Abstract: When heterologous proteins (especially eukaryotic proteins) are expressed by E.coli, due to lack of post-translational modification in prokaryotic expression system, excessive rapid synthesis rate results in mismatch of the disulfide bond. Hence, target proteins are usually expressed by insoluble inclusion bodies.
Keywords: Inclusion Bodies Protein, Protein Purification and Expression, Protein Refolding Protocol, FineTest Recombinant Protein
1. Four Advantages of Inclusion Bodies Protein Expression
Although inclusion body proteins are aggregates without the biological activity, they can be expressed in the form of inclusion bodies:
- Avoid Degradation: A soluble protein in the cell is easily attacked by the protease. Expression in the form of inclusion bodies can avoid degradation of the foreign protein by the protease;
- Increase Expression Level: Decreased concentration of intracellular foreign protein can help to increase the expression level;
- Beneficial to Separation and Purification: Inclusion bodies are beneficial to separation and purification, because they contain less impure proteins and just require the simple low-speed centrifugation for separating soluble proteins;
- Effective Protein Production: The inclusion body protein is insensitive to mechanical stirring and sonication technique. It will be one of the effective methods for the mass production of recombinant proteins, if the in vivo refolding is successful.
2. Protein Refolding Protocol
The processing for inclusion bodies before refolding is important. Besides target proteins, inclusion bodies also contain some bacterial components, outer membrane proteins, plasmid DNA and other impurities. Wash with neutral detergent below 1%, e.g. Tween, Triton and NP40 etc. Then add EDTA and reductants like DTT, β-mercaptoethanol etc for rewashing many times.
2.1. Removal of Impure Proteins
Most insoluble impure proteins adsorbed on the surface of inclusion bodies can be removed by guanidine hydrochloride or urea with low concentration/neutral detergent/EDTA/reductants. The pH of washing buffer should be close to the physiological condition of engineering bacteria. The reductant range is between 0.1-5mM. The EDTA range is between 0.1-0.3 mM.
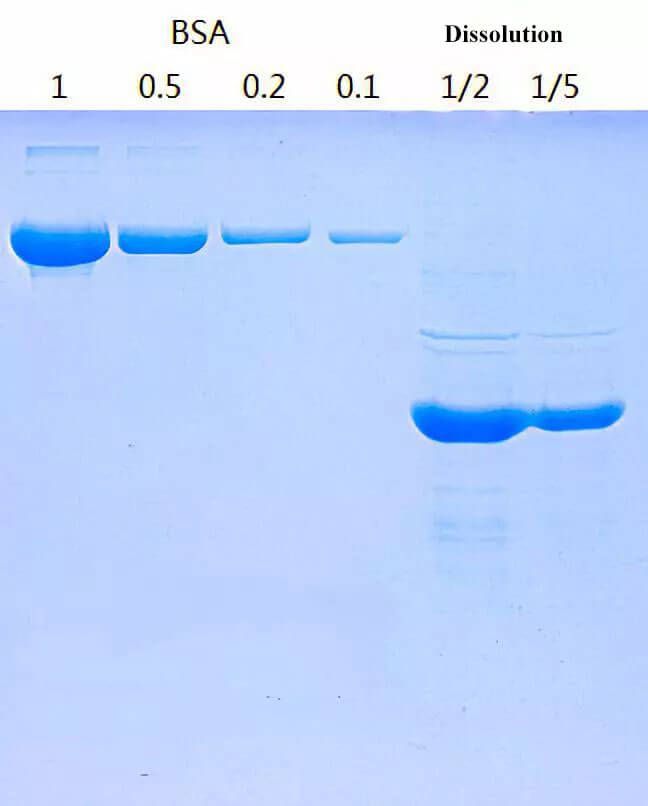
Figure 1. Protein Dissolution Process.
2.2. Denaturants for Inclusion Bodies Protein
After several washing-centrifugation cycles, there are very few impurities. Generally, the purer the inclusion body protein is, the better the refolding effect is. Usually, dissolution is completed by denaturants with high concentration like 6-8M guanidine hydrochloride or urea. In alkaline conditions, the urea will modify the amino in the protein and is usually used with Tris-HCl buffer system. However, the guanidine hydrochloride has a stronger denaturing ability. It's usually trial when the urea is incapable of completing the dissolution.
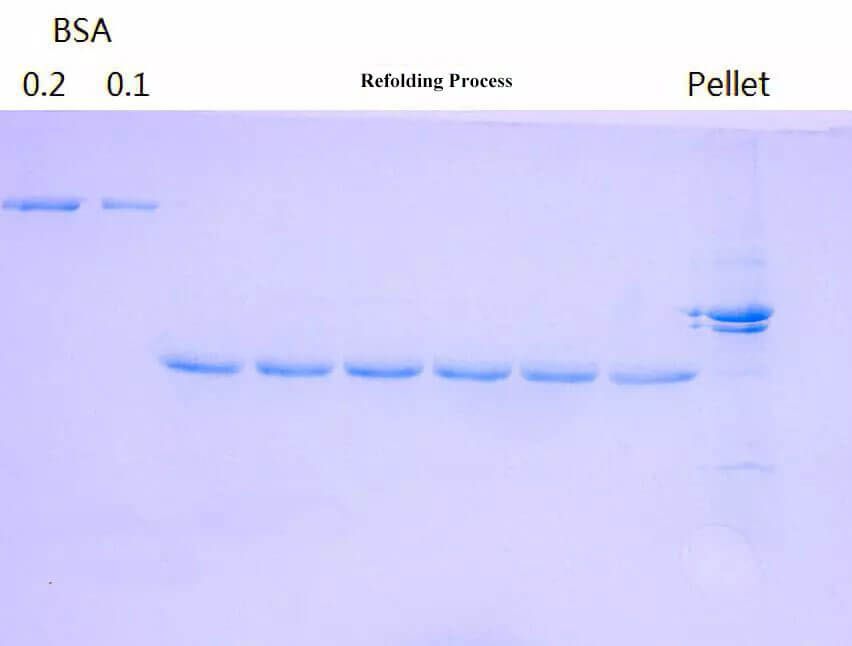
Figure 2. Protein Refolding Process.
3. Conclusion
The refolding of inclusion body is a complex work containing the theory, experience and luck. There is no any theorem. But some basic principles should be followed. The initial concentration of refolding should be below 0.1mg/ml. Exorbitant initial concentration easily results in the accumulation and precipitation. For dilution or dialysis method, changes in denaturant concentrations should be smooth. Glutathione is applied in promoting the reasonable combination of disulfide bonds and its concentration depends on the amount of disulfide bonds.
4. FineTest Recombinant Protein
Browse a list of recombinant proteins and contact us for ordering your protein products.
