of meningeal lymphatic drainage exacerbates secondary hydrocephalus after intraventricular hemorrhage
Journal Title: Theranostics
DOI: 10.7150/thno.91653
IF: 12.4
PMID: 38505607
Abstract: Rationale: Hydrocephalus is a substantial complication after intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) or intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) that leads to impaired cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulation. Recently, brain meningeal lymphatic vessels (mLVs) were shown to serve as critical drainage pathways for CSF. Our previous studies indicated that the degradation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) after ICH/IVH alleviates hydrocephalus. However, the mechanisms by which NET degradation exerts beneficial effects in hydrocephalus remain unclear. Methods: A mouse model of hydrocephalus following IVH was established by infusing autologous blood into both wildtype and Cx3cr1-/- mice. By studying the features and processes of the model, we investigated the contribution of mLVs and NETs to the development and progression of hydrocephalus following secondary IVH. Results: This study observed the widespread presence of neutrophils, fibrin and NETs in mLVs following IVH, and the degradation of NETs alleviated hydrocephalus and brain injury. Importantly, the degradation of NETs improved CSF drainage by enhancing the recovery of lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs). Furthermore, our study showed that NETs activated the membrane protein CX3CR1 on LECs after IVH. In contrast, the repair of mLVs was promoted and the effects of hydrocephalus were ameliorated after CX3CR1 knockdown and in Cx3cr1-/- mice. Conclusion: Our findings indicated that mLVs participate in the development of brain injury and secondary hydrocephalus after IVH and that NETs contribute to acute LEC injury and lymphatic thrombosis. CX3CR1 is a key molecule in NET-induced LEC damage and meningeal lymphatic thrombosis, which leads to mLV dysfunction and exacerbates hydrocephalus and brain injury. NETs may be a critical target for preventing the obstruction of meningeal lymphatic drainage after IVH.
Keywords: CX3C chemokine receptor 1, Hydrocephalus, Intraventricular hemorrhage, Meningeal lymphatic vessels, Neutrophil extracellular traps, Brain Damage
Immunoassay
| FineTest Product | Sample | Species | Detection Target |
| Mouse VEGFC(Vascular endothelial growth factor C) ELISA Kit(EM0217) | meninges | Mouse | VEGFC |
| Mouse Foxc2 (Forkhead box protein C2) ELISA Kit(EM6948) | Foxc2 |
Validated Image
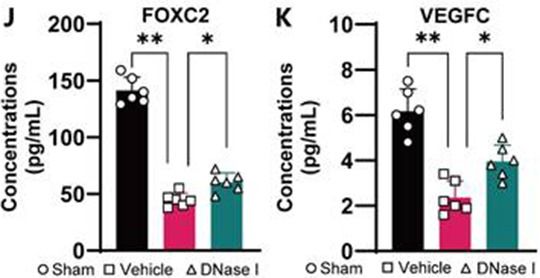
Figure Source: Theranostics. 2024 Feb 24;14(5):1909-1938. doi: 10.7150/thno.91653.
