Abstract: GM-CSF (also called CSF2) is a monomeric glycoprotein generated by various cells. Initially, GM-CSF is identified as the hemopoietic factor and functions as a cytokine by secreting macrophage, T cell, mast cell, natural killer cell, endothelial cell and fibroblast. Actually, GM-CSF regulates innate and adaptive immunity as an inflammatory factor instead of the key factor in regulating bone marrow cell in the homeostatic environment.
Keywords: GM-CSF Therapy, Growth Factor, Cytokine, Immunity, Inflammation
1. Function of GM-CSF
Unlike G-CSF, GM-CSF promotes proliferation and mature of neutrophils, and also affects more cell types(especially macrophage and eosinophil). Imbalanced expression of GM-CSF extremely increases the amount of bone marrow cells in multiple organs and mediates tissue inflammation by affecting these mature bone marrow cells. In the inflammatory environment, GM-CSF is mainly produced by Th cell and maintains intercellular communication between T cell and bone marrow cell.
2. Pulmonary Macrophage Homeostasis
GM-CSF is undetectable in healthy human blood, which is a key homeostatic factor in pulmonary alveoli. In the low level, GM-CSF is applied in the growth and long-term maintenance of alveolar macrophage. The deficiency of GM-CSF will cause pulmonary alveolar proteinosis(PAP). Besides, functional deficiency of pulmonary macrophages increases the susceptibility to pulmonary infection.
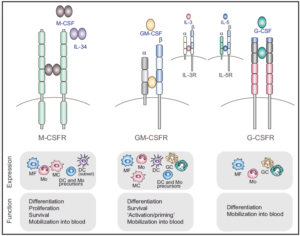
3. GM-CSF in Inflammation
GM-CSF is secreted by epithelial cell and leukocyte etc(e.g. specific Th cell subpopulation). GM-CSF receptor is expressed in myeloid cell. Its two main roles in immune response include: 1. polarization of mature myeloid cell into pro-inflammatory phenotype(paracrine/autocrine function); 2. control of acute bone marrow generation, differentiation of progenitor cell into myeloid cell, inflammatory amplification and mobilization (endocrine function).
Activated myeloid cell secretes active oxygen. Pro-inflammatory cytokines(e.g. IL-1, IL-6, TNF) in higher expression level and some chemokines(e.g. CCL2, IL-8, CCL17) can attract monocyte, neutrophil and leukomonocyte respectively. CD4T helper cell (TH cell) generating GM-CSF improves immune reaction by activating and recruiting pro-inflammatory myeloid cells to inflammatory site.
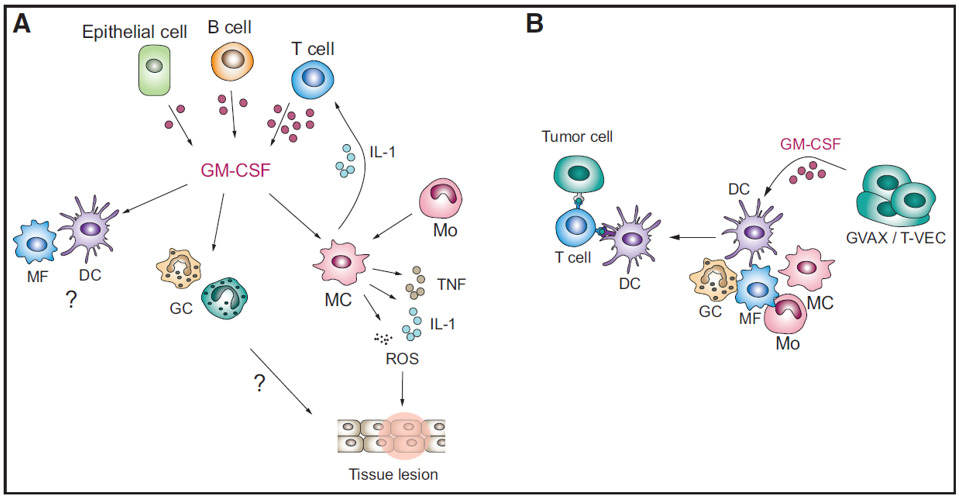
4. GM-CSF Related Diseases
The abnormal expression of GM-CSF can cause excessive inflammation, pain, chemotaxis and tissue damage, and also promote the generation of pathogenic cytokines. GM-CSF network promotes diseases by continuous and overactive inflammatory response. The network is a positive feedback loop, and involved in monocyte/macrophage, TH cell and adjacent cell population. They secrete GM-CSF and pro-inflammatory cytokines/chemokines. Typical cytokines in the network are IL-1, IL-6 and TNF, which have successfully targeted for various inflammatory diseases.
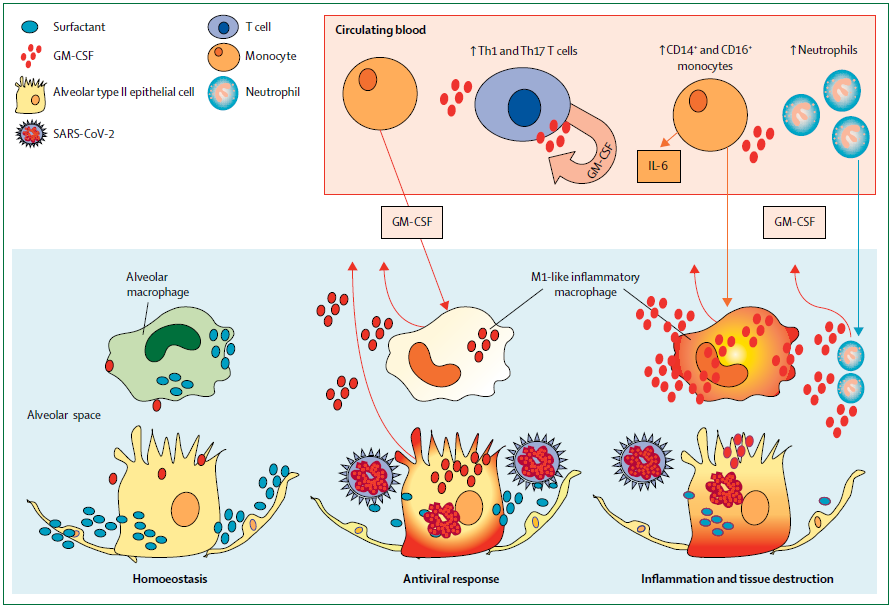
The pro-inflammatory effect of GM-CSF is involved in a series of inflammatory diseases: e.g. COVID-19 ARDS, CRS, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, GVHD, cardiovascular diseases etc. Th cells generating GM-CSF are found to be involved in various autoimmune diseases. A large number of inflammatory myeloid cells infiltrate into lungs(especially monocyte, macrophage and neutrophil) and the disease similar to macrophage activation syndrome(MAS) happens.
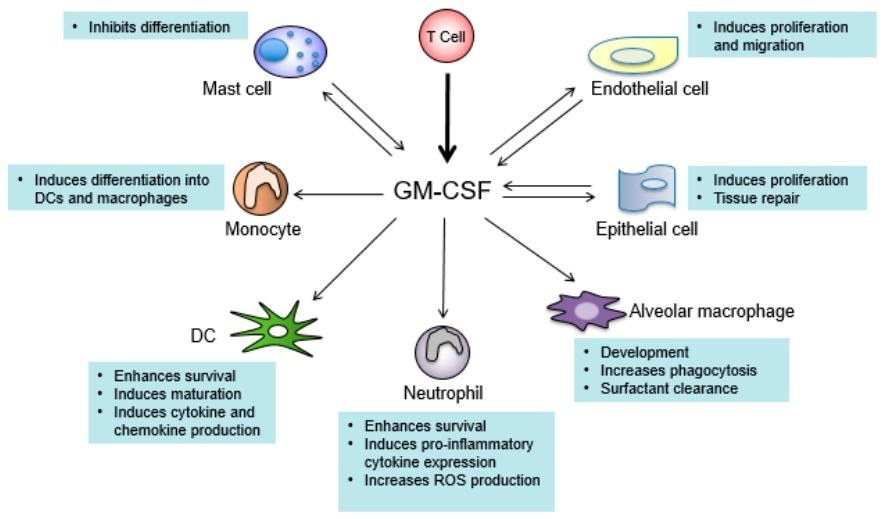
5. Role in Target Cells
5.1. Monocyte
Pathogenic T cells(Th) produce GM-CSF-induced activation of inflammatory genes in monocyte and promote to involve in formation of inflammatory corpuscles, inflammatory phagocytosis and chemotaxis. Meanwhile, IL-1β secreted by monocyte-derived cells can have a feed-back effect on T cell, and also induce T cell to re-express GM-CSF and form a signal enhancement loop.
In kidney, GM-CSF generated by Th1 cell affects monocyte-derived cells, and promote to produce MMP-12. The tissue is damaged through cutting glomerular basement membrane. Thus, glomerulonephritis is more severe and end-stage renal disease occurs.
5.2. Macrophage
Macrophage is the main target cell of GM-CSF. In the inflammation, GM-CSF generated by T cell regulates macrophage function as the messenger, and promotes recruitment of macrophage to inflammatory site. IL-1β is also produced to induce tissue damage. In the physiological homeostasis condition, GM-CSF is very important for maintaining alveolar macrophage development. The deficiency of GM-CSF receptor will cause serious pulmonary alveolar proteinosis(PAP), and respiratory failure during virus infection.
5.3. DC Cells
GM-CSF is the first cytokine found to promote differentiation of monocyte and hemopoietic progenitor cell into DC cell in vitro. It's always the differentiation solution in vitro for DC cell. In the homeostatic condition, the expression level of GM-CSF is very low. In the normal mouse model, the deficiency of GM-CSF has a low effect on the production of DC cell.
In the lung, GM-CSF maintains the macrophage development, and also drives Th2/Th17 cell for antigen presentation via DC cell. GM-CSF produced by DC cell promotes the recruitment of neutrophil to airway and induce allergic airway inflammation. Thus, GM-CSF is the potential target for the treatment of chronic asthma.
5.4. Eosinophils
GM-CSF can mediate the migration of eosinophil. In chronic colitis, increased eosinophils are thought to be the main factor for driving disease. GM-CSF also promotes the migration of eosinophil to lung, which is related to acute allergic asthma.
5.5. Neutrophils
GM-CSF produced by inflammatory site can remotely control hematopoietic cell, and promotes the production, mobilization and recruitment of inflammatory cells, resulting in the increase of tissue inflammation. In chronic inflammations, GM-CSF produced by Th cell improves the hematopoietic function of spleen and extramedullary sites, and promotes aggravation of the disease due to tissue toxicity and neutrophil aggregation.
GM-CSF can also recruit neutrophil in circulation to infection site via paracrine and improve immune defense of the organism. Recombinant GM-CSF has been applied in the treatment of neutropenia syndrome but off-target effects exist.
6. Recommended Proteins
|
Catalog No. |
Product Name |
Host |
Delivery |
|
Recombinant Human GM-CSF |
HEK293 cells |
In Stock |
|
|
Recombinant Mouse GM-CSF |
HEK293 cells |
In Stock |
|
|
Recombinant Rat GM-CSF |
HEK293 cells |
In Stock |
REFERENCES
[1]Adenoviral vector-mediated GM-CSF gene transfer improves anti-mycobacterial immunity in mice - role of regulatory T cells, PMID: 29089144.
[2]GM-CSF drives myelopoiesis, recruitment and polarisation of tumour-associated macrophages in cholangiocarcinoma and systemic blockade facilitates antitumour immunity, PMID: 34413131.
[3]Modulation of Airway Epithelial Innate Immunity and Wound Repair by M(GM-CSF) and M(M-CSF) Macrophages, PMID: 32289801.
